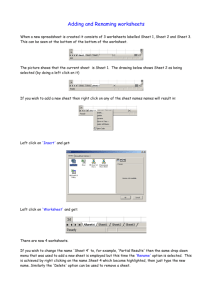
Scheme of work AQA Business UNIT 3 2010 (new window)
advertisement

Scheme of Work 2010-2011 A2 Business Studies Think Active! What Are The Learners Doing? Course Overview Module / Unit Title Unit 3 – BUSS3 Strategies for Success Prepared by Gill Greenwood Lesson Duration 1.5 x 3 per week Start Date 13th September 2010 End Date 1 D:\533584499.doc 24th January 2011 Learning Outcomes Functional Objectives and Strategies: Financial Strategies and Accounts Marketing Strategies Operational Strategies Human Resource Strategies Assessment Details EXAM MONDAY 24TH JANUARY 2011 25% of A Level 1 hour 45 minutes examination 80 marks Date 13th Sept 20th Sept 27th Sept What topic(s) and learning objectives will be covered? Introduction to A2 What will learners do? Using Objectives and Strategies Functional objectives and their relationship with corporate objectives The relationship between functional objectives and strategies Candidates should understand a range of functional objectives that businesses might pursue, (eg minimising costs, gaining market share) and how these contribute to the achievement of corporate objectives Using Financial Data to Measure and Assess Performance Analyzing balance sheets Analyzing income 2 D:\533584499.doc How will learning be checked? Review AS results Set targets Discuss active learning Discuss homework booklet Analysing financial data should focus on performance and potential. Candidates should understand the importance of FS / Basic Skills/ECM What resources are needed? Target forms Pro-monitor Homework Booklets Effective coverage: Corporate objectives; functional objectives; functional strategies Learning will be checked by discussion, q and a. Completion of exercises Learning will be checked by discussion, q and a. Completion of exercises Marcouse: Corporate Objectives and Strategy (and use case B2). A2 book, Chapter 2; Full book, Ch 50. Marcouse: Functional Objectives and Strategy (and use case B1). A2 book, Chapter 4; Full book, Ch 52. What Independent Learning/ Homework will be set? HOMEWORK WILL BE SET EACH WEEK IN HOMEWORK BOOKLET Extra Independent learning is detailed below Topical Cases: Ferrari – Corporate strategy A-Z A2 Worksheets: Functional Objectives Marcouse: Key AS Finance Issues (and do the 12 Qs). A2 book, Chapter 6. Marcouse: Income Statements, A2 book, Chapter 8; Full book, A-Z A2 Worksheets: Analysing balance sheets A-Z A2 Worksheets: Analysing income statements 4th Oct statements Using financial data for comparisons, trend analysis and decision making Assessing strengths and weaknesses of financial data in judging performance working capital, depreciation, profit utilization and profit quality. Interpreting Published Accounts Conducting ratio analysis: the selection, calculation and interpretation of ratios to measure financial performance Assessing the Candidates should understand the following ratios: liquidity (current and acid test), profitability (ROCE), financial efficiency (asset turnover, stock turnover, creditor and debtor days), gearing and 3 D:\533584499.doc Ch 55. Balance Sheets, A2 book, Ch 9; full bk Ch 56 No construction of accounts or calculation of depreciation will be required Learning will be checked by discussion, q and a. Completion of exercises Business Review: Profitable Primark, November 2006, P36 (10 years of sales and profit data, but most udeful for placing profit in context) Accounting Nutshell:, esp Chapters 2 & 3 (for you) plus section 1.4 (pp17-19) for students. Creative Accounting: v helpful on weaknesses of financial data Marcouse: Accounting Ratios (and use Qs B1 & B3). A2 book, Chapter 10; Full book, Ch 57. Business Review: Ratio Analysis, Sept 2006, P24 (focus on Tesco, using ratios all of which are on the new Spec); Topical Cases: General Motors v Toyota; Halfords; Goals (5-a-side) value and limitations of ratio analysis in measuring a business’s performance shareholder ratios (dividend per share and dividend yield). Candidates will be given a table of relevant formulae for ratios as part of the examination paper where appropriate. Accounting Nutshell, Chapters 6&7: v good on ratios (for staff) Marcouse: Limitations of Accounts (and use case B2). A2 book, Chapter 11; Full book, Ch 58. Business Review: Aggressive Accounting (Gillespie), April ’04, P4 A-Z A2 Worksheets: Ratios - Financial Efficiency A-Z A2 Worksheets: Ratios: - Gearing and shareholders A-Z A2 Worksheets: Ratios - limitations for decision making A-Z A2 Worksheets: Ratios - liquidity A-Z A2 Worksheets: Ratios - profitability 11th Oct Making investment decisions Conducting investment appraisal: selection of appropriate methods, 4 D:\533584499.doc Candidates should understand the reasons why businesses invest and the ways in which investment can help Learning will be checked by discussion, q and a. Completion of exercises Marcouse: Investment Appraisal (and use Qs A, B1 and B2). A2 book, Chapter 13; Full book, Ch 60. Business Review: A-Z A2 Worksheets: Payback and ARR calculation and interpretation of findings Investment criteria Assessing the risks and uncertainties of investment decisions Evaluating quantitative and qualitative influences on investment decisions businesses to reach functional objectives. Quantitative measures of investment should include: payback, average rate of return, and net present value Investment Appraisal (Coates), April 2004, P19 Accounting Nutshell: very good intro to investment appraisal, then good on payback period; copy pp 321 – 326 for students (beware of DCF as it goes into the formula for calculating discount factors) Topical Cases: Investment appraisal simulation; Qualitative factors; Advanced exercise; Investment & Extrapolation A-Z A2 Worksheets: Allocating capital expenditure A-Z A2 Worksheets: NPV A-Z A2 Worksheets: Investment risk and uncertainty 18th Oct Understanding financial objectives Financial objectives Assessing internal and external influences on financial objectives Selecting financial 5 D:\533584499.doc Financial objectives should include: cash flow targets, cost minimization, ROCE targets and shareholders’ returns Learning will be checked by discussion, q and a. Completion of exercises Marcouse: Financial Objectives and Constraints (and use case B1 on Man Utd). A2 book, Chapter 7; Full book, Ch 54. A-Z A2 Worksheets: Marcouse: Integrated Finance – raises 5 big, A grade issues; has 20 short qs and 4 longer ones; A2 Ch 14, Full book Ch 61 Topical Cases: Land strategies Raising finance Implementing profit centres Cost minimization Allocating capital expenditure Candidates should understand how these strategies interrelate with other functions and be able to assess their value in given circumstances Financial Objectives Marcouse: Financial Strategies and Accounts – covers all 4 topics A2 book, Chapter 12; Full book, Ch 59. A-Z A2 Worksheets: Selecting financial strategies A-Z A2 Worksheets: Allocating capital expenditure Business Review: Strategic Finance (Marcouse), Feb 2004, P20 Business Review: Profit Centres (M Surridge), February 2005, P2 Topical Cases: Strategy – financial; Potterless – financial strategy 25th Oct 6 D:\533584499.doc of Leather – ratios and strategy A-Z A2 Worksheets: Revision Calculations for Unit 3 1st Nov Understanding Marketing Objectives Marketing objectives Analysing Markets and Marketing Reasons for, and the value of, market analysis Methods of analyzing trends The use of IT in analyzing markets Difficulties in analyzing market data 7 D:\533584499.doc Marketing objectives Marketing strategy Reasons for analyzing markets should include: gathering evidence for devising a new strategy, identifying significant patterns in sales. Candidates should be familiar with moving averages, test markets and extrapolation as methods of measuring and forecasting sales. Candidates should understand how correlation can be used in analyzing markets Learning will be checked by discussion, q and a. Completion of exercises Marcouse: Marketing Objectives (and use case B1 on Heinz in Russia). A2 book, Chapter 16; Full book, Ch 62. A-Z A2 Worksheets: Marketing objectives and strategies FAQs on Marketing: terrific on marketing strategy, eg P43 on differentiation (and nice distinction between strategies for the market leader versus the market challenger Business Review: Strategic Marketing (Marcouse), November ‘03 Marcouse: Analysing The Market (and use case B1 on Cadbury). A2 book, Chapter 17; Full book, Ch 63. Business Review: Prince’s Free CD, Feb 2008, P8 – good on how market analysis can lead to a new marketing strategy; Marketing A-Z Worksheets: AQA Test Marketing Mistakes, September 2004, P2, showing market analysis isn’t easy sA-Z A2 Worksheets: Analysing trend Marcouse: Measuring and Forecasting Trends (and use Section A Qs plus case B1 on Boeing). A2 book, Chapter 18; Full book, Ch 64 Topical Cases: John Lewis – forecasting 8th Nov Selecting Marketing Strategies Low cost versus differentiation Market penetration Product development and market development strategies Diversification Assessing effectiveness of marketing strategies 8 D:\533584499.doc Ansoff’s matrix should be used to assess marketing strategies in a national and international context. Marketing strategies should consider the methods, risks and benefits involved in entering international markets Learning will be checked by discussion, q and a. Completion of exercises Marcouse: Selecting Marketing Strategies (and use case B1 on Apple iPod). A2 book, Chapter 19; Full book, Ch 65. FAQs on Marketing: good section on differentiation Business Review: Marketing Models and Mobile Phones, November 2006, P32; September 2005, Cobra Beer – using Ansoff’s matrix; Michael Porter, April Topical cases on Ansoff: Coke Plus 2005 (article by Stephen Barnes) A-Z A2 Worksheet: Ansoff’s Matrix 15th Nov Developing and Implementing Marketing Plans Components of marketing plans Assessing internal and external influences on marketing plans Issues in implementing marketing plans Assessing internal and external influences on marketing objectives 9 D:\533584499.doc Components of marketing plans include: objectives, budgets and sales forecasts and marketing strategies. Influences on the marketing plan might include: finance available, operational issues and competitors’ actions Internal influences on marketing should include finance, HR, operational issues and corporate objectives. External influences include: competitors’ actions, market factors and technological change Learning will be checked by discussion, q and a. Completion of exercises ; Ansoff takeover Marcouse: Developing and Implementing Marketing Plans (consider using the big B2 case). A2 book, Chapter 20; Full book, Ch 66. FAQs on Marketing: terrific on marketing plans (pp 95-99) Business Review: Marketing Plans, Sept 2006, P28; Strategic Thinking in Marketing, April 2006, P34 Business Review: Fisherman’s Friend, Feb 2008, P28 (useful look at one small firm coping with competition) Marcouse: Integrated Marketing (and use case B3 on Emirates Airline). A2 book, Chapter 21; Full book, Ch 67. A-Z A2 Worksheets: Influences on Marketing Objectives 22nd Nov Operational objectives The focus should be on expansion and/or relocation Operational (including offstrategies: Location shoring) Methods of making Methods of location decisions deciding on Benefits of optimal location should location take into account The advantages quantitative and disadvantages (investment of multi-site appraisal, for locations example) and Issues relating to qualitative factors. international Reasons for location international location include: global markets, cost reduction and avoidance of trade barriers 10 D:\533584499.doc Learning will be checked by discussion, q and a. Completion of exercises Marcouse: Industrial and International Location (and use case B1 on Offshoring). A2 book, Chapter 33; Full book, Ch 77. Business Review: February 2007: Relocating a Business, P20; Location, Location, Location, September 2004 (M Surridge) P27; The Exodus Abroad (on relocating), April 2004, P16 Topical Cases: Location role play; International location A-Z A2 Worksheets: Optimal Location Decisions 29th Nov Operational strategies: scale and resource mix Choosing the right scale of production: economies and diseconomies of scale Choosing the optimal mix of resources: capital and labour intensity 11 D:\533584499.doc Operational objectives should include: meeting quality, cost and volume targets, innovation, efficiency (including time) and environmental targets. Candidates should be aware of a range of economies of scale including: purchasing, technical and specialization. Diseconomies of scale include communication and coordination Candidates should understand the benefits and drawbacks of capital and labour intensive strategies Learning will be checked by discussion, q and a. Completion of exercises Marcouse: Understanding Operational Objectives (and use case B2 on Renault). A2 book, Chapter 30; Full book, Ch 74. A-Z A2 Worksheets: Operational Objectives and Strategies Business Review: Strategic Operations (Marcouse), September 2003, P10 Marcouse: Economies and Diseconomies of Scale (and use case B2 on McDonalds). A2 book, Chapter 31; Full book, Ch 75. A-Z A2 Worksheets: Economies and Diseconomies of Scale Business Review: Methods of production (and stock control), Feb 2008, P34 – it has a useful Table showing pros and cons of Job, Batch and Flow; Labour v Capital Intensity, Nov 2003, P28 A-Z A2 Worksheets: Capital and Labour intensity 6th Dec Operational strategies: Innovation Innovation, research and development Purpose, costs, benefits and risks of innovation Candidates should be aware that a strategy of innovation has implications for finance, marketing and human resources Learning will be checked by discussion, q and a. Completion of exercises Marcouse: Research & Devt and Innovation (and use case B1 on the Gillette Mach 3). A2 book, Chapter 32; Full book Ch76 A-Z A2 Worksheets: Innovation: purposes, benefits and risks Management of Techno Innovation: some short, studentfriendly bits, eg pp 160+161: Why do firms do R&D? Also important is Business Review: Research & Development, February 2005, P22 12 D:\533584499.doc 13th Dec Operational strategies: Lean Production The effective management of time Assessing the value of critical path analysis The effective management of other resources through methods of lean production Understanding Operational Objectives Assessing internal and external influences on operational objectives 13 D:\533584499.doc Candidates should be able to interpret and complete critical path networks by entering ESTs and LFTs and understand the significance of critical and noncritical activities. Candidates should be aware of lean production techniques including just-intime production and kaizen Influences on operational objectives might include: competitors’ performance, resources available, the nature of the product and demand Learning will be checked by discussion, q and a. Completion of exercises Marcouse: Planning Operations (and use case B2, especially for girls). A2 book, Chapter 34; Full book, Ch 78. Marcouse: Continuous Improvement (and use case B2 on Toyota). A2 book, Chapter 35; Full book, Ch 79. Business Review: Critical Path Analysis, November 2003, P2 Business Review: What is Lean Production?, February 2005, P14 A-Z Worksheets: AQA Lean Management A-Z A2 Worksheets: CPA for A-Z A2 Worksheets: Influences on Operational ObjectivesAQA Marcouse: Integrated Operations Management (use the 20 Qs and case B3). A2 book, Chapter 36; Full book, Ch 80. 20th Dec 27th Dec Holidays 3rd Jan Understanding HR Objectives and Strategies HR objectives HR strategies Developing and Implementing Workforce Plans Components of workforce plans Assessing internal and external influences on workforce plans Issues in implementing 14 D:\533584499.doc HR objectives might include: matching workforce skills, size and location to business needs, minimizing labour cost, making full use of the workforce’s potential and maintaining good employer/employee relations. Candidates should be aware of ‘hard’ Learning will be checked by discussion, q and a. Completion of exercises Marcouse: HRM Objectives and Strategy (and use case B2 covering Hard and Soft HRM). A2 book, Chapter 23; Full book, Ch 68. Business Review: Financial Incentives, April 2008, P10 (very good at showing the unintended consequences of financial incentives); Strategic People Management workforce plans The value of using workforce plans 15 D:\533584499.doc and ‘soft’ strategies to HR and the strengths and weaknesses of each Candidates should be aware of the influences on workforce planning, including other functional decisions, eg innovation may require greater diversity, legislation and labour market trends including migration. Issues involved in implementing workforce plans might include: employer/employee relations, cost, corporate image and training. Candidates should recognize that these issues can have positive and negative effects (Marcouse), April 2004, P34 Marcouse: Workforce Planning (and use case B1). A2 book, Chapter 24; Full book, Ch 69. Business Review: Human Resource Planning, Sept 2006, P20; The Business Implications of Migration, April 2007: P20 A-Z Worksheets: Workforce Plans 10th Jan 17th Jan Competitive Organisational Structures Factors determining choice of organizational structures Adapting organizational structures to improve competitiveness Effective Employer/Employee Relations Managing communications with employees Methods of employee representation Methods of 16 D:\533584499.doc Methods of adapting organizational structures to improve competitiveness should include: centralization and decentralization, delayering and flexible workforces. Candidates should be aware of the issues involved with implementing and operating each of these approaches. Flexible workforces should include the notion of core and peripheral workers, outsourcing and homeworking Learning will be checked by discussion, q and a. Completion of exercises Candidates should understand the importance of communication in employer/employee relations. Candidates should know the advantages and disadvantages of Learning will be checked by discussion, q and a. Completion of exercises Business Review: Importance of Organisational Structure to Business Performance, April 2008, P33 A2 Revision Calculations A-Z A2 Worksheets: Competitive Organisational Structures Marcouse: Flexibility and Insecurity (and use cases B1 and B2). A2 book, Chapter 25; Full book, Ch 70. A-Z Worksheets: AQA Competitiveness Business Review, Sept 2008: P28, article by Mark Burns on the benefits to Hornby of outsourcing to China Marcouse: Employee Relations (and use cases B1 and B2). A2 book, Chapter 27; Full book, Ch 72. A-Z A2 Worksheets: Communication Truth About Managing People: pp109-120, A-Z Worksheets: Revision for Unit 3 (1) A-z Worksheets: Revision for Unit 3 (2) avoiding and resolving industrial disputes employee representation. Methods of employee representation might include: works councils, employees groups as well as trade unions especially the section called ‘Listen to the Grapevine’; also useful is ‘The Case For Conflict’ on pp150-151 Business Review: Trade Unions, Disputes and ACAS, February 2005, P34 A-Z A2 Worksheets: Employer-Employee Relations 24th Jan Revision and Review 31st Jan 7th Feb 17 D:\533584499.doc A-Z Exam Pack: 3 Mock Exam papers with full mark schemes Topical Cases: Tesco – Unit 3 Revision CPA and Unit 3 Revision 14th Feb 21st Feb Half Term 28th Feb 7th Mar 14th Mar 18 D:\533584499.doc 21st Mar 28th Mar 4th Apr 11th Apr Easter Hols 18th Apr Easter Hols 19 D:\533584499.doc 25th April 2nd May 9th May 16th May 23rd May 20 D:\533584499.doc 30th May Half Term 6th Jun 13th Jun 20th Jun 27th Jun 21 D:\533584499.doc