Chapter 1

Name: __________________________________ Class Period: _______ Date: ____________
Chapter 1-What is Economics?
Economics- the study of how people, individuals and groups, choose to use their
______________ resources to satisfy their ___________wants.
Needs- minimal requirements of things.
Wants- things that are desired but are not essential to life.
Scarcity- people do not have and cannot have enough _________, time, and other resources to ____________their every want.
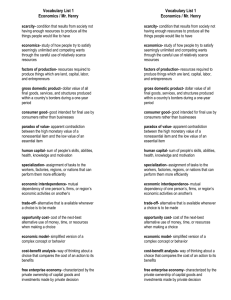
Factors of Production- _______________ needed to produce goods and services.
Land- natural ___________________present without human intervention.
Examples: _______________________________
Labor- includes anyone who works to ______________________and services. a.
Goodstangible __________that people buy. b.
Services_________________done for others for a fee.
Examples: _____________________________________
Capital- anything long lasting that is ___________________to use in the
______________of other things. a.
Physical Capital-long lasting goods used to ___________________and services.
Examples: b.
Human Capital-skill and __________________of workers.
Entrepreneurshipthe ability of individuals to______________________, to introduce new products and processes, and to improve management techniques.
Inputs- include the 4 types of resources (land, labor, capital and entrepreneurship) along with anything made with these resources
______________________________.
Trade-Off- _______________ one good or service to purchase or produce another.
The result of a trade-off is what you give up in order to get or do something else.
Opportunity Cost- the value of the next __________________given up for the alternative that was chosen.
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)- a curve that shows the
______________quantity of one good that can be produced for each possible
______________of another good produced.
It is also used to illustrate __________________________.
Models- simplified ____________________of reality.
Microeconomicsthe study of how people make __________and how those decisions ____________others in the economy.
Ex: Is college education a good investment? How does natural disaster (Gulf Oil
Spill 2010) affect the price businesses charge for fish in the U.S. and the earnings of people who fish for a living?
Macroeconomics- the study of the economy as a ___________.
Ex: why do the prices of goods and services tend to rise over time? What effect does government borrowing have on the economy?
Positive Economics- the study of what the world is like and why it works the way it does. It’s about ________________________relationships.
Ex: How many teenagers live in poverty? Do people buy more or less Starbucks when their income increases? Do salary limited for professional soccer players affect team performance?
Normative Economics- the study of the way things _________________rather than the way things are.
Ex: Should our country do more to help the poor? Should soda be sold n high school vending machines? Should college athletes be paid?
The Language of Economics
Economics have special meaning for certain words.
To an Economists:
Capital- is anything long lasting.
Ordinary language: capital is money.
To an Economist:
Market- is a collection of buyers and sellers.
Ordinary Language: a place where you buy goods- grocery store, flea market.
Seven Principals that Support Economic Thinking
1.
Scarcity Forces Tradeoffs- _________________force people to make choices and face ______________when they choose.
2.
Cost Versus Benefits- People choose something when __________of doing so are
___________than the costs.
3.
Thinking at the Margin- Most decisions _______________about a little more or a little less of something.
4.
Incentives Matter- People respond to incentives in generally_________________.
5.
Trade Makes People Better Off- By focusing on ____________________and then
____________with others, we will end up with more and better choices than by doing everything for ourselves.
6.
Markets Coordinate TradeMarkets usually do better than anyone or anything else at ___________________________between buyers and sellers.
7.
Future Consequences Count- _______________made today have future (and often unintended) ______________________.