Economic Principles
advertisement

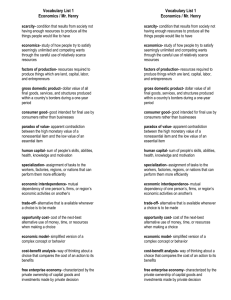
GOODS AND SERVICES • Goods- production output in the form of material items such as books, movies, or automobiles • Services- Work performed for someone else (hair stylist, home repair, entertainment) • Factors of Production • Resources necessary to produce goods and services • Natural Resources- Actual surface land, fish, animals, forest, mineral deposits • Labor- includes anyone who works to produce goods and services (human resource) • Capital- manufactured goods to make other goods and services (machines, buildings, tools used for assembly- capital goods) • Entrepreneurs- individual who starts a business, introduces new products, and improve processes GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT • GDP is total value, in dollars, if all the final goods and services produced in country during a single year • Measuring GDP- multiply price of each good by the quantity produced and then add the amounts • Quantity vs. Quality- GDP measures quantity produced, not quality produced • Net Domestic Product- accounts for the fact that some production is only due to depreciation • Cars and refrigerators will depreciate at moment of purpose ECONOMIC SECTORS AND CIRCULAR FLOW • Market- Free and willing exchange of goods and services between buyers and sellers • Economic activity is shown by a circular flow of resources among consumer sector, business, government and foreign sector Consumer Sector • Consumers earn their income in factor markets • workers earn wages, tips, and salaries • Business Sector • Individuals spend money in product markets where goods and services are sold • Will purchase capital goods to continue producing more goods • Government Sector • Federal, state and local • purchases resources in factor markets • Taxes, fees, tuition, hospital fees are examples of revenue • The Foreign Sector • Sell and buy goods and services from other countries • PROMOTING ECONOMIC GROWTH • Economic growth occurs when country’s goods and services increases over time • Productivity- efficient use of resources/ measured by amount of output for produced by a given level of inputs over a specific period of time • Specialization- concentrating on producing goods and services that they can do better than anyone else • Division of Labor- breaking jobs down into small tasks performed by different workers • Human Capital- the sum of people’s skills, abilities, and motivation • Economic Interdependence- we rely on others, and they rely on us to provide goods and services HOMEWORK!! • Write 4 clarifying questions that relate to the notes on this power point and bring them in next class. It should be ready to be checked at beginning of class. • What if I have no questions….Sure you do!! Create questions that you would like to see on the quiz or test, or that other students may want to know the answer to