File - Social Studies Made Easy!
advertisement

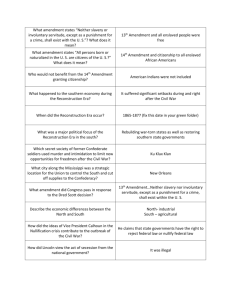
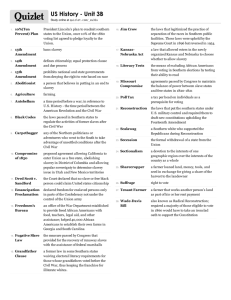
SEMESTER 2 REVIEW-ANSWERS I. THE EARLY PRESIDENTS 1. Who wrote the words to the national anthem? Francis Scott Key 2. Why was the Louisiana Purchase important? It doubled the size of the US beginning westward expansion and gave US control of the Mississippi River 3. What was the Lewis and Clark Expedition? An expedition to explore the LA Purchase and Oregon Country 4. Which court case established the principle of judicial review? Marbury v. Madison 5. Who was John Marshall? Chief Justice of the Supreme Court that helped establish many precedents such as judicial review 6. Why did the War Hawks want war with Great Britain? The British were impressing American sailors 7. Describe the Battle of New Orleans. Andrew Jackson emerged as a hero due to a great American victory. 8. What were the basic facts of the War of 1812? No territory exchanged, White House was burned, Andrew Jackson becomes a hero 9. What were the characteristics of the Era of Good Feelings? It was a period of nationalism 10. What did the Monroe Doctrine Say? European powers needed to stay out of affairs in the Americas II. JACKSON 1. What happened during the Trail of Tears? Native Americans were forced to move west off of their land 2. How did Andrew Jackson’s upbringing affect his political beliefs? He grew up poor so he supported efforts to improve the lives of the “common man” 3. What was the Spoils System? Rewarding your friends/ supporters with positions in government after being elected to the office of the President. 4. Why did Jackson want to dismantle the Bank of the United States? He felt it was unconstitutional and worked only for the privileged III. THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION AND REFORM MOVEMENTS 1. What is the name of the reform group that worked to end slavery? Abolitionists 2. What reform movement did Dorothea Dix help start? She wanted to reform the way the mentally ill were treated and conditions of prisons 3. How did the 2nd Great Awakening influence early reform in the U.S.? It caused people to approach reform with a more open mind 4. What conclusions can be drawn from the early Reform Movements? We became more enlightened on issues of race, gender, mental states, and alcohol abuse 5. Why was the cotton gin an important invention? It made it much easier to remove the seeds from cotton 6. How did improvements in transportation change trade in the United States? It made trade cheaper and easier 7. What were some characteristics of the early Industrial Revolution? Textile mills located next to rivers and powered by water wheels. Young girls and women worked in the mills IV. WESTWARD EXPANSION 1. What is Manifest Destiny? The belief that the US was destined to reach the Pacific Ocean 2. What caused the Mexican War? A border dispute between the US and Mexico 3. What did the Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo say? The Rio Grande was the border between the US and Mexico, and the Mexican Cession would become territory of the US 4. Why did the United States make the Gadsden Purchase? For the railroad 5. What was the main reason that settlers and trappers pushed farther west? More land and resources and the prospect of finding gold 6. What caused most of the conflict between Native Americans and pioneers during Westward Expansion? White settlers took Native American’s land. In many cases treaties had been signed protecting Native land and the settlers ignored these treaties. V. THE CAUSES OF THE CIVIL WAR 1. What did the 3/5 Compromise say? 3 out of 5 slaves would count for representation and taxation 2. Why did popular sovereignty become a big issue in the 1850’s? To determine whether a state would be free or slave 3. List the parts of the Kansas-Nebraska Act. 1) Nebraska Territory was divided into two territories, Kansas and Nebraska 2) Each territory would decide the issue of slavery based on popular sovereignty 4. What was the Underground Railroad? A network of abolitionists that helped runaway slaves escape 5. What was the main reason why southerners supported slavery? They felt it was necessary for the health of their economy. 6. List the parts of the Missouri Compromise. Missouri was admitted as a slave state and Maine was admitted as a free state and all territory north of 36’ 30 would be free in the future 7. What did the Dred Scott Decision say about the legal status of slaves? Slaves were considered property and not people 8. Why did the Compromise of 1850 cause controversy? The Fugitive Slave Act forced northerners to turn in escaped slaves. 9. What effect did the book Uncle Tom’s Cabin, by Harriet Beecher Stowe, have on northerners before the Civil War? It showed many northerners the cruel side of slavery and caused support for abolition to increase. 10. What were the results of John Brown’s raid? The raid was a failure 11. How did the Election of 1860 reflect the nation at that time? It showed that the country was deeply divided due to each section of the country voting for their candidate. Lincoln in the north and Pacific coast, Breckinridge in the Deep South 12. What happened as a result of Abraham Lincoln’s election? South Carolina seceded and was followed shortly by other southern states. VI. THE CIVIL WAR AND RECONSTRUCTION 1. What was the bloodiest battle of the whole Civil War? Gettysburg 2. What advantages and disadvantages did each side have in the Civil War? North- more men, railroads, supplies South- leadership, only had to keep the war going as a stalemate 3. What was each side’s strategy at the beginning of the war? North- Anaconda plan South- fights a defensive war and force an armistice 4. What did the Emancipation Proclamation say? All slaves in Confederate States were free but just on paper 5. Why was Vicksburg an important victory for the Union? It gave them control of the Mississippi River 6. Why was the Battle of Gettysburg a turning point in the Civil War? It turned back the Confederate advance to the north. 7. What is an example of total war from the U.S. Civil War? Sherman’s “March to the Sea” 8. Why did Grant offer Lee generous terms when Lee surrendered? He knew that the process of Reconstruction lay ahead 9. What was life like for free blacks living in the U.S. after the Civil War? Harsh, many of their rights were severely restricted 10. What were some characteristics of Southern Reconstruction? The Freedmen’s Bureau: set up schools in the south as well as provide food, clothing, and help former slaves find jobs. Many whites did whatever they could to intimidate blacks and make sure they did not have the same freedoms as other citizens. 11. What was the main reason why groups like the Ku Klux Klan formed? To intimidate blacks so that they did not vote or pursue roles in government. 12. Who led the South in the early part of Reconstruction? Who led it during Radical Reconstruction? The Radical Republicans led the south through radical reconstruction 13. Which amendment guarantees equal protection under the law? 14th Amendment 14. Which amendment abolished slavery? 13th Amendment 15. How did southern states try to get around the 15th amendment? Poll taxes, tests, etc. 16. What were the provisions of the Compromise of 1877? Rutherford B. Hayes was given all disputed electoral votes VII. VOCABULARY 1. Secede to withdraw 2. Import to bring in 3. Suffrage the right to vote 4. Compromise both sides agree to meet in the middle 5. Amend to change 6. Export to take out 7. Nullifications to void 8. States’ Rights granting more power to the states as opposed to the federal government 9. Judicial Review the power of the judicial branch to determine the constitutionality of laws (Marbury v Madison) 10. Sectionalism loyalty to one’s section of the country as opposed to the nation 11. Urbanization the growth of urban areas, people move from countryside to cities