US History: Civil War & Reconstruction Study Guide
advertisement
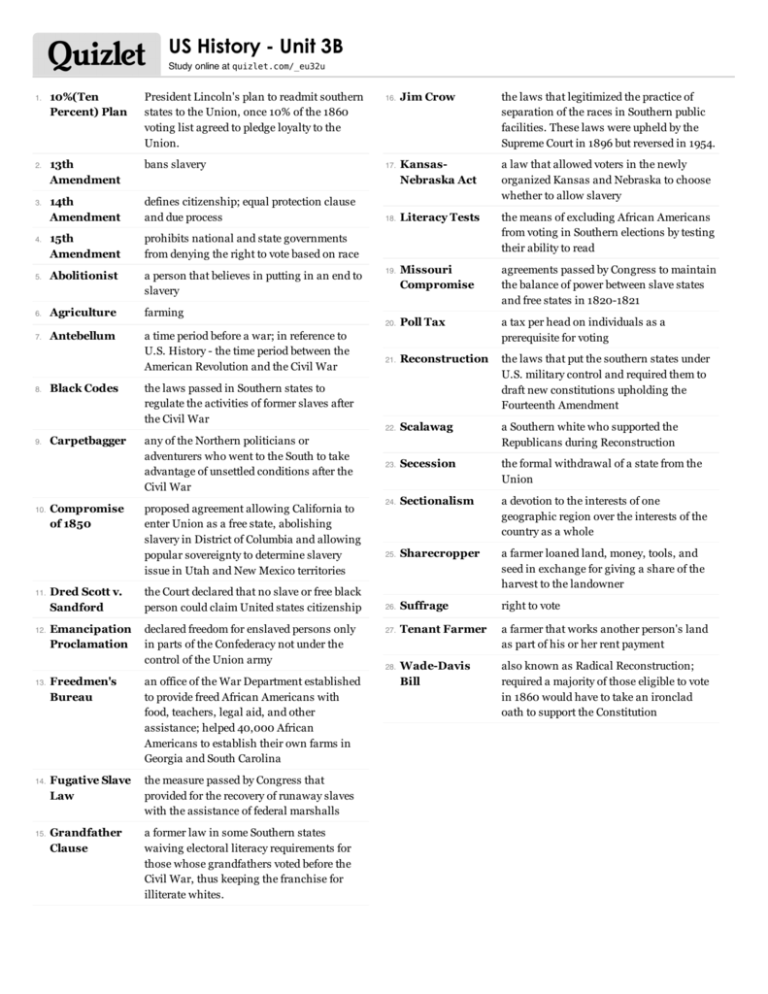
US History - Unit 3B Study online at quizlet.com/_eu32u 10%(Ten Percent) Plan President Lincoln's plan to readmit southern states to the Union, once 10% of the 1860 voting list agreed to pledge loyalty to the Union. 13th Amendment bans slavery 17. 14th Amendment defines citizenship; equal protection clause and due process 18. 15th Amendment prohibits national and state governments from denying the right to vote based on race 5. Abolitionist a person that believes in putting in an end to slavery 6. Agriculture farming 7. Antebellum a time period before a war; in reference to U.S. History - the time period between the American Revolution and the Civil War 1. 2. 3. 4. 8. Black Codes the laws passed in Southern states to regulate the activities of former slaves after the Civil War 9. Carpetbagger any of the Northern politicians or adventurers who went to the South to take advantage of unsettled conditions after the Civil War 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Compromise of 1850 proposed agreement allowing California to enter Union as a free state, abolishing slavery in District of Columbia and allowing popular sovereignty to determine slavery issue in Utah and New Mexico territories Dred Scott v. Sandford the Court declared that no slave or free black person could claim United states citizenship Emancipation Proclamation declared freedom for enslaved persons only in parts of the Confederacy not under the control of the Union army Freedmen's Bureau an office of the War Department established to provide freed African Americans with food, teachers, legal aid, and other assistance; helped 40,000 African Americans to establish their own farms in Georgia and South Carolina Fugative Slave Law the measure passed by Congress that provided for the recovery of runaway slaves with the assistance of federal marshalls Grandfather Clause a former law in some Southern states waiving electoral literacy requirements for those whose grandfathers voted before the Civil War, thus keeping the franchise for illiterate whites. Jim Crow the laws that legitimized the practice of separation of the races in Southern public facilities. These laws were upheld by the Supreme Court in 1896 but reversed in 1954. KansasNebraska Act a law that allowed voters in the newly organized Kansas and Nebraska to choose whether to allow slavery Literacy Tests the means of excluding African Americans from voting in Southern elections by testing their ability to read Missouri Compromise agreements passed by Congress to maintain the balance of power between slave states and free states in 1820-1821 20. Poll Tax a tax per head on individuals as a prerequisite for voting 21. Reconstruction the laws that put the southern states under U.S. military control and required them to draft new constitutions upholding the Fourteenth Amendment 22. Scalawag a Southern white who supported the Republicans during Reconstruction 23. Secession the formal withdrawal of a state from the Union 24. Sectionalism a devotion to the interests of one geographic region over the interests of the country as a whole 25. Sharecropper a farmer loaned land, money, tools, and seed in exchange for giving a share of the harvest to the landowner 26. Suffrage right to vote 27. Tenant Farmer a farmer that works another person's land as part of his or her rent payment Wade-Davis Bill also known as Radical Reconstruction; required a majority of those eligible to vote in 1860 would have to take an ironclad oath to support the Constitution 16. 19. 28.











