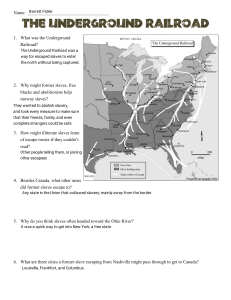
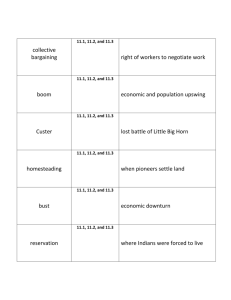
Civil War Vocabulary Words
advertisement

A very large farm. A person who fought to end slavery. President of the Confederacy (the South) during the Civil War. United States President during the Civil War. He wrote the Emancipation Proclamation and worked to reconstruct the country after the war. The North’s strategy during the Civil War to cut off supplies from the South by blocking their trade. A law requiring men to register for military service. Money owed after a war. An above-ground series of escape routes for slaves traveling from the South to the North to gain their freedom. People who led runaway slaves to freedom on the Underground Railroad. A former slave, she made over 19 journeys from the South to the North helping slaves escape. Songs sung by slaves and members of the Underground Railroad to encourage hope, defy slave-masters, and send secret messages. The time period when the United States was rebuilt after the Civil War. A newly free slave. An office established in 1865 by Congress to help former black slaves and poor whites in the South after the Civil War. Lincoln's plan for Reconstruction, which stated that a southern state could rejoin the United States once 10 percent of its voters swore an oath of loyalty to the Union. An official pardon for people who have been convicted of political crimes. Laws passed by Southern states in 1865 and 1866, after the Civil War, that restricted African Americans' freedoms and opportunities (such as jobs and education) Acts passed by the Radical Republicans (who took charge of Reconstruction) that put strict requirements in place if a southern state wanted to rejoin the Union. Republicans who favored drastic and sometimes harsh measures against the southern states in the period following the Civil War. To charge a politician with misconduct or crimes. A person from the northern states who went to the South after the Civil War to profit from the Reconstruction. A secret society of white Southerners in the United States; used threats and violence to suppress black people. A farmer who rents a piece of land from the owner and pays him back with a portion of the crop he harvests. A tax that had to be paid every time a person voted. Poll taxes were used after the Civil War to prevent free blacks, who often could not afford to pay them, from voting. A test of someone’s ability to read and write that had to be passed before voting; used to keep freedmen and the poor from voting. A law that stated that if your grandfather was allowed to vote (as of 1867), then you can vote, too, without having to pass a literacy test. Legal separation of races (for example, in schools, bathrooms, or trains) Racial segregation laws enacted between 1876 and 1965 in certain U.S. states; greatly restricted the rights and opportunities for free black citizens.