1 - kjpederson
advertisement

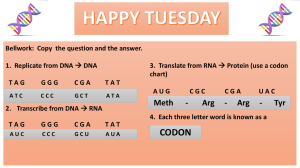
Chapter 11 End of Chapter Questions 1. An operator is a DNA segment that serves as a binding site for an inhibitor protein that blocks transcription; a promoter is a DNA segment that recognizes the enzyme RNA polymorse and promotes transcription. 2. A gene is a short segment of DNA that codes for a polypeptide or protein; a genome is the complete genetic material in an individual. 3. In eukaryotes, an exon is a section of a structural gene when expressed codes for a protein, an intron is a section of a structural gene that does not code for protein. After being transcribed into messenger RNA, the introns must drop out before the mRNA leaves the nucleus and protein synthesis begins. 4. A gene is a short segment of DNA that codes for a polypeptide or protein; a homeotic gene is a regulatory gene that determines where certain anatomical structures like appendages will develop in an organism. 5. A carcinogen is any substance that increases the risk of cancer. A mutagen is a substance that causes mutations to occur within a cell. Carcinogens are mutagens. An oncogene 16. The lac operon was studied in the E coli bacterium lives in the human intestines 18. Because protein synthesis requires materials and energy, it is more efficient to make the enzymes needed for lactose utilization only when is in the cell 21. When a malignant tumor metabolizes cancerous cells break away from the original tumor and forms new tumors in others parts of the body. 22. Tobacco, Asbestos, Ultraviolet light, drugs. 25. a). the promoter recognizes RNA polymerase and promotes transcription. The operator serves as a binding site for the reproser protein. The structural genes encode for particular polypeptides. b) when genes are able to be transcribed by RNA polymerase, they are considered to be turned on. c). yes