A.P. Psychology 6 (B) - Classical Conditioning
advertisement

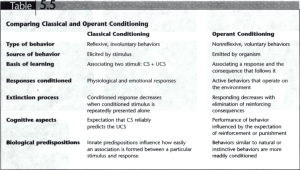
Name: Date: A.P. Psychology Unit 6: Learning “Classical Conditioning” Acquisition: o Classical Conditioning: Initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus Neutral stimulus begins triggering conditioned response o Operant Conditioning: The strengthening of a reinforced response o Neutral stimulus should come (.5 seconds) before the unconditioned stimulus Higher-Order Conditioning: o The conditioned stimulus in one experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus o E.g. An animal that learns that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and may begin responding to the light alone Generalization: o The tendency, once a response has been conditioned, for stimuli similar to the conditioned stimulus to elicit similar responses o John B. Watson, Rosalie Rayner: “Little Albert” Discrimination: o The learned ability to distinguish between a conditioned stimulus and stimuli that do not signal an unconditioned stimulus Extinction: o The diminishing of a conditioned response o Classical Conditioning: An unconditioned stimulus (US) does not follow a conditioned stimulus (CS) o Operant Conditioning: A response is no longer reinforced Spontaneous Recovery: o The reappearance, after a pause, of an extinguished response