Red Onion Osmosis Lab
advertisement

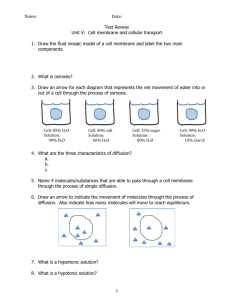
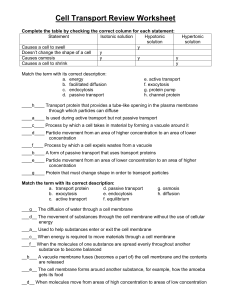
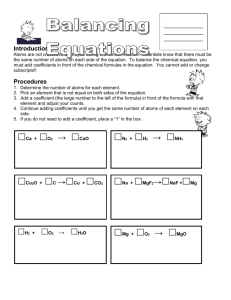
Name: _____________________________ Block: _______ Onion Osmosis Lab Activity Problem: How does salt influence osmosis in relation to an onion cell? Materials: (per group): red onion epidermis, forceps, dropper, distilled water, sodium chloride (salt) solution, paper towels, microscope, slide, and cover slip Important information: Plant cells are surrounded by a cell membrane and a tough cell wall. The cell membrane will shrink and grow depending on how much water is in the cell. The cell wall will not move, and because of this it determines how much water a cell can actually take in. The cell wall keeps the cells from bursting from too much water. PROCEDURE: 1. Peel off a very, very thin piece of red onion (have your teacher help you). Make a wet mount of the red onion epidermis. 2. Examine under low power. When you have a clear view of several cells, switch to medium power. Make a drawing of ONE CELL in the circle to the right. Use colored pencils; this will give you a record of the original appearance of the onion cells. Label the cell wall, cell membrane, and cytoplasm. 3. Take a dropper and add several drops of salt solution to one side of your cover slip (not on top of the coverslip), then take a small piece of paper towel and place it along the opposite edge of the cover slip. The paper should draw out the water and draw in the salt solution. 4. Make sure you are looking at the cells nearest to where you put the salt solution. Observe the effects of the saline (salt) solution on the onion cells. Make a drawing of ONE CELL in the circle to the right. Label the cell wall, cell membrane, and cytoplasm. 5. Using a pipette, flood the onion with distilled water in the same way that the salt solution was added. Make a drawing of ONE CELL in the circle to the right. Label the cell wall, cell membrane, and cytoplasm. CONCLUSION QUESTIONS (answer in complete sentences!): 1. The picture below is of a cell in a solution. If osmosis is going to occur draw arrows telling me whether water is going to move in or out of the cell. Then draw another picture to the right… of what that cell will look like after osmosis occurs. H2O H2O H2O H22O O H H2O NaCl NaCl H2O H2O H2O H2O H2O H2O 2. The picture below is of a cell in a solution. If osmosis is going to occur draw arrows telling me whether water is going to move in or out of the cell. Then draw another picture to the right… of what that cell will look like after osmosis occurs. NaCl NaCl H2O NaCl H2O H2O NaCl H2O H2O H2O H2O H2O NaCl NaCl 3. Red blood cells (and other animal cells) placed in a distilled water solution usually swell up and burst. What prevented the red onion cells from swelling up and bursting when they were placed in the distilled water? 4. What does this movement of water have to do with homeostasis in a cell? 5. What would happen to a plant cell when placed in a solution that matched it’s internal salt content? Why? 6. How does the cell membrane help to maintain the homeostasis of water content? 7. If a bowl of fresh strawberries is sprinkled with sugar, a few minutes later the berries will be covered with juice. Why? Use the terms: osmosis, concentration gradient, high concentration, low concentration and cell membrane to explain your answer. 8. Roads are sometimes salted to melt ice. What does this do to plants around the roadside and why? You must be specific in terms of osmosis. 10. If a person drinks a very large amount of water in a short time without consuming any salt, this can result in confusion, seizures, coma, or even death, due to abnormal functioning of nerve cells in the brain. Explain how these problems could result from drinking too much water too rapidly. 11. What do you think is the reason that a person who is stranded at sea should not drink ocean water? How could drinking salty water harm a person's cells? Be thorough in your explanation.