Prokaryote Cells Color and label the following structures: Bacteria
advertisement

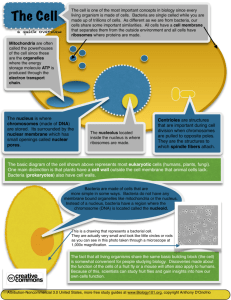
Prokaryote Cells Color and label the following structures: Bacteria have a very simple cell design. Most of them have a thick outer covering called the cell wall. On the picture, color the cell wall purple (it’s the outermost layer). Just within the cell wall is the cell membrane. Color the cell membrane pink. Along the surface of the bacteria cell, you might encounter structures called pilus, whose job is to help the bacteria stick to surfaces. Color all the pilus light green. Bacteria might also need to move around in their environment, so they can have structures called flagella, which resemble tails. Find the two flagella pictured and color them dark green. The watery interior of the cell is called cytoplasm, and it has the texture of jello. Color the cytoplasm light blue. Sprinkled throughout the cell are small roundish structures called ribosomes. Ribosomes make proteins for the cell. Color all of the ribosomes red. Every prokaryote cell has DNA floating within the cytoplasm, which usually looks like a twisted strand of spaghetti. DNA contains the instructions for the cell, basically it is the control center. Find the DNA and color it yellow. Questions: 1. What bacteria cause strep throat? _________________ 2. What are the oldest life forms on earth? ______________________ 3. What type of bacteria causes food poisoning?____________________ 4. What part of the bacteria cell helps it stick to surfaces?_____________ 5. Name two foods that bacteria help make:_____________________ 6. What does “decompose” mean? ________________ 7. What is the control center of the bacteria cell?_________________ 8. What part of the bacteria cell helps it move?___________________ 9. Where do Archaebacteria live? ___________________ 10. To what kingdom do common bacteria belong? _______________ Eukaryote Cells Color and label the following structures: Eukaryotic cells are more complex in design in that they have a nucleus and organelles. Since the nucleus holds the DNA, color letters E and K yellow. Unlike bacteria cells, plant cells have a cell wall made of a complex sugar called cellulous. On the picture, color the cell wall purple (it’s the outermost layer). The outermost part of an animal cell, and just within the cell wall of plants, is the cell membrane. Color the cell membrane pink. The watery interior of the cell is called cytoplasm, and it has the texture of Jello. Color the cytoplasm light blue. While both cells contain them, the animal cell’s cytoplasm is clearly sprinkled with small roundish structures called ribosomes. Ribosomes make proteins for the cell. Color all of the ribosomes red. These ribosomes have come from the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER). Color the rough ER orange. In contrast, the Smooth ER, to be colored green, does not have ribosomes attached. “G” stands for Golgi apparatus (or body). This organelle collects proteins produced in the cell and packages them up to be shipped out to parts of the body where the protein will carry out its function. Color the Golgi Apparatus brown. Often confused for the nucleus, the largest organelle in the plant cell is the vacuole. The vacuole holds the life-supporting water for the plant in every one of its cells. Color the vacuole dark blue. Questions: 1. Heterotrophs are made of what type of cell? ______________________ 2. What type of cells have a lot of structure F? ______________________ 3. Describe the difference between rough and smooth ER. ______________________ 4. Which organelle acts like UPS? ______________________ 5. What structure provides a plant cell with energy? ______________________ 6. Two structures that animal cells do not have. ______________________ 7. Controls what goes in and out of the cell. ______________________ 8. Autotrophs are made of what type of cell? ______________________ 9. What is the larges organelle in a plant cell used for? ______________________ 10. Write the name of each structure next to each letter in the diagrams.