Review Book Worksheets
advertisement

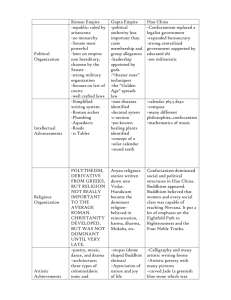
Name:_____________________________________________ Ancient Civilizations Review 1. Describe the life of Paleolithic peoples: Nomadic, hunted, gathered, lived in small groups of people 2. Describe the first tools used by man: Very simple – made of stone, bone and wood 3. When was language developed and why was it developed? It was developed during Paleolithic times to help communicate during a hunt 4. Where did the earliest people live? Africa (East) 5. Describe the life of people in the Neolithic Revolution Lived in permanent settlements, domesticated food and animals 6. How did humans’ lives changed due to the Agricultural Revolution? People lived together in villages New Social Classes developed New technology was developed (tools & skills) 7. Why were governments developed? To make sure enough food was produced and that cities were protected 8. Economies based primarily on farming were known as what? Traditional economies 9. Belief in many gods? Polytheistic 1 Geographic Setting Egypt (~5000 yrs ago) Desert Nile River AFRICA –MIDDLE EAST Sumerian Civ (~5000 yrs ago) Mesopotamia along the Tigris and Euphrates MIDDLE EAST Religion Polytheistic Sun god – Amon-Re Life after death - mummification Polytheistic Ziggurats – pyramid like structure w/ shrine of the cities gods/goddesses Government Ruler – Pharaoh (both a king and a God) Ruling families were dynasties City-state Hereditary ruler Social Structure Classes – Pharaoh, Priests, Nobles, Craftsmen and merchants, farmers, slaves Distinct social classes Ruling Family & high priests Small Middle class Peasant Farmers Economy CONTRIBUTIONS Women had a higher status in Egypt than any other ancient civ. Trade Farming Mummification – learn about human body, diagnose illness, perform surgery Hieroglyphics Pyramids Trade Farming 1st wheeled vehicles Metal plow 12 month calendar Cuneiform – wedged shaped writing Number system based on 60 10. Define empire: Groups of states or territories governed by one ruler 11. What is Hammurabi best known for? Describe. Codified set of laws – established standards of justice to all classes – they were unequal between classes – favored high classes 12. What is India dependant on for growth of crops? Monsoons 2 Geographic Setting: Government: Early Chinese Civilizations (1027BCE – 220CE) Civilizations started in river valleys – Huang He (Yellow), Yangzi Mountains, Jungles, & ocean – isolated China Called themselves the Middle Kingdom Clans controlled most of the land Shang set up first dynasty (1650BCE) Social Structure Similar to other ancient civs Noble warriors owned land Merchants/craftsmen lived in cities Majority of people were poor peasants/farmers Religion Polytheistic – prayed to Gods Prayed to nature spirits Looked to dead ancestors to help Yin/Yang CONTRIBUTIONS Written Chinese – pictographs and ideographs (objects) (ideas) Ten’s of thousands of characters 13. Describe the meaning behind this symbol: The Universe is a delicate balance between two forces. When the forces are in balance peace and prosperity will result. 14. Define Demography: The study of human populations 15. What was the role of water to Ancient Civilization? Civilizations started near rivers – fertile land Highways for trade and transportation Drinking Irrigation 16. Where were the Bantu people from? West Africa 17. Why did the Bantu peoples move? In search of fertile land – the Sahara region began to dry out Zhou (1027BC-221-BC) Han (206BCE-220CE): 3 Government/ Economy: Took over from the Shang Ruled though the Mandate of Heaven Economy Grew Trade expanded - Confucian values were in the government - Strengthened the economy Society: Feudal society - Civil Service system - Confucian values were part of everyone’s life - Men superior to women Contributions: Made first Chinese books Astronomers studied planets Developed an accurate calendar Learned to make silk Technology: - Improved/built roads & canals - Paper our of wood pulp - Wheelbarrow - Rudder - Fishing reel Science: Acupuncture Herbal remedies Anesthesia Books on chemistry, zoology, biology Arts: - Jade and ivory carvings Artists used bronze, ceramics, silk 18. What route was opened by the Han dynasty? Silk Road 19. What did this route link? China with lands as far west as Mesopotamia 20. Who was the most famous of the Han emperors? Why? Wudi – he removed harsh laws from Chinese government - he secured and expanded China’s borders 21. Where did the Han Empire expand to? Manchuria, Korea, Northern Vietnam, Tibet, Central Asia 22. List the reasons for DECLINE of the HAN: a. Political : Rulers were unable to control powerful warlords b. Economic: Canal and roads were not maintained, economy suffered, increase in taxes c. Military: Warlords overthrew the last Han emperor, invaders overran the empire 4 23. Describe the three geographic areas of India: Northern Plain – fertile, well watered by Indus & Ganges Deccan Plateau – dry & sparsely populated Coastal Plain – flat land along E & W coasts for farming, fishing & trading 24. Who were the Indo –European warriors that moved into India from Europe and Asia? Aryans 25. What dynasty ruled over the 1 st united Indian Empire, and who led this empire? Maurya dynasty led by Chandragupta Maurya 26. Define Bureaucracy and what it did: A system of managing government through departments that are run by appointed officials - they collected taxes and oversaw building of roads and harbors 27. Who was Asoka? Chandragupta’s grandson 28. What was a lasting contribution by the Maurya Dynasty (321BCE-185CE)? Spreading of Buddhism through missionaries United much of India for the first time 29. Describe Ancient Greece (1750BCE-133BCE): a. Geographic Setting: SE Europe, many mountains, isolated valleys, small islands b. Rise of City-States: i. Why was Greece made up of City-States? Mountains divide the land into isolated valleys ii. What 2 parts made up a polis? Hilltop acropolis Main city on the flat ground iii. Define Aristocracy: Government ruled by the landholding elite - - c. Describe Sparta: Warrior society – boys trained for a lifetime in the military o age 7 they move into the military barracks Girls trained to be mothers of soldiers o Obey men o Can own property Trade and travel not allowed Had a monarchy with 2 kings 5 - d. Describe Athens: Direct democracy (limited) Women were inferior to men Education for boys Trade with other city states was allowed Laws were made by assembly (only males were in the assembly) - e. Describe the rule of Alexander the Great: Built an empire that included the Nile valley, Persia, and India More rights and opportunities were given to women Spread Greek culture Hellenistic culture arose (combined Greek, Persian, Egyptian and Indian life) - f. What aspects of culture did Athens and Sparta share? Common language Shared heroes Olympic games Same gods and religious beliefs g. GREEK and HELLENISTIC Contributions: Greek Philosophers: SOCRATES Socratic Method: learning by asking questions PLATO Government should control the lives of people ARISTOTLE Believed one strong ruler &good leader should rule Government put him to death Divided society into 3 classes: workers, philosophers, soldiers Believed people learn through reason h. Art and Architecture: i. What was reflected in Greek art? beauty, balance and order ii. How was the human body portrayed? In its most perfect form iii. Most famous Greek building? Parthenon i. Science: i. Hippocrates: Studied the causes of illness and looked for cures 6 j. Mathematics: i. Pythagoras: developed a formula to measure the sides of a right triangle ii. Euclid: wrote a book that became the basis for modern geometry 30. Describe Ancient Rome (509 BCE-476 CE) a. Geographic Setting: located in the center of Italy, a peninsula in the Mediterranean b. Republic: i. Define Republic: officials are chosen by the people ii. Senate: most powerful governing body iii. Patricians: members of the landholding upper class iv. Plebeians: farmers, merchants, artisans, & traders who made up most of the population c. Empire: i. 48 BCE, Who was in control? Julius Caesar ii. Describe the accomplishments of Octavian (aka. Augustus (absolute rule)) a. Ended Republic – started the Roman Empire b. d. Pax Romana Roman Contributions: i. LAW: 12 Tables (greatest achievement – applied to all), basis for today’s law - created a stable empire - ii. ART/ARCHITECTURE: borrowed Greek concepts Used Latin language – united the empire Grand and mighty buildings - iii. ENGINEERING: roads, bridges, harbors, and aqueducts built improved the arch and the dome 31. When did Roman trade flourish? during the Pax Romana 32. What 2 empire reached their height between 200 BCE and 200 CE? Han and Roman 33. Define monopoly: 7 Complete control of a product or business by one person or group 34. Define Silk Road: caravan route stretching from China to the Mediterranean Sea 35. Why were the Romans able to conquer areas? They had a strong well disciplined army 36. Ruler of Rome from 31 BCE to 14 CE? Augustus 37. What did Rome experience under him? Pax Romana 38. What served as a natural highway for trade? The Mediterranean Sea 39. What did the Romans build that will affect their wealth? Miles of roads 40. Where did the Roman Empire expand to? Throughout the Mediterranean region, Spain, parts of Asia minor, France and Great Britain 41. List the Causes for DECLINE (weakening) of the ROMAN EMPIRE: - Overexpansion of the empire - High Taxes - Foreign invaders 8