Rome Gupta and Han Comparison 5
advertisement
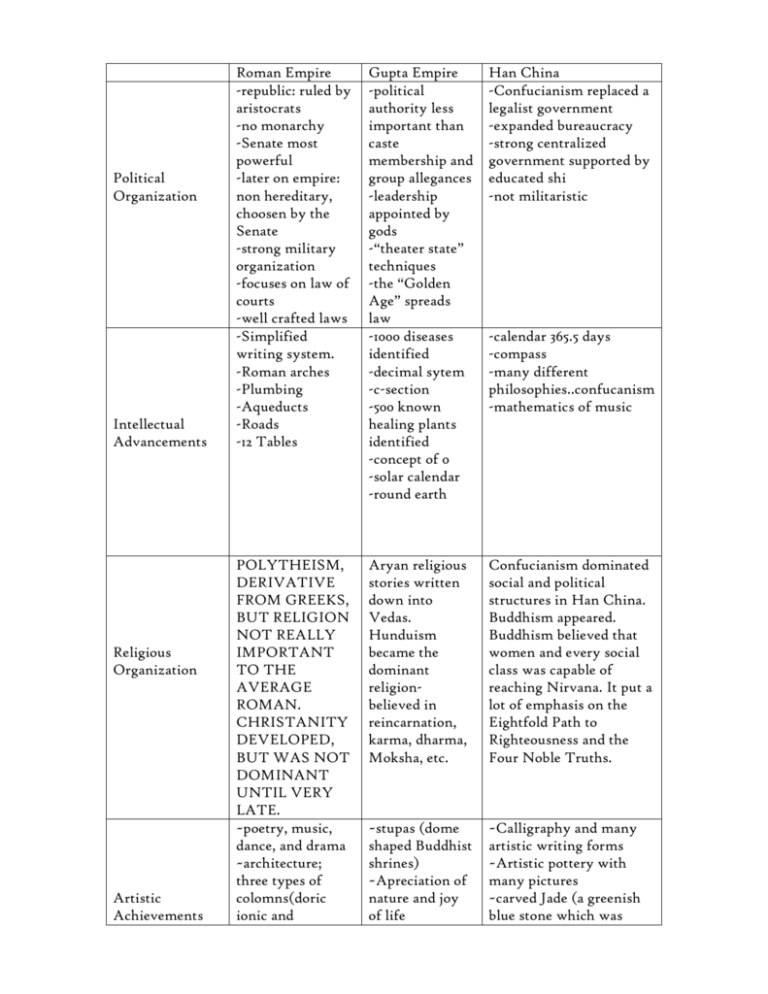
Political Organization Intellectual Advancements Religious Organization Artistic Achievements Roman Empire -republic: ruled by aristocrats -no monarchy -Senate most powerful -later on empire: non hereditary, choosen by the Senate -strong military organization -focuses on law of courts -well crafted laws -Simplified writing system. -Roman arches -Plumbing -Aqueducts -Roads -12 Tables Gupta Empire -political authority less important than caste membership and group allegances -leadership appointed by gods -“theater state” techniques -the “Golden Age” spreads law -1000 diseases identified -decimal sytem -c-section -500 known healing plants identified -concept of 0 -solar calendar -round earth Han China -Confucianism replaced a legalist government -expanded bureaucracy -strong centralized government supported by educated shi -not militaristic POLYTHEISM, DERIVATIVE FROM GREEKS, BUT RELIGION NOT REALLY IMPORTANT TO THE AVERAGE ROMAN. CHRISTANITY DEVELOPED, BUT WAS NOT DOMINANT UNTIL VERY LATE. ~poetry, music, dance, and drama ~architecture; three types of colomns(doric ionic and Aryan religious stories written down into Vedas. Hunduism became the dominant religionbelieved in reincarnation, karma, dharma, Moksha, etc. Confucianism dominated social and political structures in Han China. Buddhism appeared. Buddhism believed that women and every social class was capable of reaching Nirvana. It put a lot of emphasis on the Eightfold Path to Righteousness and the Four Noble Truths. ~stupas (dome shaped Buddhist shrines) ~Apreciation of nature and joy of life ~Calligraphy and many artistic writing forms ~Artistic pottery with many pictures ~carved Jade (a greenish blue stone which was -calendar 365.5 days -compass -many different philosophies..confucanism -mathematics of music Technological Advancements Economic Organization Social Organization Geographic Expansion Decline of The Empire corinthian) Athletic performances ~Celebrated religion often carved into the shape of Buddha) Roman Empire -roads -Harbors -Military transportation -Aquaducts -Public baths -Sewer system Gupta Empire -Plastic surgery -Bone setting -concept of “0” -Negative numbers -Pi Han Dynasty -Medicine -Ox-drawn plow/collar for animals -Iron smithing and mining -Water powered mills -Paper Very influential in trading between the central Asian nomads. Romans traded horses, alfalfa, grapes, melons, walnuts. They received silk, peaches, apricot, pottery and paper. Part of the silk road and Indian ocean trade set up many stations to trade. Trade was essential to economy. Traded between the Romans. Helped expand the silk road as a part of the economic stimulus. Traded mostly horses, created the stirrup. Asian nomads were the centralized part of the overall trade in the area. Paterfamalies-Male dominated families. Wealth based on land ownership. Middle class of merchants grew during the empire as well as inequality Guptan society was based off the caste system’s social hierarchy. Women’s status declined during the empire. Family was the basic unit in Han society. Wealth was based on the amount of land a person owned. Rural and urban areas were extremely divided. The society was basically Patriarchal and reinforced be Confucianism Rome gained total control of the Meditarranean in the Punic wars. Began in the Italian Peninsula. Northern India, Central India, not as far south as the Mauryan dynasty Extended Borders, opened trade into the Meditarranean Began after about 180 CE Decline in population because of Invasions of nomads Many invaders integrated to warrior catse of Invasions of the Huns Deterioration of political institutions Protection/ maintenance of borders growing difficulties Most discrivitce of all dynasties Series of weak emperors Plague Had to hire German soldiers which cost more money India Gupta lost control of their local princes Diseases from trade Social Disorder Mandate of Heaven was supposed to end the dynasty











