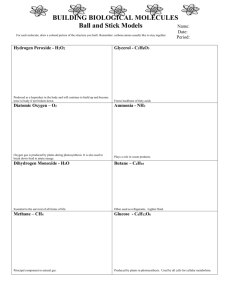
1 BIOS 1300 SI WORKSHEET 2 (Chapter 2) SI Leader: Merrin
advertisement

1 BIOS 1300 SI WORKSHEET 2 (Chapter 2) SI Leader: Merrin Jeffries (email: mj983011@ohio.edu ) 22 January 2015 1.What are the six major elements of the human body: (list from most abundant to least abundant) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 2.List the 4 Molecules (organic compounds) which compose living organisms: 1. 2. 3. 4. 3.The number and arrangement of electrons in an atom’s outer energy level determines the atom’s a. atomic weight b. atomic number c. molecular weight d. chemical properties 4.Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called ________________. 5.Isotopes of an element differ from each other in the number of: (circle one) a. protons in the nucleus b. neutrons in the nucleus c. electrons in the outer shells d. a, b, and c are all correct 6. Ions with a positive charge (+) are called a. cations b. anions c. radicals d. positrons e. isotopes 7. A substance containing atoms of different elements that are bonded together is called a(n) a. molecule 2 b. compound c. mixture d. isotope e. solution 8.Which kind of bond holds atoms in a water molecule together? What attracts water molecules to one another? 9. If a pair of electrons is unequally shared between two atoms, a(n) _________ occurs. a. single covalent bond b. double covalent bond c. triple covalent bond d. polar covalent bond e. hydrogen bond 10.The equal sharing of electrons in a molecule is an example of: a.An ionic bond b.A polar covalent bond c.A nonpolar covalent bond d.A hydrogen bond 11. The weakest bond between two atoms is the ___________ bond. a. ionic b. covalent c. polar d. nonpolar e. hydrogen 12. Molecules that have few if any polar covalent bonds and do not dissolve in water are described as ________________________________________. 13.Acids release _______ and are therefore proton ___________ (Example: HCl H+ + Cl-) 14.Bases release _________ and are therefore proton ________________ (Example: NaOH Na+ + OH-) 15.A solute that dissociates to release hydroxide ions and cause an increase in pH is: a. A base b. A salt c. An acid d. Water 3 16.Compared to a solution with a pH of 8, a solution with a pH of 6 has: e. 2 times more H+ f. 100 times more H+ g. 100 times less H+ h. 2 times less H+ Fill In: Chemical Reactions: 17.___________________________: reactions which always involve bond formation (2 reactants give you 1 product) A + B → AB 18.____________________________:Molecules are broken down into smaller molecules (this occurs in digestion – breaking down food) (1 reactant gives you 2 products) AB → A + B 19.____________________________: Bonds are both broken and made first decomposition and then synthesis AB + C → AC + B *Arrows show which way the reaction is going 20.All the chemical reactions that occur in the human body are collectively referred to as: a. anabolism b. catabolism c. metabolism d. homeostasis 21.A dehydration synthesis reaction between glycerol and a single fatty acid would yield a(n) a. micelle b. monoglyceride c. triglyceride d. omega – 3 fatty acid e. diglyceride 22. The process that breaks a complex molecule into smaller fragments by the addition of a water molecule is ____________________________________ . Questions 23-25: Complex Sugars: 23.Glucose + Fructose = __________________ 4 24. ______________ + Glucose = Maltose 25.Galactose + _____________ = Lactose 26. Which of the following is a polysaccharide? a. starch b. sucrose c. glucose d. galactose 27.Neutral fats or Triglycerides are composed of _________ Fatty Acids bonded to a glycerol molecule 28. Which of the following characteristics do all lipid molecules have in common? a. They are composed of three six-sided rings and one five-sided ring. b. They consist of three fatty acids linked to a glycerol molecule. c. They are all hydrophobic. d. They are made entirely of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. 29. Lipids are characterized as being _________ molecules a. hydrophilic b. hydrophobic c. hydroponic d. hypocephalic 30. Those fatty acids with one or more double covalent bonds in the hydrocarbon chain are said to be _________ fatty acids. a. saturated b. trans c. unsaturated d. omega -3 31. Which of the following is/are needed to form a triglyceride molecule? a. 3 glycerol molecules b. 1 glycerol molecule c. 3 fatty acid molecules d. both a and c e. both b and c 32. A steroid may be best described as a a. highly branched polysaccharide molecule. b. lipid that consists of four carbon rings c. diglyceride attached to a phosphate group and choline. d. polypeptide covalently bonded to a carbohydrate 5 33. Although we hear much about the evils of cholesterol, it is actually very important to the human body. Among other things it serves as a. a component of cell membranes b. the precursor for the formation of blood c. a surfactant which aids in digestion of water molecules. d. a blood vessel lubricant which aids in blood flow. 34. Cholesterol is a member of the class of lipids known as _________ a. diglyceride b. phospholipids c. steroids d. triglyceride