Final Exam Review Sheet
advertisement

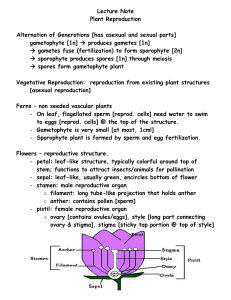
Final Exam Review Sheet for General Biology (BIO 10) Wednesday December 17, 2014 8:00 – 11:00 am Please bring 2 scantrons if possible!! Exam Format: 100 (2 pts each) multiple choice questions + 20 extra credit (1 pt each) multiple choice questions. Study Hints: Read through each chapter carefully. Review your notes and fill out any parts that you missed. Make sure to get a copy of someone’s notes for any days you missed. Study vocabulary so that you can recognize words used in context. Make sure that you understand the concepts that we discussed. Chapter 28 Central vs peripheral nervous system Motor vs sensory neurons Sympathetic vs parasympathetic Neuron structure Schwann cells Simplest animals with a nervous system? Major parts of the brain & function Action Potential – resting membrane potential, all-or-nothing Synapse Neurotransmitter Chapter 29 Major sensory organs and what types of stimuli they pick up including echolocation Generally how they work – what are hair cells? Parts of the eye, ear Chapter 30 What is a hormone? How does it send a signal? (electric = nervous system & chemical = hormones) Where are they produced? Why don’t all cells respond to hormones traveling in the blood Insulin & glucagon Growth hormone Estrogen Chapter 31 Sexual vs asexual reproduction Internal vs external fertilization Oviparous, Ovoviviparous, Viviparous Hermaphroditism Parthenogenesis Production of gametes (eggs/sperm) Haploid vs diploid Zygote Fertilization process Cleavage, Morula, blastula (blastocyst), gastrula Ectoderm, endoderm, mesoderm Chapter 32 Major events in plant evolution Alternation of generations Vascular system Seeds Flowers Water conservation Stomata; Vascular system Major groups of plants and their main characteristics Chapter 33 Primary vs. secondary growth Vascular cambium Xylem & phloem Bark vs. wood – at what layer do they separate? Different cell types in plants Monocots vs dicots Transpiration Stomata Meristems Chapter 34 Male & female reproductive structures in flowers Purpose of flowers Purpose of fruits Methods of pollination & fertilization Germination Whorls of flowers Plant hormones Phototropism, Gravitropism, thigmotropism Photoperiodism Coevolution Endosperm Double fertilization Chapter 35 Population, Community, Ecosystem, biome Trophic levels Energy flows through the system, while nurients cycle within the system Water cycle – evaporation, transpiration Major characteristics of each major ecosystem covered Eutrophic & oligotrophic Chapter 36 Major characteristics of r- and K-selected species Carrying capacity Population growth – what affects growth rate Exponential vs logistic growth Type I, II, III survivorship curves - know examples given. Niche, fundamental vs realized Competition & different types covered Symbiosis (different types: commensalism, mutualism, and parasitism) Batesian vs Müllerian mimicry Succession – primary and secondary Chapter 37 Proximate vs ultimate causes Learning – nonassociative vs associative Fixed action pattern & sign stimulus Habituation Territoriality Optimal foraging theory Altruism / kin selection Chapter 38 Greenhouse effect & Climate change Acid rain Causes of extinction Importance of biodiversity How can environmental problems be solved?