Angiosperm reproduction
advertisement

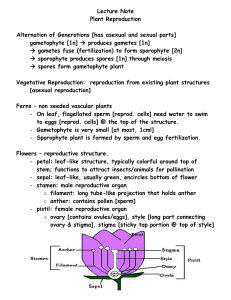
Angiosperm Reproduction Chapter 19 Major Evolutionary Advances Life - 3,800 mya Prokaryotic cell/autotrophic Eukaryotic cell - 1,400 mya Multicellar plants - 1,000 mya Vascular tissue - 430 mya Needed on land - why? Seeds - 350 mya Place on the time scale, the following events: 1. Earth 2. Prokaryotes 3. Eukaryotes 4. Multicellular life 5. Vascular tissue 6. Seeds 7. Flowers Flowers - 140 mya Earth Forms 5,000 mya Prokaryotic Cells 4,000 mya Eukaryotic Cells 3,000 mya 2,000 mya Multicellular Plants 1,000 mya Vascular tissue Seeds Flowers Flower variation Complete • has all 4 whorls Incomplete • lacks one or more of whorls (sepals, petals, stamens or carpels) Flower variation Perfect • both androecium and gynoecium Imperfect • carpellate or staminate flower only • if both carpellate and staminate flowers are on same plant called monoecious • if on different plants called dioecious Fertilization • Pollination: transfer of pollen grains from anther to pistil • Pollen grain onto stigma • Germination - tube cell produces pollen tube, generative cell divides to form 2 sperm cells • Double Fertilization: • 2 sperm enter embryo sac: • • 1 sperm fertilizes egg to form zygote other sperm fertilizes polar nuclei to form endosperm Sexual Reproduction Four events must occur for successful reproduction in angiosperms: 1. 2. 3. 4. Pollination Pollen grain growth to ovule Successful fertilization Successful seed development Sexual Reproduction • Inbreeding • Result of self-pollination & self-fertilization • Results in inbreeding depression • Outcrossing • Result of cross-pollination & cross-fertilization • Results in hybrid vigor • What process is “best”? Why? • How do plants promote this? Sexual Reproduction • Unisexual flowers • Monoecious plants • Dioecious plants Sexual Reproduction Bisexual flowers • Protandry - stamens mature before stigma • Protogyny - stigma matures before stamens • Heterostyly - physical separation between stigma and stamen Hibiscus Protandry Epilobium (fireweed) Magnolia Sexual Reproduction Bisexual flowers Self-incompatibility • Pollen grain-stigma surface: no germination • Pollen tube growth: tube “dies” • Fertilization: inviable zygotes Amarylis Pollination • Define: • transfer of pollen to stigma • How is self-fertilization prevented (or reduced) through pollination mechanisms? • • • • • unisexual flowers (monoecious plants) unisexual flowers (dioecious plants) protandry protogyny heterostyly Fertilization: • Define: • combining of sperm + egg AND sperm + polar nuclei = double fertilization ovule Fertilization megagametophyte (female gametophyte) ovule microgametophyte (male gametophyte) Fertilization Fertilization • What occurs after double fertilization? • embryo development • next generation • endosperm development • nourishment for embryo • What structure is formed? • seed • embryo • endosperm • seed coat • Where is the seed housed? • inside ovary • matures into a fruit • ovary wall = pericarp Seed germination & growth How might reproductive success be measured in an angiosperm? Funk, Lisa. 1997. A comparison of reproduction in self and outcrossed purple poppy mallow flowers (Callirhoe involucrata). Results presented at the 1997 Nebraska Academy of Sciences Annual Meeting. Gyno-dioecious species Hermaphroditc flowers on some plants Male-sterile flowers on other plants Funk, Lisa. 1997. A comparison of reproduction in self and outcrossed purple poppy mallow flowers (Callirhoe involucrata). Results presented at the 1997 Nebraska Academy of Sciences Annual Meeting. 4 Treatments • • • • Selfed Outcrossed Pollinator excluded Control Fruit set measured Pollination study in purple poppy mallow (Callirhoe involucrata). Lisa Funk, 1997 What conclusions can be drawn? 90 80 70 60 % fruit 50 formed 40 30 20 10 0 self outcross pollinator excluded control Funk, Lisa. 1997. A comparison of reproduction in self and outcrossed purple poppy mallow flowers (Callirhoe involucrata). Results presented at the 1997 Nebraska Academy of Sciences Annual Meeting. • What conclusions can be drawn? • What is the role of gyno-dioecy in plant reproduction and reproductive success in Callirhoe involucrata?