Rev. Alkyl halides
advertisement

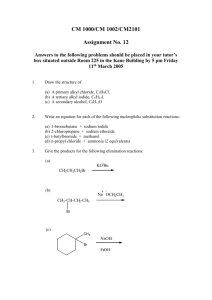
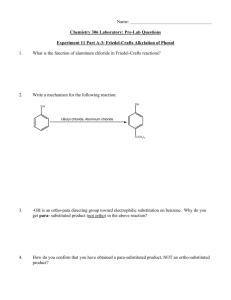
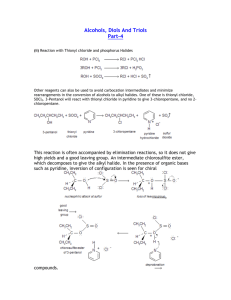
REVISION UNIT – 10 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES SUB-UNIT HALOALKANES CONCEPT SUMMARY: 1. Preparation of alkyl halides: Free radical halogenation of alkyl halides Nucleophilic substitution of alcohols with SOCl2 , PCl3 , PCl5 or HX Addition of HX to alkenes - Markovnikov rule, - Kharasch effect (for HBr only) Halogen Exchange - Finkelstein reaction - Swartz reaction) 2. Properties of Alkyl halides: Nucleophilic Substitution (SN1 an→d SN2) Elimination reaction ( β – elimination, Zaitsev rule ) Reaction with Mg to form Grignard reagent Wurtz reaction 3. Polyhalogen compounds Dichloromethane (industrial solvent) Chloroform (industrial solvent, anaesthetic) Iodoform( antiseptic) Carbon tetrachloride(solvent, degreasing agent, fire extinguisher) Freon ( aerosol propellant, refrigerant) OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS (I) 1. The poisonous gas formed when chloroform is exposed to air and sunlight is: (a) thionyl chloride (b) chloretone (c) carbonyl chloride (d) chloral 2. C2H5Br can be obtained in the laboratory by the action of ethyl alcohol with: (a) KBr (b) NH4Br (c) Br2 (d) KBr and conc. H2SO4 3. The reaction : Alcohol + HCl Alkyl halide + H2O is reversible. For the reaction to go to completion, the substance used is: (a) conc. H2SO4 (b) anhydrous ZnCl2 (c) CaCl2 (d) excess of water 4. Types of isomerism possible for 2- Chlorobutane are: (a) chain, position, optical (b) chain, position (c) only chain (d) only position 5. Alcoholic solution of KOH is used for: (a) dehalogenation (b) dehydrohalogenation (c) dehydration (d) dehydrogenation 6. The alkyl halide with maximum reactivity is: (a) CH3CH2Br (b) CH3Br (c) CH3CH2CH2Br (d) CH3CH2CH2CH2Br 7. The bond angle in CCl4 is approximately : (a) 180o (b) 120o (c) 109o 8. (d) 90o Which of the following is 2o chloride? (a) isopropyl chloride (b) isobutyl chloride (c) neopentyl chloride (d) n-butyl chloride 9. The reaction (CH3)2CHCl + NaI → (CH3)2CHI + NaCl is known as: (a) Swartz reaction (b) Stephen reaction (c) Finkelstein reaction (d) Fittig reaction 10. The antiseptic action of iodoform is due to: (a) iodoform itself (b) liberation of free iodine (c) partly due to iodine and partly due to iodoform itself (d) all the above reasons 888888888888 UNIT – 10 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES SUB-UNIT HALOALKANES CONCEPT PRACTICE: 1. Give the structures and IUPAC names of the major product(s) expected from each of the following reactions: CH3 a) C2H5 C=C H + HBr CH3 KOH(alc) b) CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl dry ether c) Br + Na 2. Explain why: a) Alkyl halides though polar are immiscible in water. b) p- dibromobenzene has higher melting point than its o- and m- isomers. c) Reactivity of isomeric alkyl halides by SN2 mechanism is in the order 1o>2o>3o 3. Write equations for the preparation of 1 – Iodobutane from : a) 1 – Butanol (b) But-1-ene 4. Dichlorodifluoromethane is an extremely stable compound, unreactive, non toxic non corrosive and an easily liquefiable gas.it is useful as a refrigerant and as an aerosol propellant. Yet it is advisable to restrict its use. State the reason for this restriction. What can you do to reduce the use of this chemical? CONCEPT MASTERY: 1. Give appropriate reason for the following: a) Optically active 2 – iodobutane on treatment with NaI in acetone undergoes racemization. b) Ethyl chloride is more reactive than vinyl chloride in nucleophilic substitution reactions. c) The chlorine atom in 2─ Chloro─2─methyl propane is more electronegative than the chlorine atom in 1─Chloro─2─methyl propane 2. What chemical test can be performed to distinguish between 1─ Chloroethene and 1─ Chloroethane 3. An alcohol (A) when treated with thionyl chloride gives another organic compound (B). (B) on treatment with sodium and dry ether gives 2,3─ dimethyl butane. Write the structures of (A) and(B). Write out the sequence of reactions which led to the identification of (A) and (B). 4. How may the following conversions be carried out? a) Tert─ butyl bromide to isobutyl bromide b) n─ propyl alcohol to isopropyl chloride CONCEPT CHALLENGE: 1. What tests can be performed to distinguish among CH3CH=CHCl, CH3CH2Cl and CH2=CHCH2Cl CH3 CH3 2. In the reaction : hν │ │ CH3CHCH3 + Br2 CH3─ C ─ CH3 + CH3─ CH ─ CH2Br │ │ CH3 Br [A] [B] Which one of the four following compositions is likely to be correct? Explain. (a) A (1%), B (99%) (b) A (99%), B(1%) (c) A (60%), B (40%) (d) A (40%), B(60%) 3. Which among the following compounds will be more reactive in SN1 reaction? a) Cl b) Cl c) Cl Cl d) CH3 CH3 4. a) Write the IUPAC name of the following compound Br b) Would SN1 or SN2 reaction be involved in the hydrolysis of this compound? c) What would be the product of hydrolysis? ************** OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS (I) (ANSWERS) 1. The poisonous gas formed when chloroform is exposed to air and sunlight is: (a) thionyl chloride (b) chloretone (c) carbonyl chloride (d) chloral 2. C2H5Br can be obtained in the laboratory by the action of ethyl alcohol with: (a) KBr (b) NH4Br (c) Br2 (d) KBr and conc. H2SO4 3. The reaction : Alcohol + HCl Alkyl halide + H2O is reversible. For the reaction to go to completion, the substance used is: (a) conc. H2SO4 (b) anhydrous ZnCl2 (c) CaCl2 (d) excess of water 4. Types of isomerism possible for 2- Chlorobutane are: (a) chain, position, optical (b) chain, position (c) only chain (d) only position 5. Alcoholic solution of KOH is used for: (a) dehalogenation (b) dehydrohalogenation (c) dehydration (d) dehydrogenation 6. The alkyl halide with maximum reactivity is: (a) CH3CH2Br (b) CH3Br (c) CH3CH2CH2Br (d) CH3CH2CH2CH2Br 7. The bond angle in CCl4 is approximately : (a) 180o (b) 120o (c) 109o (d) 90o 8. Which of the following is 2o chloride? (a) isopropyl chloride (b) isobutyl chloride (c) neopentyl chloride (d) n-butyl chloride 9. The reaction (CH3)2CHCl + NaI → (CH3)2CHI + NaCl is known as: (a) Swartz reaction (b) Stephen reaction (c) Finkelstein reaction (d) Fittig reaction 10. The antiseptic action of iodoform is due to: (a) iodoform itself (b) liberation of free iodine (c) partly due to iodine and partly due to iodoform itself (d) all the above reasons 888888888888