Chapter 10
advertisement

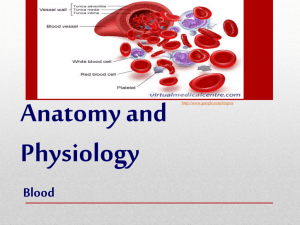
Chapter 10 Composition and Function of Blood -Connective tissue with blood cells, formed elements, and a fluid matrix, plasma. Erythrocytes- Leukocytes- Platelets- PlasmaMany things are dissolved in plasma, mainly plasma proteins Albumin- Clotting proteins- Antibodies- Hormones-Changes on a daily/hourly rate to maintain homeostasis, based on diet, internal and external stressors. -Also helps to distribute body heat throughout the body. 1 Red Blood Cells-Main function is to transport oxygen to all tissues and cells in the body -Lacks a nucleus and major organelles, packed full of hemoglobin -Hemoglobin is a protein molecule that binds easily to oxygen, and CO2 -Small disc shaped cells, allow for ease of movement through small vessels -One RBC can carry about 1 billion oxygen molecules, more practical measurement, 12-18 g of Hb per 100 mL of blood. White Blood Cells-Less numerous than RBC, but crucial to the bodies defense system. -Have the ability to move in and out of the bloodstream -WBC’s are classified into two divisions, based on visible granules in the cytoplasm; granulocytes and agranulocytes. Granulocytes- have lobed nuclei and darkly staining granules NeutrophilsEosinophilsBasophils- 2 Agranulocytes- “normal” nuclei, little or no visible granules LymphocytesMonocytesPlatelets- Blood Cell Formation- hematopoiesis-All formed elements arise from a common type of stem cell, hemocytoblast. -Hemocytoblasts- -Lymphoid stem cells- -Myeloid stem cells- -RBC live for about-Rate of RBC production is regulated by a hormone called erythropoietin -Rate of WBC production is regulated by hormones called colony stimulating factors and interleukins. 3 Hemostasis- stoppage of blood flow A fast and localized response, has three major phases, platelet plug, vascular spasms, and coagulation. 1. Vascular Spasm Phase- 2. Platelet Plug Phase- 3. Coagulation Phase Blood Groups and Transfusions -RBC’s contain membrane proteins (antigens) that are genetically inherited. -Major antigens are A, B, and Rh -During development antibodies are formed against the A and/or B antigens not present on the persons own RBC’s. -Type A blood -Type B blood -Type AB blood 4 -Type O blood -Rh + has Rh antigens, Rh – has no Rh antigens, antibodies are formed differently. Developmental Aspects of Blood -Circulatory system is developed early on -Blood is flowing through vessels by day 28 of pregnancy -Infants have a special type of Hb that binds stronger to oxygen. 5