chapter 5 objective
advertisement

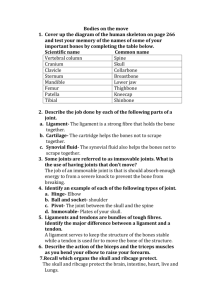
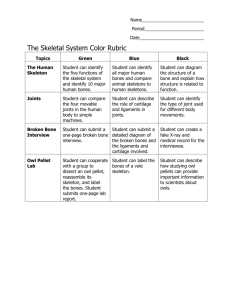
CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES SKELETAL SYSTEM Bones: An Overview (116-124) Identify the subdivisions of the skeleton as axial or appendicular. Identify the major bones of the human skeleton (Fig 5.6) List at least three functions of the skeletal system. Name the four main kinds of bones. Identify the major anatomical areas of a long bone. Explain the role of the bone matrix in making bone both hard and flexible. Describe the process of bone formation in the fetus and summarize the events of bone remodeling throughout life. Include relevant vocabulary, types of cells, and hormones involved. Name and describe the various types of fractures. Axial Skeleton (124-138) On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull. (Fig 5.7) Describe how the skull of a newborn infant (or fetus) differs from that of an adult, and explain the function of fontanels. (see page 130) Name the parts of a typical vertebra and explain in general how the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae differ from one another. (Fig 5.14) Discuss the importance of the intervertebral discs and spinal curvatures. Explain how the abnormal spinal curvatures (scoliosis, lordosis, and kyphosis) differ from one another. Appendicular Skeleton (138-141 Skip 142-144) Describe important differences between a male and female pelvis. Identify the bones of the arm and hand on a diagram (Fig 5.22) Joints (145, 153) Name the three major categories of joints and compare the amount of movement allowed by each. (especially- synovial joints) Developmental Aspects of the Skeleton (153,155) Identify some of the causes of bone and joint problems throughout life. Rickets, fracture, bursitis, sprain, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoporosis. Closer Look Protect Your Back (Page 136-137) Bone Repair (146-147) ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________