Chapter 7 – Chemical Quantities Test Review Topics
advertisement

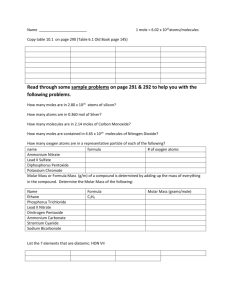
Chapter 8 – Chemical Quantities Test Topics Thursday, December 2nd The mole and Avogadro’s # (1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 atoms, molecules, ions or formula units) Representative units: o ionic compounds (start with a metal) = formula units o single element = atoms o Element or elements with a positive or negative charge = ions o molecular compounds, including diatomic molecules (start with a nonmetal) = molecules Determining molar mass for elements and compounds (units for molar mass are always grams/mole, g/mol) – round molar mass for every element to 1 number after the decimal before multiplying. Determining # of moles, grams, atoms or ions from a given amount of a compound Conversions between moles and atoms, molecules, ions, or formula units (use 1 mol = 6.02 x 1023) Conversions between moles and grams (use 1 mol = molar mass in grams for the element or compound) STP (Standard Temperature and Pressure) – 1 atm of pressure and 0oC (273 K) for the temperature Molar Volume of a Gas – at STP 1 mol = 22.4 L Conversions using molar volume (use 1 mol = 22.4 L) including going between liters, grams, moles and atoms, molecules, ions & formula units Calculating percent composition of an element in a compound Difference between empirical and molecular formulas Calculating empirical formulas given percents or grams for elements Calculating molecular formulas given the empirical formula and the molar mass of the molecular compound Calculating both empirical and molecular formulas from percentages or grams of each element. The molar mass of the molecular formula will be given to you.