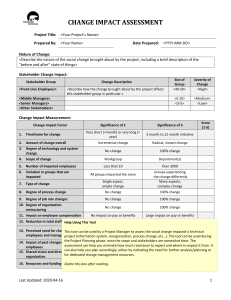
downloading
advertisement

Layer 3 - Exercises All participants will work within their groups in pairs. Each group has three routers and three switches to work with. The lab is divided into four components: 1. Basic Router Configuration 2. Static Routing 3. Dynamic routing with OSPF 4. iBGP 5. eBGP There is a certain dependency between the labs as the exercises progress. Make sure to maintain your configuration unless otherwise instructed. All exercises will use a common IP addressing scheme and network topology. Given the limited number of interfaces we will be using VLAN interfaces to facilitate the exercise and the different features we will be using. As you go through the exercises all the examples are given from the point of view of R11, the border router in group 1. Make sure that you take the examples and adapt them to your own router, network topology and addressing scheme. Address Space Allocation Group Group Group Group Group 1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 10.10.0.0/16 10.20.0.0/16 10.30.0.0/16 10.40.0.0/16 10.50.0.0/16 ASN: ASN: ASN: ASN: ASN: 10 20 30 40 50 Each group will then further partition their space: 10.X0.1.0/24 FEC0:X0:1:1::/64 10.X0.64.0/24 FEC0:X0:2:64::/64 (VLAN 64) 10.X0.65.0/24 FEC0:X0:3:65::/64 (VLAN 65) 10.X0.128.0/24 FEC0:X0:4:128::/64 (VLAN 128) 10.X0.129.0/24 FEC0:X0:4:129::/64 (VLAN 129) 10.X0.254.0/24 FEC0:X0:0:FE::/64 Loopback Subnet - Core Network - Access Subnet - Access Subnet - Access Subnet - Access Subnet - Router 1 10.254.X0.0/30 FEC0:FE:0:X0::/64 – Connection to ISP 10.255.0.X0/24 FEC0:FF::X0/64 – Connection to IXP 10.254.X0.0/30 – Connection to ISP 10.255.0.X0/24 – Connection to IXP With X being your group number (1,2,3,4,5) All equipment in the remote lab will be managed via their console ports. Access to the consoles is available via secure shell (ssh). Use the topology and device/console name reference in page X to identify your devices and ssh to console server nsrclab-console1-gw.uoregon.edu (128.223.11.137) with user nsrc:<device>. For example: ssh nsrc:router3@nsrclab-console1-gw.uoregon.edu 2 LAB TOPOLOGY 3 Network Topology 4 Network Topology Details 5 Alternate Network Topology 1 6 Alternate Network Topology 2 7 DEVICE/CONSOLE NAMES REFERENCE 8 Basic Router Configuration 1. Name the router. Router> enable Router# config terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. Router(config)# hostname R11 R11(config)# End with CNTL/Z. 2. Deactivate domain name resolution. R11 (config)# no ip domain-lookup 3. Create a username and password. R11 (config(# username walc secret nsrc R11 (config)# enable secret nsrc R11 (config)# service password-encryption 4. Activate remote login access to the router R11 (config)# aaa new-model R11 (config)# aaa authentication login default local R11 (config)# aaa authentication enable default enable 5. Make sure that you configure your console and vtys R11 R11 R11 R11 (config)# (config)# (config)# (config)# line con 0 login authentication default line vty 0 4 login authentication default 6. Make sure the router understands CIDR R11 (config)# ip subnet-zero R11 (config)# ip classless 7. Activate IPv6 routing. R11 (config)# ipv6 unicast-routing 8. Save the configuration and checkpoint. 9 R11(config)#^Z R11# write memory Building configuration... [OK] R11# 9. Configure your interfaces. R11(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1 R11(config-if)# ip address 10.10.1.1 255.255.255.0 R11(config-if)# description Link to Core R11(config-if)# ipv6 enable R11(config-if)# ipv6 address FEC0:10:1:1::1/64 R11(config-if)# no ip redirects R11(config-if)# no ip directed-broadcast R11(config-if)# no ip proxy-arp R11(config-if)# no shutdown R11(config)#^Z R11# Or from the point of view of R12 & R13 where you will use VLANs R12(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1 R12(config)# no ip address R12(config)# no shutdown R12(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1.64 R12(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1Q 64 R12(config-subif)# ip address 10.10.64.2 255.255.255.0 R12(config-subif)# description Link VLAN 64 R12(config-subif)# ipv6 enable R12(config-subif)# ipv6 address FEC0:10:2:64::2/64 R12(config-subif)# no ip redirects R12(config-subif)# no ip directed-broadcast R12(config-subif)# no ip proxy-arp R12(config-subif)# no shutdown R12(config-subif)#^Z R12# R13(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1 R13(config)# no ip address R13(config)# no shutdown R13(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1.64 R13(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1Q 64 R13(config-subif)# ip address 10.10.64.3 255.255.255.0 R13(config-subif)# description Link VLAN 64 R13(config-subif)# ipv6 enable R13(config-subif)# ipv6 address FEC0:10:2:64::3/64 R13(config-subif)# no ip redirects R13(config-subif)# no ip directed-broadcast R13(config-subif)# no ip proxy-arp R13(config-subif)# no shutdown R13(config-subif)#^Z 10 R13# 10. Do some ping tests. R11# ping 10.10.2.2 and then very the output of the following commands IPv4: show arp show interface <int> <number> show ip interface : Shows ARP cache : Shows interface state and configuration : Shows interface IP state and config IPv6: show ipv6 neighbors show ipv6 interface <int> <number> show ipv6 interface 11. : Shows IPv6 neighbors : Shows interface state and configuration : Shows interface state and configuration Create loopback interface. R11(config)#interface loopback 0 R11(config-if)#ip address 10.10.254.1 255.255.255.255 R11(config-if)#ipv6 address FEC0:10:0:FE::1/128 R11(config-if)#^Z R11# 12. Save the configuration and checkpoint. R11# write memory Building configuration... [OK] R11# 11 Static Routing 1. Try pinging some of the addresses with your AS. R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# ping ping ping ping ping ping ping ping 10.10.1.1 10.10.1.2 10.10.1.3 10.10.254.1 10.10.254.2 10.10.254.3 10.10.64.2 10.10.64.3 R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# ping ping ping ping ping ping ping ping ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 FEC0:10:1:1::1 FEC0:10:1:1::2 FEC0:10:1:1::3 FEC0:10:0:FE::1 FEC0:10:0:FE::2 FEC0:10:0:FE::3 FEC0:10:2:64::2 FEC0:10:2:64::3 2. What is happening? Why can’t we ping some of the addresses? 3. Create static routes. R11(config)# ip route 10.10.254.2 255.255.255.255 10.10.1.2 R11(config)# ip route 10.10.254.3 255.255.255.255 10.10.1.3 R11(config)# ip route 10.10.64.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.1.2 R11(config)# ip route 10.10.65.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.1.2 R11(config)# ip route 10.10.128.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.1.3 R11(config)# ip route 10.10.129.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.1.3 R11(config)# ipv6 route FEC0:10:0:FE::2/128 FEC0:10:1:1::2 R11(config)# ipv6 route FEC0:10:0:FE::3/128 FEC0:10:1:1::3 R11(config)# ipv6 route FEC0:10:2:64::/64 FEC0:10:1:1::2 R11(config)# ipv6 route FEC0:10:2:64::/64 FEC0:10:1:1::3 R11(config)#^Z R11# 4. Do the same ping tests. R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# ping ping ping ping ping ping ping ping 10.10.1.1 10.10.1.2 10.10.1.3 10.10.254.1 10.10.254.2 10.10.254.3 10.10.64.2 10.10.64.3 R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# ping ping ping ping ping ping ping ping ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 FEC0:10:1:1::1 FEC0:10:1:1::2 FEC0:10:1:1::3 FEC0:10:0:FE::1 FEC0:10:0:FE::2 FEC0:10:0:FE::3 FEC0:10:2:64::2 FEC0:10:2:64::3 5. STOP -- Checkpoint. What happens when a new network is added? 6. Save the configuration and checkpoint. 12 R11# write memory Building configuration... [OK] R11# R11# show running-config R11# show startup-config 13 Dynamic Routing with OSPF 1. Configure a new OSPF routing process. IPv4: R11(config)#router ospf 100 R11(config)#^Z R11# IPv6: R11(config)#ipv6 router ospf 200 R11(config)#^Z R11# 2. Add the networks. IPv4: R11(config)#router ospf 100 R11(config-router)#network 10.10.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R11(config-router)#network 10.10.254.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 R11(config)#^Z R11# IPv6: R11(config)#interface loopback 0 R11(config-if)#ipv6 ospf 200 area 0 R11(config)#^Z R11# 3. Disable OSPF for interfaces. IPv4 R11(config)#router ospf 100 R11(config-router)#passive-interface Loopback 0 R11(config-router)#passive-interface FastEthernet0/0 R11(config)#^Z R11# IPv6: Don’t configure OSPF in the given interface 4. Log OSPF Adjacencies. 14 IPv4: R11(config)#router ospf 100 R11(config-router)#ospf log-adjacency-changes R11(config)#^Z R11# IPv6: R11(config)#ipv6 router ospf 200 R11(config-rtr)#log-adjacency-changes R11(config)#^Z R11# 5. STOP -- Checkpoint 1. IPv4: show show show show ip ip ip ip route ospf ospf interface ospf neighbor : show routes in routing table : shows general OSPF information : shows the status of OSPF in an interface : shows OSPF neighbor list. IPv6: show show show show ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 route ospf ospf interface ospf neighbor 6. Which routes are preferred? 7. Remove the old static route entries. R11(config)# no R11(config)# no R11(config)# no R11(config)# no R11(config)# no R11(config)# no R11(config)# no R11(config)# no R11(config)# no R11(config)# no R11(config)#^Z R11# ip route 10.10.254.2 255.255.255.255 10.10.1.2 ip route 10.10.254.3 255.255.255.255 10.10.1.3 ip route 10.10.64.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.1.2 ip route 10.10.65.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.1.2 ip route 10.10.128.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.1.3 ip route 10.10.129.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.1.3 ipv6 route FEC0:10:0:FE::2/128 FEC0:10:1:1::2 ipv6 route FEC0:10:0:FE::3/128 FEC0:10:1:1::3 ipv6 route FEC0:10:2:64::/64 FEC0:10:1:1::2 ipv6 route FEC0:10:2:64::/64 FEC0:10:1:1::3 8. STOP -- Checkpoint 2. 15 IPv4: show ip route : show routes in routing table IPv6: show ipv6 route 9. Try pinging some of the addresses with your AS. R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# ping ping ping ping ping ping 10.10.254.2 10.10.254.3 10.10.64.2 10.10.65.1 10.10.128.1 10.10.129.1 16 First Hop Redundancy We will be using HSRP for this exercise. All the examples are presented from the point of view of R12 & R13. You will also want to reconfigure the switches that are connected to R13 to support VLAN64 and re-cable the switches to build a redundant L2 network. 1. Configure HSRP for the interfaces R12(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1.64 R12(config-if)# ip address 10.10.64.2 255.255.255.0 R12(config-if)# standby 1 name 10.10.64.0/24 R12(config-if)# standby 1 ip 10.10.64.1 R12(config-if)# standby 61 name FEC0:10:1:64::/64 R12(config-if)# standby 61 ipv6 FE80::1 R13(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1.64 R13(config-if)# ip address 10.10.64.3 255.255.255.0 R13(config-if)# standby 1 name 10.10.64.0/24 R13(config-if)# standby 1 ip 10.10.64.1 R13(config-if)# standby 61 name FEC0:10:1:64::/64 R13(config-if)# standby 61 ipv6 FE80::1 2. STOP – Checkpoint. Verify the active router show standby FastEthernet0/1.64 a. b. c. d. e. f. : Shows HSRP status Which is the active router? Which is the standby router? What is the address for the virtual IP? What is the virtual MAC (Ethernet) address? Ping from the workstations out towards the border Traceroute from the workstations towards the border 3. Change the interface’s HSRP priority for one of the routers serving subnet 10.X0.64.0/24 R12(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1.64 R12(config-if)# standby 1 priority 110 R12(config-if)# standby 61 priority 110 4. STOP – Checkpoint. Verify the active router show standby FastEthernet0/1.64 : Shows HSRP status a. Which is the active router? b. Which is the standby router? 17 c. d. e. f. What is the address for the virtual IP? What is the virtual MAC (Ethernet) address? Ping from the workstations out towards the border Traceroute from the workstations towards the border 5. Modify other HSRP parameters R12(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1.64 R12(config-if)# standby 1 preempt delay minimum 0 R12(config-if)# standby 1 timers 3 10 R12(config-if)# standby 1 authentication md5 key-string CLAVE R12(config-if)# standby 61 preempt delay minimum 0 R12(config-if)# standby 61 timers 3 10 R12(config-if)# standby 61 authentication md5 key-string CLAVE R13(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1.64 R13(config-if)# standby 1 preempt delay minimum 0 R13(config-if)# standby 1 timers 3 10 R13(config-if)# standby 1 authentication md5 key-string CLAVE R13(config-if)# standby 61 preempt delay minimum 0 R13(config-if)# standby 61 timers 3 10 R13(config-if)# standby 61 authentication md5 key-string CLAVE 6. Track the status of the uplink interface R12(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1.64 R12(config-if)# standby 1 track FastEthernet0/0 20 R12(config-if)# standby 61 track FastEthernet0/0 20 R13(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1.64 R13(config-if)# standby 1 track FastEthernet0/0 20 R13(config-if)# standby 61 track FastEthernet0/0 20 7. STOP – Checkpoint show standby FastEthernet0/1.64 : Shows HSRP status a. Ping from the workstations out towards the border b. Traceroute from the workstations towards the border Shutdown the interface FastEthernet0/0 for the active router and answer the following questions c. Which is the active router? d. Which is the standby router? e. What happened to your ping? 18 8. Save the configuration and checkpoint. R11# write memory Building configuration... [OK] R11# R11# show running-config R11# show startup-config 19 iBGP 1. Verify that we still have good connectivity to each of the loopback interfaces. R11# R11# R11# R11# ping ping ping ping 10.10.254.2 10.10.254.3 10.10.64.2 10.10.64.3 R11# R11# R11# R11# ping ping ping ping ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 FEC0:10:0:FE::2 FEC0:10:0:FE::3 FEC0:10:2:64::2 FEC0:10:2:64::3 IPv4: show show show show ip ip ip ip ospf ospf interface ospf neighbor ospf database : shows general OSPF information : shows the status of OSPF in an interface : shows OSPF neighbor list. : shows OSPF topology DB IPv6: show show show show ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 ipv6 ospf ospf interface ospf neighbor ospf database 2. Log the BGP neighbor changes and other global parameters. R11(config)#router bgp 10 R11(config-router)# bgp log-neighbor-changes R11(config-router)# no synchronization R11(config-router)# no auto-summary R11(config)#^Z R11# 3. Configure iBGP neighbors. R11(config)# router R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# bgp 10 neighbor neighbor neighbor neighbor 10.10.254.2 10.10.254.2 10.10.254.2 10.10.254.2 remote-as 10 update-source loopback 0 description iBGP to R12 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor neighbor neighbor neighbor 10.10.254.3 10.10.254.3 10.10.254.3 10.10.254.3 remote-as 10 update-source loopback 0 description iBGP to R13 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor neighbor neighbor neighbor FEC0:10:0:FE::2 FEC0:10:0:FE::2 FEC0:10:0:FE::2 FEC0:10:0:FE::2 remote-as 10 update-source loopback 0 description iBGP a R12 soft-reconfiguration in neighbor FEC0:10:0:FE::3 remote-as 10 neighbor FEC0:10:0:FE::3 update-source loopback 0 20 R11(config-router)# neighbor FEC0:10:0:FE::3 description iBGP a R13 R11(config-router)# neighbor FEC0:10:0:FE::3 soft-reconfiguration in R11(config-router)# address-family ipv6 R11(config-router-af)# neighbor FEC0:200:8:11::224 activate R11(config-router-af)# neighbor FEC0:200:16:19::224 activate R11(config-router-af)# exit R11(config-router)# exit R11(config)#^Z R11# R11# 4. STOP -– Checkpoint 1. IPv4: show ip bgp summary show ip bgp show ip route : shows BGP infomration and neighbors : shows a list of learned BGP paths : shows all installed routes IPv6: show bgp ipv6 summary show bgp ipv6 show ipv6 route 5. Create BGP networks to advertise. R11(config)# router bgp 10 R11(config-router)# network 10.10.0.0 mask 255.255.192.0 R11 (config-router)# address-family ipv6 R11 (config-router-af)# network FEC0:10:1::/48 R11 (config-router-af)# exit R11 (config-router)# exit R11(config)#^Z R11# 6. STOP –- Checkpoint 2. R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# show show show show show show ip bgp neighbors ip bgp neighbors ip bgp neighbors bgp ipv6 unicast bgp ipv6 unicast bgp ipv6 unicast 10.10.254.2 advertised-routes 10.10.254.2 routes 10.10.254.2 received-routes neighbors FEC0:10:0:FE::2 advertised-routes neighbors FEC0:10:0:FE::2 routes neighbors FEC0:10:0:FE::2 received-routes Why isn’t the prefix being announced? 7. Create a static route for your prefix. 21 R11(config)# ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.192.0 Null0 R11(config)# ipv6 route FEC0:10:1::/48 Null0 250 R11(config)#^Z R11# 8. Check connectivity. R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# ping ping ping ping ping ping ping ping ping ping 10.10.254.2 10.10.254.3 10.10.10.1 10.10.11.1 10.10.128.1 10.10.129.1 ipv6 FEC0:10:0:FE::2 ipv6 FEC0:10:0:FE::3 ipv6 FEC0:10:2:64::2 ipv6 FEC0:10:2:64::3 9. Save the configuration and checkpoint. R11# write memory Building configuration... [OK] R11# R11# show running-config R11# show startup-config 22 eBGP 1. Configure your interface to the ISP. Some networks will only connect to the ISP. R11(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0.10 R11(config-if)# description Link to ISP R11(config-if)# ip address 10.254.10.2 255.255.255.252 R11(config-if)# ipv6 enable R11(config-if)# ipv6 address FEC0:FE:0:10::2/64 R11(config-if)# no ip redirects R11(config-if)# no ip directed-broadcast R11(config-if)# no ip proxy-arp R11(config-if)# no shutdown R11(config)#^Z R11# 2. Make sure you add the networks to your IGP IPv4: R11(config)#router ospf 100 R11(config-router)#network 10.254.10.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R11(config-router)#network 10.255.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R11(config)#^Z R11# IPv6: R11(config)#interface GigabitEthernet0/0.10 R11(config-if)#ipv6 ospf 200 area 0 R11(config)#interface GigabitEthernet0/0.255 R11(config-if)#ipv6 ospf 200 area 0 R11(config)#^Z R11# 3. Configure eBGP session to external peers. R11(config)# router bgp 10 R11(config-router)# neighbor 10.254.10.1 remote-as 254 R11(config-router)# neighbor 10.254.10.1 description eBGP to ISP R11(config-router)# neighbor FEC0:FE:0:10::1 remote-as 254 R11(config-router)# neighbor FEC0:FE:0:10::1 description eBGP to ISP R11(config-router)# address-family ipv6 R11(config-router-af)# neighbor FEC0:FE:0:10::1 activate R11(config-router-af)# exit R11(config-router)# exit R11(config)#^Z R11# 23 4. STOP -– Checkpoint 1. R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# show show show show show show show show show show show show ip bgp summary ip bgp neighbors ip bgp neighbors ip bgp neighbors ip bgp neighbors ip bgp bgp ipv6 unicast bgp ipv6 unicast bgp ipv6 unicast bgp ipv6 unicast bgp ipv6 unicast bgp ipv6 unicast 10.254.10.1 10.254.10.1 advertised-routes 10.254.10.1 routes 10.254.10.1 received-routes summary neighbors neighbors neighbors neighbors FEC0:FE:0:10::1 FEC0:FE:0:10::1 advertised-routes FEC0:FE:0:10::1 routes FEC0:FE:0:10::1 received-routes 5. Aggregate CIDR blocks. R11(config)# router bgp 10 R11(config-router)# aggregate-address 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 R11(config-router)#^Z R11# 6. STOP –- Checkpoint 2. R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# show show show show show show ip bgp neighbors ip bgp neighbors ip bgp neighbors bgp ipv6 unicast bgp ipv6 unicast bgp ipv6 unicast 10.254.10.1 advertised-routes 10.254.10.1 routes 10.254.10.1 received-routes neighbors FEC0:FE:0:10::1 advertised-routes neighbors FEC0:FE:0:10::1 routes neighbors FEC0:FE:0:10::1 received-routes 7. Advertise only a summary aggregate. R11(config)# router bgp 10 R11(config-router)# no aggregate-address 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 R11(config-rtr)# aggregate-address 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 summary-only R11(config-router)# exit R11(config)# ipv6 route FEC0:10::/32 Null0 250 R11(config-router)#^Z R11# Another option would be: R11(config)# router bgp 10 R11(config-rtr)#no aggregate-address 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 summary-only R11(config-router)# network 10.10.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 R11(config-router)# exit R11(config)# ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0 250 R11(config)#^Z 24 R11# 8. Create prefix lists for inbound/outbound policies. R11(config)# ip prefix-list out-peer permit 10.10.0.0/16 le 32 R11(config)# ip prefix-list out-peer deny 0.0.0.0/0 le 32 R11(config)# ip prefix-list isp-in-peer deny 10.10.0.0/16 le 32 R11(config)# ip prefix-list isp-in-peer permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32 R11(config)# ipv6 prefix-list ipv6-out-peer permit FEC0:10::/32 le 128 R11(config)# ipv6 prefix-list ipv6-out-peer deny ::/0 le 32 R11(config)# ipv6 prefix-list ipv6-isp-in-peer deny FEC0:10::/32 le 128 R11(config)# ipv6 prefix-list ipv6-isp-in-peer permit ::/0 le 32 R11(config)#^Z R11# 9. Create input and output policies. R11(config)# router R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config)#^Z R11# 10. 10.254.10.1 remote-as 254 10.254.10.1 description to ISP AS254 10.254.10.1 prefix-list out-peer out 10.254.10.1 prefix-list isp-in-peer in FEC0:FE:0:10::1 remote-as 254 FEC0:FE:0:10::1 description to ISP AS254 FEC0:FE:0:10::1 prefix-list ipv6-out-peer out FEC0:FE:0:10::1 prefix-list ipv6-isp-in-peer in STOP -– Checkpoint 3. R11# R11# R11# R11# 11. bgp 10 neighbor neighbor neighbor neighbor neighbor neighbor neighbor neighbor show ip bgp summary show ip bgp ping <ip_address> traceroute <ip_address> Save the configuration and checkpoint. R11# write memory Building configuration... [OK] R11# R11# show running-config R11# show startup-config 25 Exchange Points 1. Configure the interface that connects to the IXP. Some networks will connect to both an ISP and to the Exchange point. R11(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0.255 R11(config-if)# description Link to IXP R11(config-if)# ip address 10.255.0.10 255.255.255.0 R11(config-if)# ipv6 enable R11(config-if)# ipv6 address FEC0:FF::10/64 R11(config-if)# no ip redirects R11(config-if)# no ip directed-broadcast R11(config-if)# no ip proxy-arp R11(config-if)# no shutdown R11(config)#^Z R11# 2. Make sure to carry your IXP network into your IGP. IPv4: R11(config)#router ospf 100 R11(config-router)#network 10.255.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R11(config)#^Z R11# IPv6: R11(config)#interface GigabitEthernet0/0.255 R11(config-if)#ipv6 ospf 200 area 0 R11(config)#^Z R11# 3. Configure your eBGP peering sessions for every neighbor you will have at the IXP. R11(config)# router bgp 10 R11(config-router)# neighbor 10.255.0.20 remote-as 20 R11(config-router)# neighbor 10.255.0.20 description IXP to AS20 R11(config-router)# neighbor FEC0:FF::20 remote-as 20 R11(config-router)# neighbor FEC0:FF::20 description IXP to AS20 R11(config-router)# address-family ipv6 R11(config-router-af)# neighbor FEC0:FE::20 activate R11(config-router-af)# exit R11(config-router)# exit R11(config)#^Z R11# 26 4. STOP – Checkpoint 1. R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# show show show show show show show show show show show show ip bgp summary ip bgp neighbors ip bgp neighbors ip bgp neighbors ip bgp neighbors ip bgp bgp ipv6 unicast bgp ipv6 unicast bgp ipv6 unicast bgp ipv6 unicast bgp ipv6 unicast bgp ipv6 unicast 10.255.0.20 10.255.0.20 advertised-routes 10.255.0.20 routes 10.255.0.20 received-routes summary neighbors neighbors neighbors neighbors FEC0:FF::20 FEC0:FF::20 advertised-routes FEC0:FF::20 routes FEC0:FF::20 received-routes 5. Aggregate your CIDR blocks. If you already did this for the eBGP exercise then you can jump to step #8. R11(config)# router bgp 10 R11(config-router)# aggregate-address 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 R11(config-router)#^Z R11# 6. Advertise only a summary aggregate. R11(config)# router bgp 10 R11(config-router)# no aggregate-address 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 R11(config-rtr)# aggregate-address 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 summary-only R11(config-router)# exit R11(config)# ipv6 route FEC0:10::/32 Null0 250 R11(config)#^Z R11# Another option would be: R11(config)# router bgp 10 R11(config-rtr)#no aggregate-address 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 summary-only R11(config-router)# network 10.10.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 R11(config-router)# exit R11(config)# ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0 250 R11(config)# ipv6 route FEC0:10::/32 Null0 250 R11(config)#^Z R11# 7. STOP – Checkpoint 2. R11# show ip bgp neighbors 10.255.0.20 advertised-routes R11# show ip bgp neighbors 10.255.0.20 routes R11# show ip bgp neighbors 10.255.0.20 received-routes 8. Create prefix lists for your output policies. 27 R11(config)# R11(config)# R11(config)# R11(config)# ip prefix-list out-peer permit 10.10.0.0/16 le 32 ip prefix-list out-peer deny 0.0.0.0/0 le 32 ipv6 prefix-list ipv6-out-peer permit FEC0:10::/32 le 128 ipv6 prefix-list ipv6-out-peer deny ::/0 le 32 9. Create prefix lists for your inbound policies. R11(config)# ip prefix-list as20-in-peer permit 10.20.0.0/16 le 32 R11(config)# ip prefix-list as20-in-peer deny 0.0.0.0/0 le 32 R11(config)# ipv6 prefix-list ipv6-as20-in-peer permit FEC0:20::/32 le 128 R11(config)# ipv6 prefix-list ipv6-as20-in-peer deny ::/0 le 32 R11(config)#^Z R11# 10. Create input and output policies. R11(config)# router R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config-router)# R11(config)#^Z R11# 11. 10.255.0.20 10.255.0.20 10.255.0.20 10.255.0.20 FEC0:FE::20 FEC0:FE::20 FEC0:FE::20 FEC0:FE::20 remote-as 20 description IXP to AS20 as20-out-peer out as20-in-peer in remote-as 20 description IXP to AS20 prefix-list ipv6-as20-out-peer out prefix-list ipv6-as20-in-peer in STOP – Checkpoint 3. R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# R11# 10. bgp 10 neighbor neighbor neighbor neighbor neighbor neighbor neighbor neighbor show ip bgp summary show ip bgp ping <ip_address> traceroute <ip_address> show bgp ipv6 unicast summary show bgp ipv6 unicast ping ipv6 <ipv6_address> traceroute ipv6 <ipv6_address> Save the configuration and checkpoint. R11# write memory Building configuration... [OK] R11# R11# show running-config R11# show startup-config 28