PLANT HORMONES Auxins
advertisement

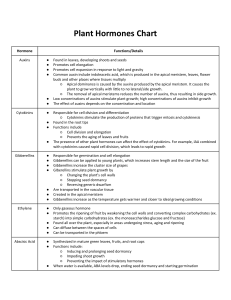
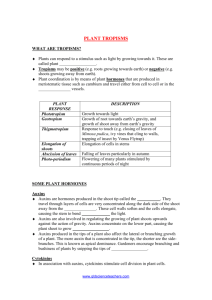
PLANT HORMONES Auxins Auxins are involved in a variety of processes including stem growth, root formation, inhibition of lateral bud development, fruit and leaf abscission, fruit development and activating cambium cells. Of all the hormones, it is the auxins which have the greatest effect on root formation in cuttings. The three most commonly used auxins are: Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) occurs naturally, but is less effective than IBA or NAA in promoting root growth. Indolebutyric acid (IBA), an artificial auxin, is the most widely used rooting hormone. It is used on its own or in combination with NAA. Napthaleneacetic acid (NAA), an artificial auxin, is used on its own or in combination with IBA. Auxins can be applied to plants as a powder, gel or a liquid. Cuttings are frequently treated with hormones which encourage root development. The strength of hormone used will vary depending on such factors as the type of cutting being struck, the variety of plant and the application method. Powder The advantages of using powder are that it is easy to apply, it comes in specific concentrations, and the user doesn't need much expertise. The major disadvantage is that the powder is only available in a limited range of concentrations. Liquid Liquid hormones offer greater flexibility because the concentration can be varied easily by adding an appropriate liquid. The length of time whish the cutting is dipped (and exposed to the hormone) can also be varied. For example, basal parts of cuttings can be soaked for 24 hours in a dilute solution (eg: 100 ppm), or dipped in a concentrated solution (500-10,000 ppm) for about 5 seconds. Gel Gel remains on the cutting well. Strength can be adjusted to some degree. Other ingredients are sometimes included in the gel (eg: vitamins). Cytokinins These are hormones which help with cell differentiation. Certain cytokinins applied to some plants at specific rates can help with root initiation, although more generally, cytokinins are found to inhibit root development. Cytokins are used in tissue culture to stimulate leafy growth. Giberellins At high concentrations gibberellins inhibit root formation. Chemicals such as "Alar" and "Arrest" are commercial preparations which work by interfering with the effect of gibberellins. Gibberellins are also sometimes used as a means of overcoming seed germination inhibitors. Paclobutryzol (eg: "bonzi") This chemical is absorbed by stems, leaves and roots. It moves to just below growing tips and inhibits gibberellin production, causing a reduction in vegetative growth and stimulation of flowering in some species. Sold as a 4 gram per litre suspension under the brand name "Bonzi". Its use may increase chlorophyll production, causing darker coloured foliage. Daminozide (eg: "alar") This hormone slows down and reduces cell expansion, causing shorter internodes. It also reduces dominance of the apical tip, causing more branching. It is mainly absorbed through leaves, therefore it is best applied under slow drying conditions. The use of Alar has been banned in some countries due to health concerns. Chlormequat (eg: "cycocel") An anti-gibberellin which reduces internode spaces on sensitive plants. Absciscic acid (ABA) This naturally occurring compound plays an important role in inhibiting germination of many types of seeds, particularly those with immature embryos. ABA applications have been used to inhibit the germination of non-dormant seeds, and to offset the effects of gibberellic acid applications. The natural Plant Growth Hormones and their main synthetic counterparts useful in nursery production: GROUP Auxins NATURAL SUBSTANCES Indoleacetic acid (IAA)* SYNTHETIC COUNTERPARTS Indolebutyric acid (IBA) Naphthalene acetic acid (NAA) USES Control of flower and fruit drop. Rooting of cuttings. Control of suckering. 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) Gibberellins Gibberellic acid (GA3) and over 70 other forms Cytokinins Zeatin, etc Abscisins Abscisic acid Ethylene Ethylene* Article by B. Balaba Kinetin. Benzyladenine (BA) = Benzylaminopurine (BAP) PBA Ethephon is a synthetic product which releases ethylene gas inside the plant Release of dormancy in seeds and buds. Increased stem length. Promotion of flowering in some "long day plants". Release of dormancy in seeds and buds. No significant practical applications. Shortening and thickening of stems. Possible increase in branching. Flowering in bromeliaeds. Release of dormancy in seeds and buds.