c5. definitive course document and course file
advertisement

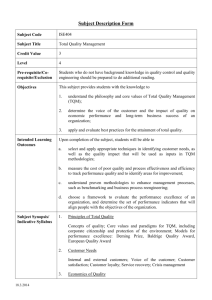
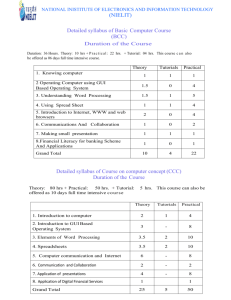
Subject Description Form Subject Code ISE456 Subject Title Managing Information Systems Credit Value 3 Level 4 Pre-requisite/Corequisite/Exclusion Nil Objectives This subject will enable students to Intended Learning Outcomes Subject Synopsis/ Indicative Syllabus 1. examine how information systems are used as a strategic asset to improve competitive advantage and to change organizational processes; 2. understand how to plan information systems strategy and develop information systems; 3. manage information systems and end-user computing. Upon completion of the subject, students will be able to a. understand the roles of information systems and their potential to impact on strategic business planning; b. understand how information system strategic directions can be integrated with an organization’s business and strategic planning; c. plan information system strategy and develop an information system; d. be aware of development; e. manage information systems and end-user computing. 1. Business Strategies with Information Systems issues in information systems planning and Business strategy concepts; Strategic role of information systems; Information systems strategy and its implications; Establishing effective processes; Application of strategic information systems to enterprise 2. Information Systems Planning and Development Information system auditing; Information system and technology infrastructure analysis; Information systems planning: information, systems, resources, and technology; Information system design; Approaches in building information systems; System development cycle; In-house versus IS outsourcing; Project management and risk analysis; Success and failure factors; Software vendor selection and processes 18.3.2014 3. Managing Information Systems Data and network management; Legal and ethical issues; Security control and management; Managing firm infrastructure and enterprise systems. Managing IS departments and end user-computing; Managing international information systems; Organizational change and knowledge management Teaching/Learning Methodology A mixture of lectures, tutorial exercises, projects, and case studies are used to deliver the various topics in this subject, some of which are covered in a problem-based format and exercises to enhance learning objectives. Others will be covered through directed study in order to enhance the students’ ability of “learning to learn.” Some case studies, largely based on business and industrial experience, are used to integrate these topics and thereby demonstrate to students how the various principles and techniques are inter-related and how they apply in real-life situations. The assignments are designed to facilitate teaching students to plan information system strategy and develop information system. Assessment Methods in Alignment with Intended Learning Outcomes Specific assessment methods/tasks % weighting 1. Laboratory work 20% 2. In-class Assignment 10% 3. Individual Assignment 10% 4. Quiz 30% 5. Group Project 30% Total 100% Intended subject learning outcomes to be assessed a b c d e Laboratory work and the group project are designed to assess students’ understanding of the functions and structure of information systems, and the management skills in managing information systems. The assignments and quiz are designed to assess students’ knowledge of different plans and strategies involved in designing and developing an information system. Student Study Effort Expected 18.3.2014 Class contact: Lectures 21 Hrs. Tutorial/Laboratory work 18 Hrs. Other student study effort Self-learning and practice for laboratory work 20 Hrs. Self-learning and practice for project 23 Hrs. Assignment and quiz preparation 25 Hrs. Total student study effort Reading List and References 107 Hrs 1. Boddy, D, Boonstra, A & Kennedy G 2005, Managing Information Systems: An Organisational Perspective, New York: Prentice Hall 2. McNurlin, B.C. & Sprague R.H. 2006, Information Systems Management in Practice, 7th edn, Upper Saddle River N.J: Prentice Hall 3. McLeod, R. & Schell, G. 2007, Management Information Systems, 10th edn, Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice Hall 4. Laudon, K.C. & Laudon, J.P. 2006, Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm, 9th edn, Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice Hall 5. O'Brien, J.A. 2005, Management Information Systems: Managing Information Technology in the Networked Enterprise, Irwin, Chicago 6. Bronzite, M. 2000, System Development: a Strategic Framework, Springer, London, Hong Kong 7. Fitzgerald, B., Russo, N.L. & Stolterman, E. 2002, Information Systems Development: Methods in Action, Berkshire: McGraw-Hill 8. Fortune, J. & Peters, G. 2005, Information Systems: Achieving Success by Avoiding Failure, Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley 9. Hall, J.A. 2000, Information Systems Auditing and Assurance, South Western College, Cincinnati, Ohio 10. Kirikova, M., 2002, Information Systems Development: Advances in Methodologies, Components, and Management, New York: Kluwer Academic /Plenum Publishers 18.3.2014