Economic Theory
advertisement
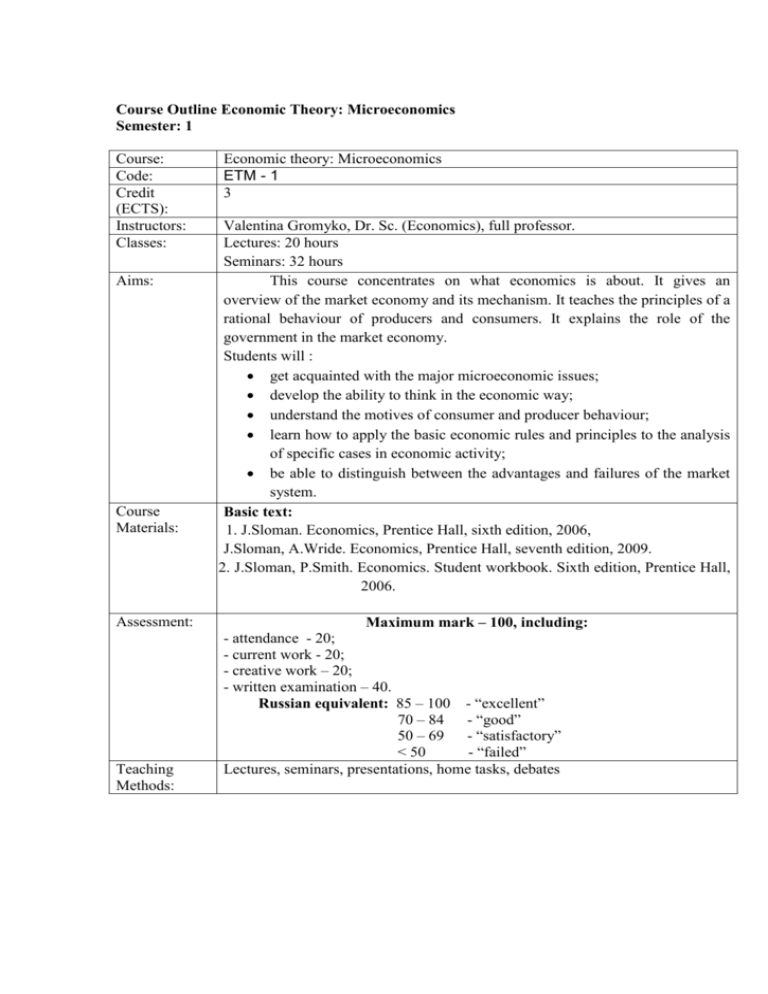
Course Outline Economic Theory: Microeconomics Semester: 1 Course: Code: Credit (ECTS): Instructors: Classes: Aims: Course Materials: Assessment: Teaching Methods: Economic theory: Microeconomics ETM - 1 3 Valentina Gromyko, Dr. Sc. (Economics), full professor. Lectures: 20 hours Seminars: 32 hours This course concentrates on what economics is about. It gives an overview of the market economy and its mechanism. It teaches the principles of a rational behaviour of producers and consumers. It explains the role of the government in the market economy. Students will : get acquainted with the major microeconomic issues; develop the ability to think in the economic way; understand the motives of consumer and producer behaviour; learn how to apply the basic economic rules and principles to the analysis of specific cases in economic activity; be able to distinguish between the advantages and failures of the market system. Basic text: 1. J.Sloman. Economics, Prentice Hall, sixth edition, 2006, J.Sloman, A.Wride. Economics, Prentice Hall, seventh edition, 2009. 2. 2. J.Sloman, P.Smith. Economics. Student workbook. Sixth edition, Prentice Hall, 2006. Maximum mark – 100, including: - attendance - 20; - current work - 20; - creative work – 20; - written examination – 40. Russian equivalent: 85 – 100 - “excellent” 70 – 84 - “good” 50 – 69 - “satisfactory” < 50 - “failed” Lectures, seminars, presentations, home tasks, debates Course schedule №№ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Topics Subject and method of economics; Introduction to microeconomics Key economic problem: scarcity and choice Pure market model Market mechanism: demand, supply, prices Marginal utility theory and consumer’s equilibrium First module test (9 th week) The theory of the firm and the equilibrium of producer Profit maximization under various market structures Income distribution and behaviour of a firm in inputs markets Market advantages, market failures and the economic role of government Economic role of government Second module test (17 th week) Written examination (January) TOTAL Lectures Seminars Self work 2 2 2 Total 2 4 2 8 2 2 2 4 2 2 6 8 2 4 2 8 2 4 2 8 2 2 2 6 2 4 2 8 2 2 2 6 2 4 2 8 20 36 108 20 32 6 Course Outline Economic Theory: Macroeconomics Semester: 2 Course: Code: Credit (ECTS): Instructors: Classes: Aims: Course Materials: Assessment: Teaching Methods: Economic theory: Macroeconomics ETM - 2 5 Marina Savinova, associated professor of economics, Ph.D; Rakouta N.V., assistant Lectures: 22 hours Seminars: 34 hours This course provides understanding of the nature of macroeconomics, its historical development, the main macroeconomic problems and their possible causes, comparative analysis of the Keynesian – monetarist – new classical ideas and debates over fiscal, monetary and supply-side policies. The student will: - be able to distinguish between micro- and macroeconomic equilibrium; - become acquainted with the major macroeconomic issues; - receive a basic knowledge of the main macroeconomic ideas and theoretical debates; - identify various schools of the macroeconomic thought as a basis for political divisions; - be able to examine macroeconomic policies and government promises. Basic text: J.Sloman. Economics, Prentice Hall, sixth edition, 2006, J.Sloman, A.Wride. Economics, Prentice Hall, seventh edition, 2009 J.Sloman, P.Smith Economics. Student workbook. Sixth edition, Prentice Hall, 2006 Economics for marketing (Macroeconomics). Study guide (prepared by Savinova M.V.) – REU, 2012 / IBS Plekhanov, 2013 // http://www.rea.ru/Main.aspx?page=year_1_ Additional text: 1. C.R.McConnell, S.L.Brue, S. Flynn. Macroeconomics: Principles, Problems, and Policies. – 18th edition. - McGraw-Hall University, 2009 N.G.Mankiw. Macroeconomics. - 7th edition. – Worth Publishers, 2009 Maximum mark – 100, including: - attendance - 20; - current work - 20; - creative work – 20; - written examination – 40. Russian equivalent: 85 – 100 - “excellent” 70 – 84 - “good” 50 – 69 - “satisfactory” < 50 - “failed” Lectures, seminars, presentations, home tasks, debates Course schedule №№ 1 2 3 4 5 6 Topics Introduction to macroeconomics. Basic macroeconomic equilibrium models: aggregate demand/aggregate supply analysis and the circular flow of income. Macroeconomic issues: economic growth and business cycles, unemployment, inflation, balance of payments and exchange rates. Macroeconomic ideas. The main points of the Keynesian theory. Mid-term test (9 th week) Money and financial system. Money market: supply, demand and equilibrium. Fiscal and monetary policy: comparative effectiveness. Demand-side policies versus supply-side policies. Introduction to the International Economics: international trade and alternative exchange rate regimes. Globalization and the problem of instability. Final test (17 th week) Written examination (June) TOTAL Lectures Seminars Self work 4 6 12 Total 6 4 6 16 12 4 4 14 8 4 6 16 14 4 6 16 8 2 6 14 10 22 34 88 36 180