Macroeconomics-2
advertisement

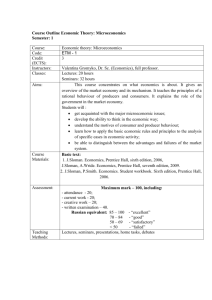
Course Outline Macroeconomics – 1 Semester: 3 Course: Code: Credit (ECTS): Instructor: Classes: Aims: Course Materials: Assessment: Teaching Methods: Macroeconomics-1 MAE-2 3 Marina Savinova, associated professor of economics, Ph.D; Lectures: 24 hours Seminars: 44 hours This course provides understanding of the nature of macroeconomics, its historical development, the main macroeconomic problems and their possible causes. The student will: - be able to distinguish between micro- and macroeconomic equilibrium; - become acquainted with the major macroeconomic issues; - know the principles, ways and various complications of measuring macroeconomic aggregates; - receive a basic knowledge of the main macroeconomic ideas and theoretical debates. Basic text: 1. J.Sloman. Economics, Prentice Hall, sixth edition, 2006, J.Sloman, A.Wride. Economics, Prentice Hall, seventh edition, 2009 2. J.Sloman, P.Smith Economics. Student workbook. Sixth edition, Prentice Hall, 2006 3. Macroeconomics - 1 for Economists. Study guide (prepared by Savinova M.V.) – REU, 2012 / IBS Plekhanov, 2013 // http://www.rea.ru/Main.aspx?page=year_2_ Additional text: 1. C.R.McConnell, S.L.Brue, S. Flynn. Macroeconomics: Principles, Problems, and Policies. – 18th edition. - McGrawHall University, 2009 2. N.G.Mankiw. Macroeconomics. - 7th edition. – Worth Publishers, 2009 Maximum mark – 100, including: - attendance - 20; - current work - 20; - creative work – 20; - written examination – 40. Russian equivalent: 50 – 100 - “pass” < 50 - “failed” Lectures, seminars, presentations, home tasks, debates Course schedule №№ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Topics Introduction to macroeconomics Macroeconomic equilibrium I: aggregate demand/aggregate supply analysis. Macroeconomic equilibrium II: the circular flow of income. Macroeconomic issues I: economic growth and business cycles Macroeconomic issues II: unemployment. Macroeconomic issues III: inflation. Mid-term test (9 th week) Lectures Seminars Self work 2 2 2 4 4 4 Total 6 12 2 2 4 8 2 4 4 10 2 2 4 8 2 2 4 8 Measurement of national output and income. Measurement of unemployment and inflation. Background to money market 1: role of money in the economy and money definitions. Background to money market 2: financial system and its functions. Macroeconomic ideas: classical macroeconomics, Keynesian revolution and modern development. Written examination (pass/failed). – 16 th week 2 8 4 14 2 4 2 8 2 4 4 10 2 6 4 12 2 6 4 12 TOTAL 24 44 40 108 Course Outline Macroeconomics – 2 Semester: 4 Course: Code: Credit (ECTS): Instructor: Classes: Aims: Course Materials: Assessment: Teaching Methods: Macroeconomics-2 MAE-3 5 Marina Savinova, associated professor of economics, Ph.D; Lectures: 26 hours Seminars: 44 hours This course provides a detailed examination and comparative analysis of the Keynesian – monetarist – new classical ideas and debates about fiscal, monetary and supplyside policies. The student will: - identify various schools of the macroeconomic thought as a basis for political divisions; - know the different macroeconomic policies aimed at solution of the macroeconomic problems; - be able to examine macroeconomic policies and government promises. Basic text: 1. J.Sloman. Economics, Prentice Hall, sixth edition, 2006, J.Sloman, A.Wride. Economics, Prentice Hall, seventh edition, 2009 2. J.Sloman, P.Smith Economics. Student workbook. Sixth edition, Prentice Hall, 2006 3. Macroeconomics - 2 for Economists. Study guide (prepared by Savinova M.V.) – REU, 2012 / IBS Plekhanov, 2012 // http://www.rea.ru/Main.aspx?page=year_2_ Additional text: 1. C.R.McConnell, S.L.Brue, S. Flynn. Macroeconomics: Principles, Problems, and Policies. – 18th edition. - McGrawHall University, 2009 2. N.G.Mankiw. Macroeconomics. - 7th edition. – Worth Publishers, 2009 Maximum mark – 100, including: - attendance - 20; - current work - 20; - creative work – 20; - written examination – 40. Russian equivalent: 85 – 100 - “excellent” 70 – 84 - “good” 50 – 69 - “satisfactory” < 50 - “failed” Lectures, seminars, presentations, home tasks, debates Course Schedule Topic №№ 1 The simple Keynesian analysis: consumption function, withdrawals and injections. 2 The simple Keynesian analysis: determination of national income. 3 Keynesian analysis of inflation. 4 Keynesian trade cycles theory. 5 Government finance and the debates over national debt. 6 Fiscal policy. Mid-term test (9 th week) Lectures Seminars Self work Total 2 4 6 12 2 2 6 10 2 2 2 2 2 2 4 4 6 8 8 10 2 2 6 10 Money supply and credit creation process. The demand for money. Equilibrium in the money market. Monetary transmission mechanism. Monetary policy and its effectiveness. Problems and controversies in the macroeconomic policies 1: ISLM model and comparative effectiveness of the fiscal and monetary policies. 2 4 6 12 2 2 2 4 6 6 10 12 2 2 4 6 6 6 12 14 12 Problems and controversies in the macroeconomic policies 2: the inflationunemployment relationship. 2 6 6 14 13 Problems and controversies in the macroeconomic policies 3: supply-side policies versus demand-side policies. Final test (19 th week) 2 4 6 12 7 8 9 10 11 Written examination (21 th week) TOTAL 36 26 44 74 180