MA105

MOHAWK VALLEY COMMUNITY COLLEGE
UTICA, NEW YORK
COURSE OUTLINE
TECHNICAL MATHEMATICS 1
MA105
Reviewed and Found Acceptable by: Gabriel Melendez – 5/01
Reviewed and Revised by: Thomas Schink – 1/02
Reviewed and Revised by: Thomas Schink – 5/02
Reviewed and Revised by: Gabriel Melendez - 11/02
Reviewed and Found Acceptable by: Gabriel Melendez – 5/03
Reviewed and Found Acceptable by: Gabriel Melendez – 5/04
Reviewed and Found Acceptable by: Gabriel Melendez – 5/05
Reviewed and Revised by: Gabriel Melendez - 8/06
Reviewed and Revised by: Terrence Ward – 5/07
Reviewed and Found Acceptable by: Terrence Ward – 5/08
Reviewed and Revised by: Terrence Ward – 5/09
Reviewed and Revised by: David Kolb – 5/10
Reviewed and Found Acceptable by: Gabriel Melendez – 5/11
Reviewed and Found Acceptable by: Gabriel Melendez – 5/12
Reviewed and Found Acceptable by: Gabriel Melendez – 5/13
Reviewed and Revised by: Gabriel Melendez – 5/14
Reviewed and Found Acceptable by: Sean Davis – 1/16
Course Outline
Title:
Catalog Number:
Credit Hours:
Class Hours:
Technical Mathematics 1
MA105
4
2
Lab Hours: 4
Prerequisite:
Catalog
Description:
None
This course covers the four fundamental operations on integers, rational numbers, and real numbers. It includes the study of weights and measures, exponents and radicals, factoring, and linear equations, with an emphasis on technical applications.
Teaching Goals: 1. To develop those mathematical skills which
will lead to a productive entry into the
labor force.
2. To develop the mastery of the basic number facts and the ability to perform the four fundamental operations on the whole numbers and integers.
3. To develop the ability to perform the four fundamental operations on fractions, both common and decimal, and to convert from one form to the other.
4. To develop the mastery of the concepts of percent and percentage.
5. To develop the ability to manipulate exponents in simple problems in multiplication and division.
6. To develop the ability to convert units of weights and measures in both the
English and metric systems, and to convert from one system to the other.
7. To develop proficiency in solving linear equations in one variable.
8. To develop the ability to perform the four fundamental operations and factoring with polynomial expressions.
(Long division is not covered.)
Major Topics:
Topic 1. Review of Arithmetic : The basic operations are covered.
Basic operations include addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and rounding. Types of numbers include integers as well as common and decimal fractions and percents. Combined operations are included. Technical applications are emphasized.
Student Outcomes:
The student will:
1.1 Add, subtract, multiply and divide whole numbers.
1.2 Perform combined operations on whole numbers as per the
Order of Operations Agreement.
1.3 Identify prime and composite numbers.
1.4 Determine the prime factorization of given composite numbers.
1.5 Determine if given whole numbers are divisible by the numbers 2, 3, 4 and 5.
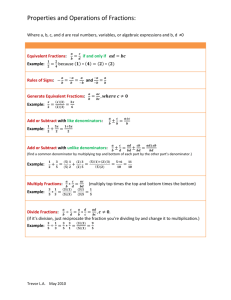
1.6 Find equivalent common fractions.
1.7 Simplify common fractions.
1.8 Convert between mixed numbers and improper common fractions.
1.9 Add and subtract given common fractions with common denominators.
1.10 Add and subtract given common fractions that are not given with common denominators.
1.11 Add and subtract mixed numbers.
1.12 Multiply and divide given common fractions.
1.13 Convert between common fractions and decimal fractions.
1.14 Add, subtract, multiply and divide decimal fractions.
1.15 Round given decimal fractions to particular place values.
1.16 Round given decimal fractions to a particular number of significant digits.
1.17 Convert between common and decimal fractions and percents.
1.18 Convert from percents that contain mixed numbers to common fractions.
1.19 Multiply and divide powers of 10.
1.20 Raise powers of 10 to exponents.
1.21 Write negative powers of 10 as positive powers of 10.
1.22 Write decimal fractions in Scientific Notation.
1.23 Write numbers given in scientific notation in decimal form.
1.24 Multiply and divide numbers in scientific notation.
Topic 2. Measurements : The English and Metric systems of weights and measures, as well as Standard International (SI) units are covered. The rules of arithmetic on measurements are covered.
Dimensions covered include length, area, volume, mass and weight, time, electrical current and resistance and temperature. Technical applications are emphasized.
Student Outcomes:
The student will:
2.1 Convert within the English system of weights and measures.
2.2 Identify the accuracy of given measurements.
2.3 Identify the precision and Greatest Possible Error of given measurements.
2.4 Add and subtract measurements in accordance to the rule of addition and subtraction of measurements.
2.5 Multiply and divide measurements in accordance with the rule of multiplying and dividing measurements.
2.6 Identify the SI units of given measurements.
2.7 Identify the common SI prefixes and their symbols.
2.8 Convert within the Metric System.
2.9 Convert between the English and metric systems.
Topic 3. Polynomials : The four fundamental operations and factoring are covered. The four fundamental operations include addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Division by polynomials is omitted.
Student Outcomes:
The student will:
3.1 Identify like terms.
3.2 Add and subtract algebraic expressions.
3.3 Identify the degrees of given polynomials of one variable.
3.4 Add and subtract polynomials.
3.5 Multiply monomials.
3.6 Raise monomials involving products to powers.
3.7 Multiply polynomials by monomials.
3.8 Multiply polynomials vertically.
3.9 Divide monomials and polynomials by monomials.
3.10 Find monomial factors of polynomials.
3.11 Multiply binomials mentally (the FOIL method)
3.12 Find binomial factors of given second-degree trinomials.
Topic 4. Equations : Linear equations of one variable are covered.
Technical applications and problem solving are emphasized.
Student Outcomes:
The student will:
4.1 Solve and check equations with variables in one member.
4.2 Solve and check equations with variables in both members.
4.3 Solve and check equations with parenthesis.
4.4 Solve and check equations involving fractions.
4.5 Translate words, phrases and sentences into algebraic expressions and equations.
4.6 Demonstrate problem solving skills and algebraic techniques by presenting complete solutions to application problems requiring the student to define the variables and write and solve linear equations.
Topic : Various technical formulas are covered. Algebraic manipulation of formulas and extraction of data from formulas are covered. Percentage is covered. Formulas for basic plane figures are covered. Area and Volume of rectangles, rectangular solids, and constructions of rectangles and rectangular solids are covered. Ratio, proportion, and direct and inverse variation are covered. Technical applications and problem solving are emphasized.
Student Outcomes:
The student will:
5.1 Enter data into formulas which are then solved for a certain variable.
5.2 Algebraically solve formulas for a given variable before entering data.
5.3 Identify Percentage, Base and Rate.
5.4 Find Percentage, base or rate when given the other two.
5.5 Calculate percent increase and percent decrease.
5.6 Find areas and perimeters of rectangles.
5.7 Find areas and perimeters of figures made up of rectangles.
5.8 Find volumes of rectangular solids.
5.9 Find volumes of solids made up of rectangular solids.
5.10 Find areas and perimeters of triangles, parallelograms and trapezoids.
5.11 Express ratios and rates in lowest terms.
5.12 Determine if two given ratios are equal.
5.13 Solve applications involving proportions.
5.14 Solve applications involving direct variation.
5.15 Solve applications involving inverse variation.
TEACHING GUIDE
Title:
Catalog No.:
Credit Hours:
Class Hours:
Technical Mathematics 1
MA105
4
2
Lab. Hours:
Prerequisite:
Catalog
Description:
4
None
This course covers the four fundamental operations on integers, rational numbers, and real numbers. It includes the study of weights and measures, exponents and radicals, factoring, and linear equations, with an emphasis on technical applications.
Text: Elementary Technical Mathematics, 11 th edition,Ewen and Nelson, Thomson Brooks/Cole.
NOTE: The suggested hours in the teaching guide include
BOTH lecture and lab hours. While in general the lab hours should be a time of supervised guided work, the instructor may also wish to use some of the lab hours to present course material.
NOTE: Chapter 1 should not be treated as review material.
Chapter 1 Basic Concepts 26 hours
1.1 Review of Basic Operations
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
1.8
Order of Operations
Area and Volume
Formulas
Prime Factorization
Introduction to Fractions
Addition and Subtraction of Fractions
Multiplication and Division of Fractions
1.9
1.10
1.11
1.12
1.13
1.14
1.15
The U.S. System of Weights and Measures
Addition and Subtraction of Decimal Fractions
Rounding Numbers
Multiplication and Division of Decimal Fractions
Percent
Rate, Base, and Part
Powers and Roots
Chapter 2 Signed Numbers and Powers of 10
2.1
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.5
Addition of Signed Numbers
Subtraction of Signed Numbers
Multiplication and Division of Signed Numbers
Signed Fractions
Powers of 10
12 hours
2.6
2.7
Chapter 3 The Metric System
Scientific Notation
Engineering Notation [Omit]
8 hours
Note: students are required to memorize only prefixes from milli to kilo (see page 137).
3.1 Introduction to the Metric System
3.2
3.3
3.4
3.5
3.6
3.7
Length
Mass and Weight
Volume and Area
Time, Current, and Other Units
Temperature
Metric and U.S. Conversion
Chapter 4 Measurement
4.1 Approximate Numbers and Accuracy
4.2
4.3
4.4
4.5
4.6
Precision and Greatest Possible Error
The Vernier Caliper - Optional
The Micrometer Caliper - Optional
Addition and Subtraction of Measurements
Multiplication and Division of Measurements
5 hours
4.7
4.8
4.9
Relative Error and Percent of Error
Color Code of Electrical Resistors - [Omit]
Reading Scales - [Omit]
Chapter 5 Polynomials: An Introduction to Algebra
5.1
5.2
5.3
5.4
Fundamental Operations
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials
Multiplication of Monomials
5.5
5.6
5.7
Multiplication of Polynomials
Division by a Monomial
Division by a Polynomial – [Omit]
Chapter 6 Equations and Formulas
6.1
6.2
6.3
6.4
6.5
6.6
6.7
6.8
6.9
Equations
Equations with Variables in Both Members
Equations with Parentheses
Equations with Fractions
Translating Words into Algebraic Symbols
Applications Involving Equations
Formulas
Substituting Data into Formulas
Reciprocal Formulas Using a Calculator
11 hours
12 hours
Chapter 7 Ratio and Proportion
7.1
7.2
7.3
7.4
Ratio
Proportion
Direct Variation
Inverse Variation
Chapter 10 Factoring Algebraic Expressions
10.1
10.2
10.3
10.4
10.5
10.6
Finding Monomial Factors
Finding the Product of Two Binomials Mentally
Finding Binomial Factors
Special Products
Finding Factors of Special Products
Factoring General Trinomials
4 hours
8 hours
The teaching guide allows 4 additional hours for the in-class assessment of student learning. A two hour comprehensive final examination will also be given.