semester 1 syllabus
advertisement
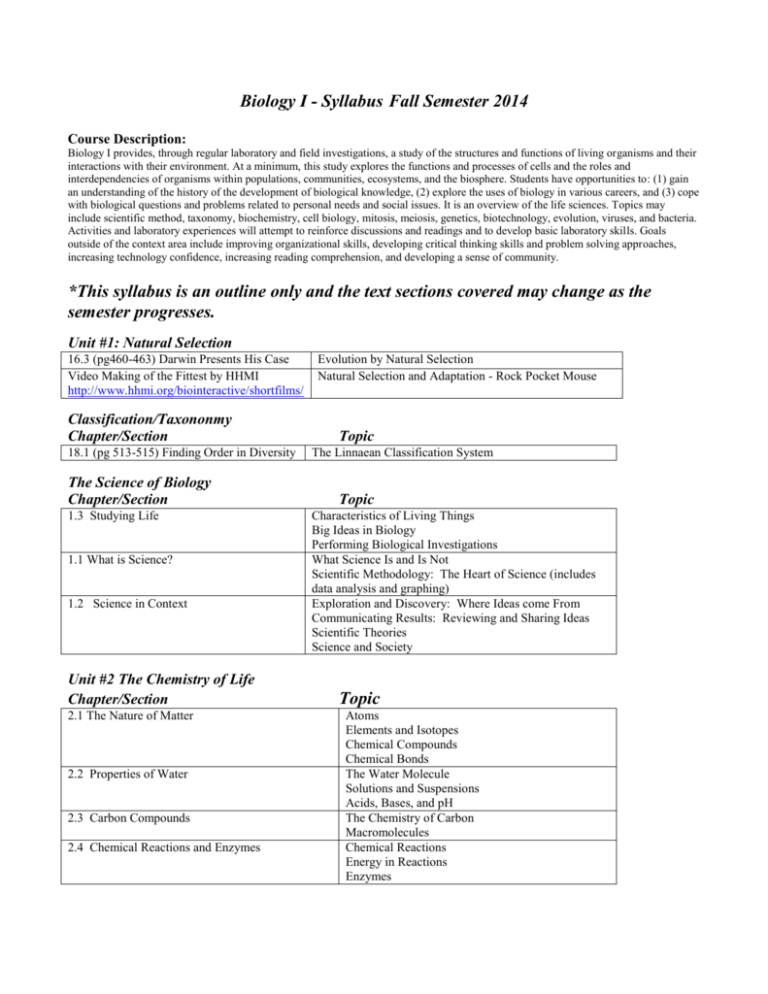
Biology I - Syllabus Fall Semester 2014 Course Description: Biology I provides, through regular laboratory and field investigations, a study of the structures and functions of living organisms and their interactions with their environment. At a minimum, this study explores the functions and processes of cells and the roles and interdependencies of organisms within populations, communities, ecosystems, and the biosphere. Students have opportunities to: (1) gain an understanding of the history of the development of biological knowledge, (2) explore the uses of biology in various careers, and (3) cope with biological questions and problems related to personal needs and social issues. It is an overview of the life sciences. Topics may include scientific method, taxonomy, biochemistry, cell biology, mitosis, meiosis, genetics, biotechnology, evolution, viruses, and bacteria. Activities and laboratory experiences will attempt to reinforce discussions and readings and to develop basic laboratory skills. Goals outside of the context area include improving organizational skills, developing critical thinking skills and problem solving approaches, increasing technology confidence, increasing reading comprehension, and developing a sense of community. *This syllabus is an outline only and the text sections covered may change as the semester progresses. Unit #1: Natural Selection 16.3 (pg460-463) Darwin Presents His Case Video Making of the Fittest by HHMI http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/shortfilms/ Classification/Taxononmy Chapter/Section 18.1 (pg 513-515) Finding Order in Diversity The Science of Biology Chapter/Section 1.3 Studying Life 1.1 What is Science? 1.2 Science in Context Unit #2 The Chemistry of Life Chapter/Section 2.1 The Nature of Matter 2.2 Properties of Water 2.3 Carbon Compounds 2.4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Evolution by Natural Selection Natural Selection and Adaptation - Rock Pocket Mouse Topic The Linnaean Classification System Topic Characteristics of Living Things Big Ideas in Biology Performing Biological Investigations What Science Is and Is Not Scientific Methodology: The Heart of Science (includes data analysis and graphing) Exploration and Discovery: Where Ideas come From Communicating Results: Reviewing and Sharing Ideas Scientific Theories Science and Society Topic Atoms Elements and Isotopes Chemical Compounds Chemical Bonds The Water Molecule Solutions and Suspensions Acids, Bases, and pH The Chemistry of Carbon Macromolecules Chemical Reactions Energy in Reactions Enzymes Unit #3 Cell Structure and Function Chapter/Section 7.1 Life is Cellular 7.2 Cell Structure 7.3 Cell Transport 7.4 Homeostasis and Cells Unit #4 Cell Growth and Division Chapter/Section 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction 10.2 Cell Division 10.3 Regulating the Cell Cycle 10.4 Cell Differentiation 11.4 Meiosis Topic The Discovery of the Cell Exploring the Cell Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes Cell Organization Organelles That Store, Clean Up, and Support Organelles That Build Proteins Organelles That Capture and Release Energy Cellular Boundaries Passive Transport Active Transport The Cell as an Organism Multicellular Life Topic Limits to Cell Size Cell Division and Reproduction Chromosomes Mitosis Cytokinesis Controls of Cell Division Cancer: Uncontrolled Cell Growth From One Cell to Many Stem Cells and Development Frontiers in Stem Cell Research Chromosome Number Phases of Meiosis Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis