Review Questions - Cellular Respiration
advertisement

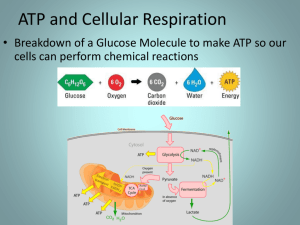
Review Questions - Cellular Respiration 1. Other than redox, what are the 3 major types of reaction in aerobic cellular respiration? 2. Is photosynthesis an exergonic or endergonic process? 3. Is cellular respiration an exergonic or endergonic process? 4. What is the difference between an obligate anaerobe and a facultative anaerobe? 5. True or false? Plant cells undergo photosynthesis, but not cellular respiration. 6. What is the difference between substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation? 7. Look at the diagram of the mitochondrion. What is the structure labelled A? What stages of respiration occur here? 8. Look at the diagram of the mitochondrion. What is the structure labelled C? What is its function? (Image from: http://www.bio12.com/ch3/CellCd%20 Remedial.htm) 9. What structures of the mitochondria does pyruvate have to pass through to get from the cytoplasm to the matrix? 10. What are all the products of glycolysis of 1 molecule of glucose? 11. What are the products of the energy investment phase (& cleavage) of 1 molecule of glucose? 12. What are the 3 things that happen to pyruvate molecules during pyruvate oxidation? 13. What happens to the carbon from acetyl-CoA during the citric acid cycle? 14. How many ATP, NADH, and FADH2 molecules are generated from 2 molecules of acetyl-CoA? 15. What are the names of the 2 mobile electron carriers in the electron transport chain (ETC)? 16. Which of the components of the electron transport chain has the highest electronegativity? 17. To which component in the ETC does FADH2 transfer its electrons? 18. Identify the type of reaction and the stage of aerobic cellular respiration during which it occurs: fructose-6-phosphate ---> fructose-1,6-bisphosphate 19. Identify the type of reaction and the stage of aerobic cellular respiration during which it occurs: citrate ---> isocitrate 20. What is the purpose of creatine phosphate? 21. What are all the products of lactic acid fermentation of 2 molecules of pyruvate? Review Questions *ANSWERS* - Cellular Respiration 1. phosphorylation, decarboxylation, isomerization 2. endergonic (it requires energy from the Sun) 3. exergonic (it releases energy in the form of ATP (and heat)) 4. obligate anaerobe cannot live in the presence of oxygen, facultative anaerobes don't need oxygen, but can survive in its presence 5. False. Both. 6. substrate-level: direct enzyme-catalyzed phosphorylation of ADP oxidative: phosphorylation of ADP using energy from series of redox reactions 7. the matrix: pyruvate oxidation, citric acid cycle, the ETC all occur here 8. crista: it increases the surface area of the inner membrane 9. outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane 10. 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP (net) + 2 NADH 11. 2 molecules of G3P 12. oxidation (reduction of NAD+), decarboxylation, addition of coenzyme A (CoA) 13. It is released as CO2 14. 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2 15. ubiquinone, cytochrome c 16. cytochrome oxidase (complex IV) 17. succinate dehydrogenase (complex II) 18. phosphorylation; during glycolysis 19. isomerization; during citric acid cycle 20. in some organisms, it allows more ATP to be produced (by phosphorylating creatine, it frees up some ADP molecules to form more ATP) 21. 2 molecules of lactate (lactic acid) + 2 NAD+