ATP & Cellular Respiration: A Biology Presentation
advertisement
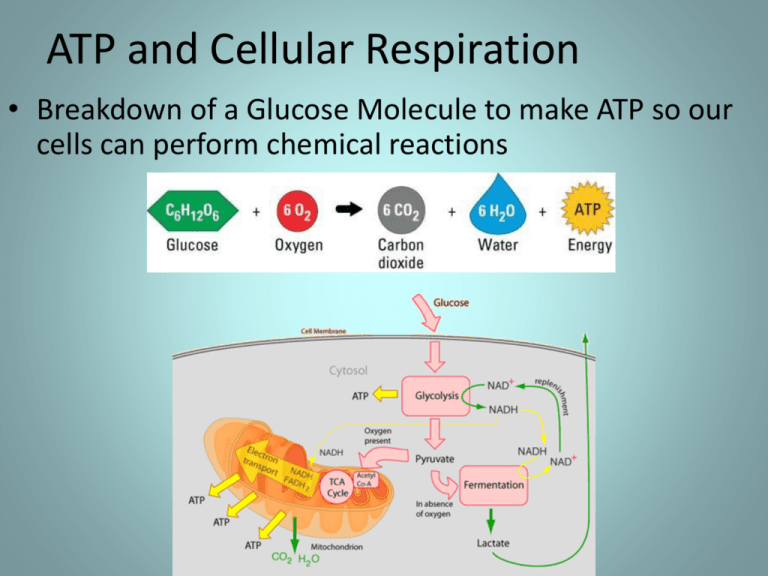
ATP and Cellular Respiration • Breakdown of a Glucose Molecule to make ATP so our cells can perform chemical reactions THE BASICS OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION • Heterotrophs – organisms that cannot make their own energy and need to consume other organisms to get energy (consumers) – All animals, fungi, and some bacteria are heterotrophs Why Make ATP? • Referred to as energy currency of the cell • Provide energy for chemical reactions to take place in our body (cells) Mitochondria • Site of cellular respiration (where ATP is made) • Conists of – Outer membrane – Inner membrane – Matrix – Cristae Cellular Respiration Breakdown • Glycolysis – Located in cytoplasm of cell • Krebs Cycle – Located in Mitochondrial Matrix • Electron Transport Chain – Located in mitochondrial cristae Glycolysis • Breakdown of a single Glucose molecule • Reactants – Glucose molecule • Products – 2 pyruvate molecules – 2 ATP molecules • Energy – 2 NADH molecules • Electron carriers Pyruvate • Pyruvate can take 2 paths from this point: 1. Aerobic Respiration (with oxygen) – Pyruvate moves into mitochondria and ATP is made via Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Chain 2. Anaerobic Respiration (without oxygen) – Pyruvate stays in cytoplasm and is converted into lactic acid -Lactic Acid Fermentation Aerobic Respiration • Krebs Cycle – Conversion of 2 pyruvate molecules • Reactants – 2 pyruvate molecules • Products – 4 CO₂ molecules – 2 ATP molecules • Energy – 6 NADH molecules • Electron carriers – 2 FADH₂ • Electron carriers Aerobic Respiration • Electron Transport Chain – Electrons are transferred to proteins from NADH and FADH₂ – Electrons are passed from one protein to the next – Final electron acceptor is Oxygen (O₂) • Reactants – NADH – FADH₂ • Products – 34 ATP molecules • Energy – Water (H₂O) Anaerobic Respiration • Lactic Acid Fermentation – Conversion of 2 molecules of pyruvate into lactic acid when oxygen is not present – Happens during vigorous muscle exercise – Liver converts lactic acid back into glucose Anaerobic Respiration • Alcohol Fermentation – Does not occur in humans – Occurs in yeast when oxygen is not available • Facultative anaerobes – Conversion of 2 molecules of pyruvate into ethanol Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration






