File
advertisement

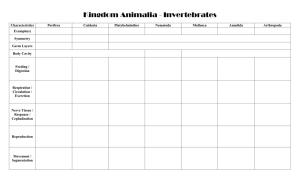
Name _________________________________________________________ Period ________ Score __________ Invertebrates Classification Challenge Most of the things living on this planet are invertebrates, so getting to know a little about them is a good idea. Invertebrates are members of the Kingdom Animalia, they are linked together by the fact that they have no backbone or vertebrae. They do not include the Protozoa (single-celled animals) who are generally considered to be part of the Kingdom Protista. Instructions: Read the descriptions of each phylum or Class of organism then decide how to classify the individual organisms shown on the cards. Make a chart with your group placing the organisms where you think they should go. Fill in your worksheet placing all of the animals in their correct classification grouping. Answer the questions on your worksheet. Porifera Annelida Nematoda Cnidaria Mollusca/Gastropoda Arthropoda/Insecta Mollusca/Bivalve Arthropoda/Arachnid Mollusca/Cephalopoda Arthropoda/Crustacea Platyhelminthes Echinodermata Questions: 1. What does Porifera mean? __________________________________________________________ 2. What animals belong to phylum Porifera? ______________________________________________ 3. Name one characteristic that is unique to phylum Porifera. ________________________________________ 4. Where do animals in the phylum Porifera live? ____________________________________________ 5. What does Arthropoda mean? _______________________________________________________ 6. What animals belong to phylum Arthropoda? ______________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Name one characteristic that is unique to phylum Arthropoda. _______________________________________ 8. Where do animals in the phylum Arthropoda live? _________________________________________ 9. What does Nematoda mean? ____________________________________________________________ 10. What animals belong to the phylum Nematoda? ________________________________________________ 11. Name one characteristic that is unique to phylum Nematoda. _________________________________________ 12. Where do animals in the phylum Nematoda live? ________________________________________ 13. What does annelida mean? __________________________________________________ 14. What animals belong to the phylum Annelida? ______________________________ 15. Name one characteristic that is unique to phylum Annelida. __________________________________________ 16. Where do animals in the phylum Annelida live? _____________________________________________ 17. What does Mollusca mean? ___________________________________ 18. What animals belong to the phylum Mollusca? ______________________________________________________________________________________ 19. Name one characteristic that is unique to phylum Mollusca. __________________________________________ 20. Where do animals in the phylum Mollusca live? ________________________________________ 21. What does Echinodermata mean? ____________________________________ 22. What animals belong to the phylum Echinodermata? ____________________________________________ 23. Name one characteristic that is unique to phylum Echinodermata. _____________________________________ 24. Where do animals in the phylum Echinodermata live? _____________________________________ 25. What does Platyhelminthes mean? ____________________________________ 26. What animals belong to the phylum Platyhelminthes? ____________________________________________ 27. Name one characteristic that is unique to phylum Platyhelminthes. _____________________________________ 28. Where do animals in the phylum Platyhelminthes live? _____________________________________ 29. What does Cnidaria mean? ____________________________________ 30. What animals belong to the phylum Cnidaria? ____________________________________________ 31. Name one characteristic that is unique to phylum Cnidaria. __________________________________________ 32. Where do animals in the phylum Cnidaria live? _____________________________________________________ Phylum Porifera: from the Latin “porus” meaning pore and “ferre” meaning to bear Sessile and usually spend their lives anchored to something underwater Body wall is made of 2 layers with no true body cavity Are asymmetrical Circulate nutrients through pores and cells Simplest animals besides single celled animals The most ancient invertebrates Phylum Cnidaria: from the Greek “knide” meaning needle Multicellular, few tissues, no organs Have radial symmetry Have stinging cells All live in the water, usually salt water Some are sessile and some are sedentary Live in aquatic environments, mostly marine Two forms: medusa and polyp Most are carnivorous All are filter feeders Live in the water; mostly salt water Phylum Platyhelminthes: from the Greek “platy” meaning flat and “helminthes” meaning worm Some are free-living, some are parasitic Have bilateral symmetry Are motile or sedentary Have eye spots to sense light Have 3 body layers with tissues and organs Dorsoventrally flattened Live in every habitat (water, land and parasitic) Phylum Annelida: From the Latin “annellus” meaning ringed Has 2 or more body layers and a true coelom Have a ventral nerve cord and a simple circulatory system Most are sedentary or motile Bilateral Symmetry Digestive system with mouth, gut and anus Nervous system No true respiratory system Closed circulatory system Live in soil and water Phylum Nematoda: from the Greek “nema” meaning thread and “eidos” meaning form Bilateral symmetry 2 or more cell layers, tissue and organs. One-way digestive system with mouth and anus No circulatory system Nervous system present Live in every habitat (water, land and parasitic) Phylum Echinodermata: from the Greek “echinos” meaning half and “derma” meaning skin Have radial symmetry No true body cavity More than 2 cell layers, tissues and organs Body shape varies, but has no head Have tube feet or feeding tentacles Live in all marine environments Open circulatory system, simple nervous system and no excretory organs Phylum Mollusca: from the Latin “molluscus” meaning soft body Have a true coelom Phylum Arthropoda: from the Greek “arthron” meaning joint and “pous” meaning foot Bilateral symmetry 2 or more cell layers with tissues and organs True coelom Straight gut with anus 3 to 400 pairs of jointed legs Open circulatory system with hemocoel (blood-type substance) Body is divided into 3 or more sections Most are motile, some are sedentary Has an external skeleton Live in most environments Live in every habitat and feed in every way Has 2 or more cell layers, tissues and organs Bilaterally symmetrical Gills for gas exchange Has a pair of kidneys Have a circulatory system, digestive system and a simple nervous system Class Bivalve: 2 shells Class Gastropoda: Stomach is used for a “foot” for locomotion Class Cephalopoda: “Foot” has evolved into tentacles Class insecta: 3 pair of jointed legs and three body segments Class Arachnidan: 4 pair of jointed legs, a cephalothorax and an abdomen are the 2 body segments Class Crustacea: many pairs of jointed legs, some for walking, some for swimming, many body segments