Econ202_Studyquestions_Test3
advertisement

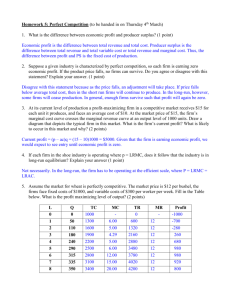
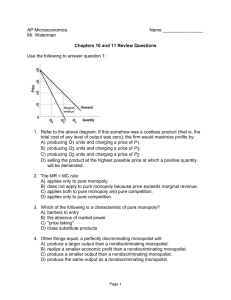
Economics 202 Study Questions Test #3 Professor Thornton 1. Which of the following is a type of market structure? a. Monopoly b. Perfect competition c. Oligopoly d. All of the above 2. According to the structure/conduct/performance paradigm, the most important determinant of firm behavior is: a. a firm’s political influence b. the size of a firm c. the structure of the market in which the firm operates d. the technology available to the firm 3. Suppose there are 100 firms in an industry and these firms produce differentiated products. Which of the following is true? a. Competition will force each firm to charge the same price for its good. b. Consumers perceive these products to be imperfect substitutes, and therefore are willing to pay different prices for the products sold by different firms. c. Firms will exit the industry in the long-run d. A firms will not attempt to minimize the cost of producing its product 4. Which of the following is a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market? a. A large number of firms exist in the industry b. Firms in the industry are approximately the same size c. It is easy for firms to enter and exit the industry in the long-run d. All of the above 5. A firm in a perfectly competitive market does not choose: a. the amount of output to produce b. the price to charge for its product c. the method of production it will use to produce its product d. All of the above 6. In a perfectly competitive industry, we are likely to find: a. firms producing a variety of differentiated products b. barriers to entry that prevent new firms from entering the industry c. firms do not spend money to advertise their product d. a few large firms that sell most of the product to consumers 1 7. Which of the following firms is most likely to be in a perfectly competitive industry? a. An automobile producer b. An airline firm c. A soybean farmer d. A gasoline station 8. If the price that a firm receives for its product is equal to the average revenue it earns from selling its product, then we can conclude that it sells its product in which of the following types of markets? a. Perfect competition b. Monopoly c. Oligopoly d. It could be selling its product in any of the above markets 9. If the price that a firm receives for its product is equal to the marginal revenue it earns from selling an additional unit of its product, then we can conclude that it sells its product in which of the following types of markets? a. Perfect competition b. Monopoly c. Oligopoly d. It could be selling its product in any of the above markets 10. Many country inns shut-down in the off-season because: a. innkeeper can’t maximize revenue b. the off-season market price is below the inn’s average fixed cost c. off-season revenue is not high enough to cover the inn’s variable cost d. innkeepers like to spend the off-season in Florida Questions 11 and 12 are based on the information given below for a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market. Output: 4,000 units Price: $1 Total Variable Cost: $2,000 Total Fixed Cost: $1,000 Marginal Cost: $1.10 11. The firm is: a. making economic profits b. making zero economic profit c. incurring losses d. producing the level of output where average total cost is equal to marginal cost 12. To maximize profits, the firm should: a. increase output b. decrease output c. leave output unchanged d. shut down its operations and produce no output 2 Questions 13 and 14 are based on the following graph for a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market. MC ATC AVC Price $40 $30 $20 $10 0 100 200 300 400 Quantity 13. If the price the firm receives for its product is $40, then it should produce which of the following amounts of output to maximize profit? a. 100 b. 200 c. 300 d. 400 14. The firm should shut down in the short-run if the price falls below: a. $10 b. $20 c. $30 d. $40 15. The short-run supply curve for a perfectly competitive firm is given by: a. the entire marginal cost curve b. the marginal cost curve at and above average variable cost c. the marginal cost curve at and above average total cost d. the average variable cost curve to the right of the marginal cost curve 16. Which of the following is not possible in long-run equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market? a. Firms making normal profits b. Firms making economic profits c. Firms making zero economic profits d. Both a and b 3 17. If firms in a competitive industry are earning zero economic profits in the short-run, then one would expect that in the long-run: a. new firms will enter the industry b. existing firms will leave the industry c. firms will neither enter nor leave the industry d. all firms will shut-down their operations so that total industry output will be zero 18. Assume the market for wine is a perfectly competitive market. Wine firms are making zero economic profit. Suppose an increase in income increases the demand for wine. Which of the following will occur in the short-run? a. Firms in the wine industry will make economic profits b. Firms in the wine industry will receive a higher price for their product c. Firms in the wine industry will produce and sell more wine d. All of the above 19. In an increasing-cost industry, the entry of new firms results in which of the following? a. an increase in input prices b. an increase in economic profits c. a decrease in demand d. a decrease in supply 20. The long-run supply industry supply curve for a constant-cost industry is: a. vertical b. horizontal c. upward sloping d. downward sloping 21. A firm in a perfectly competitive industry is maximizing profit at an output of 3,000 units per month. Assume its fixed cost increases. To maximize profit, the firm should now: a. increase output and produce more than 3,000 units per month b. decrease output and produce less than 3,000 units per month c. continue to produce 3,000 units per month d. shut down operations and produce no output 22. Assume that the dairy farm industry is a perfectly competitive constant-cost industry. It is currently in long-run equilibrium and the price of milk is $3.00 per gallon. Assume that the demand for milk increases. How will this affect the price of milk in the short-run and long-run? a. The price of milk will increase above $3.00 in both the short-run and long-run b. The price of milk will decrease below $3.00 in both the short-run and long-run c. The price of milk will increase above $3.00 in the short-run, but fall back to $3.00 in the long-run. d. The price of milk will decrease below $3.00 in the short-run, but rise back to $3.00 in the long-run 4 23. Assume that the dairy farm industry is a perfectly competitive increasing-cost industry. It is currently in long-run equilibrium and the price of milk is $3.00 per gallon. Assume that the demand for milk increases. How will this affect the price of milk in the short-run and long-run? a. The price of milk will increase above $3.00 in both the short-run and long-run b. The price of milk will decrease below $3.00 in both the short-run and long-run c. The price of milk will increase above $3.00 in the short-run, but fall back to $3.00 in the long-run. d. The price of milk will decrease below $3.00 in the short-run, but rise back to $3.00 in the long-run 24. Firms in an industry achieve production efficiency in the long-run when they: a. produce their product at minimum average cost b. produce their product at minimum marginal cost c. maximize their total revenue d. produce just the right amount of their product 25. Allocation efficiency occurs in a market when: a. firms maximize the amount of output they produce from the inputs they employ b. firms minimize the average cost of the output they produce c. the marginal social benefit of the last unit of the product produced is equal to the marginal social cost d. Both a and b 26. We may be certain that a firm is a monopoly if: a. it is the only producer of a product b. it produces the level of output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost c. it faces a highly elastic demand curve d. Both a and b 27. Which of the following is not considered an entry barrier? a. Diseconomies of scale b. Economies of scale c. Ownership of essential raw materials d. Patents 28. The demand curve of a monopolist: a. is the same as the marginal revenue curve b. is the same as the average revenue curve c. is the industry demand curve d. Both b and c 5 29. Consider the following demand schedule for a monopolist. Price Quantity $90 1 $80 2 $70 3 $60 4 $50 5 The marginal revenue of the 4th unit sold is: a. $10 b. $30 c. $60 d. $240 Questions 30, 31, and 32 are based on the following graph for a monopolist. MC ATC Price $10 ---------------------------$8 ---------------------------------------$7 ---------------------------$6 -----------------------------------$3 ----------------------------D MR 0 300 400 500 Quantity 30. To maximize profit, the monopolist must produce ________ units of output and charge a price of ________. a. 300, $4 b. 300, $10 c. 400, $6 d. 500, $8 31. At the profit maximizing level of output, the monopolist is making economic profit of: a. $0 b. $900 c. $2,400 d. $3,000 6 32. Suppose that the monopolist experiences an increase in the demand for its product. As a result: a. both price and output will increase b. price will increase, but output will remain the same c. price will increase, but output will decrease d. neither price nor output will change 33. Suppose that Southern Cable Company is a monopolist in the market for cable TV services in the rural town of Smithsburg, Virginia. If the market wage rate of the technicians it employees increases ceteris paribus, then this firm will: a. continue to charge the same price and make a smaller profit b. charge a lower price and make the same profit c. charge a higher price and make the same profit c. charge a higher price but make a smaller profit 34. The differences between a monopolistic firm and a perfectly competitive firm include all of the following except: a. the demand curve for the monopolist is downward sloping and the demand curve for the competitive firm is horizontal. b. marginal revenue is less than price for the monopolist and equal to price for the perfectly competitive firm c. marginal cost is upward sloping for the monopolist and horizontal for the perfectly competitive firm d. in short-run equilibrium the monopolist will produce the level of output for which price is greater than marginal cost and the perfectly competitive firm will produce the level of output where price is equal to marginal cost 35 In the long-run, monopolists may earn economic profits but firms in a competitive market do not. Which of the following best explains why? a. Consumers are more willing to pay high prices for the product of the monopolist because its product is highly differentiated from the products produced by its competitors b. The monopolist uses resources more efficiently than the typical firm in a competitive market c. There are entry barriers that keep firms from entering the monopolist’s market d. the monopolist has greater incentive to advertise its product 36. Of the following, which could most easily practice price discrimination? a. A record store b. An oral surgeon c. A book publisher d. A grocery store 7 37. A firm is practicing price discrimination if: a. it sells the same good to different customers at different prices because of differences in the cost of producing the good b. some individuals who want to purchase the good at the going market price cannot do so c. it sells the same good to different customers at different prices, and there is no difference in the cost of producing the good d. it sells the same good to different customers at different prices because of differences in transportation costs 38. Which of the following would not be considered price discrimination? a. Airline fares are lower if you purchase your ticket several weeks in advance b. Senior citizens pay a lower price for restaurant meals c. Doctors charge high-income patients a higher price for a physical examination than low-income patients. d. A drug company charges a higher price of a cholesterol-lowering drug than for aspirin. 39. Which of the following is an example of an actual cartel? a. The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) b. General Motors, Ford, and Chrysler c. American Airlines, United Airlines, and Delta Airlines d. All of the above 40. For a cartel to be successful in increasing the price all member firms receive for their product, it must be able to: a. increase the collective output of all members of the cartel b. restrict the collective output of all members of the cartel c. increase advertising by all members of the cartel d. decrease the prices members of the cartel pay for their inputs 41. If zinc suppliers are successful in forming an international cartel, then they will experience: a. higher zinc prices, higher zinc output, and greater profits b. lower zinc prices, higher zinc output, and greater profits c. lower zinc prices, lower zinc output, and greater profits d. higher zinc prices, lower zinc output, and greater profits 42. Each member of a cartel has an economic incentive to cheat on its agreed output quota because: a. producing more output than its quota will increase the cheating firm’s sales and and profits b. producing more output than its quota forces other members of the cartel to decrease their cost, which increases the cheating firm’s profits 8 c. d. producing less output than its quota will increase the cheating firm’s sales and profits Both a and b 43. During certain periods in the past few decades, if one of three major breakfast cereal producers in the U.S. announced a price increase, the other two followed by announcing price increases. This is a good example of: a. a cartel b. typical firm behavior in monopolistic competition c. price leadership in an oligopolistic industry d. non-profit maximizing behavior 44. Which of the following statements about is true? a. The Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 made cartels and price fixing illegal in the U.S. b. Since the Sherman Antitrust Act, no firms have attempted to fix prices c. International cartels do not currently exist in the world market d. Both a and b 9