Chapters 10 and 11 Review Questions
advertisement
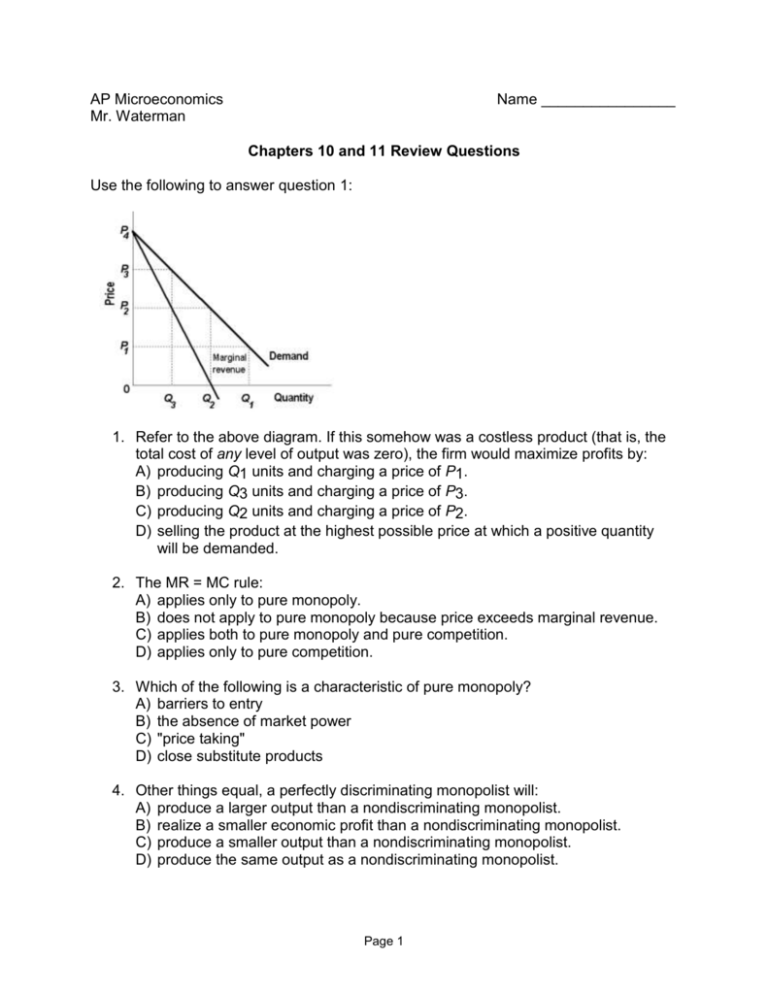
AP Microeconomics Mr. Waterman Name ________________ Chapters 10 and 11 Review Questions Use the following to answer question 1: 1. Refer to the above diagram. If this somehow was a costless product (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by: A) producing Q1 units and charging a price of P1. B) producing Q3 units and charging a price of P3. C) producing Q2 units and charging a price of P2. D) selling the product at the highest possible price at which a positive quantity will be demanded. 2. The MR = MC rule: A) applies only to pure monopoly. B) does not apply to pure monopoly because price exceeds marginal revenue. C) applies both to pure monopoly and pure competition. D) applies only to pure competition. 3. Which of the following is a characteristic of pure monopoly? A) barriers to entry B) the absence of market power C) "price taking" D) close substitute products 4. Other things equal, a perfectly discriminating monopolist will: A) produce a larger output than a nondiscriminating monopolist. B) realize a smaller economic profit than a nondiscriminating monopolist. C) produce a smaller output than a nondiscriminating monopolist. D) produce the same output as a nondiscriminating monopolist. Page 1 5. If a regulatory commission wants to establish a socially optimal price for a natural monopoly, it should select a price: A) which corresponds with the equality of marginal cost and marginal revenue. B) at which the average total cost curve intersects the demand curve. C) at which marginal revenue is zero. D) at which the marginal cost curve intersects the demand curve. 6. Which of the following is not characteristic of monopolistic competition? A) relatively easy entry to the industry B) product differentiation C) production at minimum ATC in the long-run D) relatively large numbers of sellers Use the following to answer question 7: 7. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium output will be: A) E. B) D. C) C. D) greater than E. 8. In long-run equilibrium a monopolistically competitive producer achieves: A) both productive efficiency and allocative efficiency. B) allocative efficiency, but not productive efficiency. C) productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency. D) neither productive efficiency nor allocative efficiency. 9. OPEC provides an example of: A) an international cartel. B) noncollusive oligopoly. C) a monopolistically competitive industry. D) a tacit understanding. Page 2 Use the following to answer questions 10-11: 10. Refer to the above diagram. In equilibrium total revenue will be: A) 0AJE. B) 0EHB. C) NM times 0M. D) 0EGC. 11. Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profits or minimize losses this firm should produce: A) L units and charge price LK. B) E units and charge price A. C) E units and charge price C. D) M units and charge price N. 12. One would expect that collusion among oligopolistic producers would be easiest to achieve in which of the following cases? A) a very few firms producing a homogeneous product B) a rather large number of firms producing a homogeneous product C) a rather large number of firms producing a differentiated product D) a very few firms producing a differentiated product 13. Oligopolistic industries are characterized by: A) a few dominant firms and low entry barriers. B) a large number of firms and low entry barriers. C) a few dominant firms and substantial entry barriers. D) a few dominant firms and no barriers to entry. Page 3 Use the following to answer question 14: 14. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. The profit-maximizing output for this firm will be: A) 100. B) 180. C) 160. D) 210. Page 4 Answer Key – Chapter 24 and 25 Review 1.C 2.C 3.A 4.A 5.D 6.C 7.B 8.D 9.A 10. A 11. B 12. A 13. C 14. C Page 5











