Cell Part Functions
advertisement
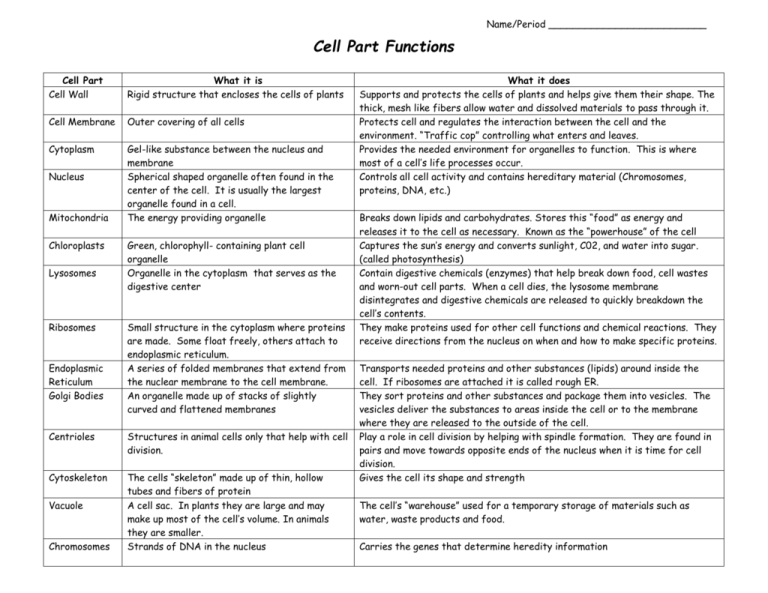
Name/Period __________________________ Cell Part Functions Cell Part Cell Wall What it is Rigid structure that encloses the cells of plants Cell Membrane Outer covering of all cells Cytoplasm Gel-like substance between the nucleus and membrane Spherical shaped organelle often found in the center of the cell. It is usually the largest organelle found in a cell. The energy providing organelle Nucleus Mitochondria Chloroplasts Lysosomes Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies Green, chlorophyll- containing plant cell organelle Organelle in the cytoplasm that serves as the digestive center Small structure in the cytoplasm where proteins are made. Some float freely, others attach to endoplasmic reticulum. A series of folded membranes that extend from the nuclear membrane to the cell membrane. An organelle made up of stacks of slightly curved and flattened membranes Centrioles Structures in animal cells only that help with cell division. Cytoskeleton The cells “skeleton” made up of thin, hollow tubes and fibers of protein A cell sac. In plants they are large and may make up most of the cell’s volume. In animals they are smaller. Strands of DNA in the nucleus Vacuole Chromosomes What it does Supports and protects the cells of plants and helps give them their shape. The thick, mesh like fibers allow water and dissolved materials to pass through it. Protects cell and regulates the interaction between the cell and the environment. “Traffic cop” controlling what enters and leaves. Provides the needed environment for organelles to function. This is where most of a cell’s life processes occur. Controls all cell activity and contains hereditary material (Chromosomes, proteins, DNA, etc.) Breaks down lipids and carbohydrates. Stores this “food” as energy and releases it to the cell as necessary. Known as the “powerhouse” of the cell Captures the sun’s energy and converts sunlight, C02, and water into sugar. (called photosynthesis) Contain digestive chemicals (enzymes) that help break down food, cell wastes and worn-out cell parts. When a cell dies, the lysosome membrane disintegrates and digestive chemicals are released to quickly breakdown the cell’s contents. They make proteins used for other cell functions and chemical reactions. They receive directions from the nucleus on when and how to make specific proteins. Transports needed proteins and other substances (lipids) around inside the cell. If ribosomes are attached it is called rough ER. They sort proteins and other substances and package them into vesicles. The vesicles deliver the substances to areas inside the cell or to the membrane where they are released to the outside of the cell. Play a role in cell division by helping with spindle formation. They are found in pairs and move towards opposite ends of the nucleus when it is time for cell division. Gives the cell its shape and strength The cell’s “warehouse” used for a temporary storage of materials such as water, waste products and food. Carries the genes that determine heredity information









