Section 3 c alkenes
advertisement

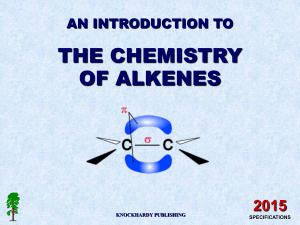
Section 3 c: alkenes 3.6 recall that alkenes have the general formula CnH2n 3.7 draw displayed formulae for alkenes with up to four carbon atoms in a molecule, and name the straight-chain isomers 3.8 describe the addition reaction of alkenes with bromine, including the decolourising of bromine water as a test for alkenes What do all alkenes have in common? same functional group; C=C : at least 1 double covalent bond between two carbon atoms in the molecule a general formula of Cn H2n each alkene has at least 1 double carbon = carbon bond; in such a carbon=carbon bond each carbon is only bonded onto 3 other different atoms. It uses up 2 of its 4 valence electrons to bond with the same atom. We say the carbon compound with 1 or more double bonds is unsaturated. We can add more atoms to the molecule by using the double bond which can pop open. because each alkene is unsaturated they are reactive; most reactions will involve the double bonds. unsaturated = has a double bond Examples of alkenes and isomers. Write down the names, molecular formulas and graphical/displayed formula for the first 3 straightchained members of the alkenes. Why does methene not exist? Isomerism: for one of the alkenes you can draw another isomer. Which alkene? Draw the isomer below. Chemical reactions of alkenes Combustion: to produce water and carbon dioxide when combustion is complete; carbon monoxide and water when combustion is incomplete. Write equations for the following combustions: 1. Combustion of ethene: Section 3c alkenes 1|Page 2. Combustion of propene: Addition reaction An addition reaction is a reaction during which a small molecule is added to an unsaturated organic compound changing it into a saturated compound. This happens because the double bond pops open and each carbon electron of the double bond can now be used to make a new covalent bond with another atom or group of atoms. The small molecule which reacts with the alkene breaks up into 2 parts and one part goes to one carbon of the double bond and the other part goes to the second carbon atom of the double bond. Example: ethene + bromine dibromoethane (=colourless) Draw a structural equation to show what happens during this addition reaction. Write a balanced equation and word equation for the above reaction. Test of alkenes – IMPORTANT!! During the reaction between an alkene and bromine (bromine water) the bromine loses its red-brown colour rapidly and a colourless solution is produced. This is the case because bromomethane is a colourless compound. This reaction is used to test for unsaturated compounds. If bromine water changes rapidly from redbrown to colourless the other reactant must be an alkene or an unsaturated compound. The more bromine water that is decolourized the greater the unsaturation of the compound. Section 3c alkenes 2|Page