Passive-Transport-Guided
advertisement

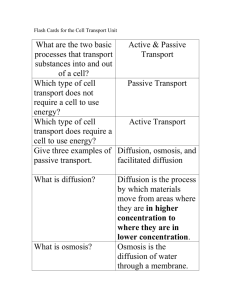
Chapter 5 Section 1: Passive Transport Use Modern Biology Textbook pgs. 97-102 1. Cell membranes help organisms maintain homeostasis (balance) by: _________________________________________________________________. Some substances can cross the cell membrane without any input of energy by the cell in a process known as _______________ _________________. 2. Define diffusion: 3. The different in concentrations of a substance across an area is called the _______________________ ____________________. 4. Molecules are constantly in ______________. 5. Define equilibrium: 6. If a molecule can pass through a cell membrane, it will diffuse from an area of ____________ concentration on one side of the membrane to an area of _________________ concentration on the other side. 7. Define osmosis: 8. List one way osmosis is different from diffusion. 9. List one way osmosis is the same as diffusion. 10. List an example of a solute. 11. List an example of a solvent. 12. Does passive transport require energy from the cell? 13. When the concentration of solute molecules outside the cell is lower than the concentration in the cytosol, the solution outside is ________________ to the cytosol. In this situation, water diffuses _______ the cell until equilibrium is established. 14. When the concentration of solute molecules outside the cell is higher than the concentration in the cytosol, the solution outside if ________________ to the cytosol. Water diffuses _______ of the cell until equilibrium is established. 15. When the concentration of solutes outside and inside the cell are equal, the outside solution is said to be _________________. 16. Look at Figure 5.2 on page 99 of the paramecia. They have _______________________________ that collect excess water that moves by osmosis into the cytosol. 17. When water diffuses into a plant cell and builds up firm pressure, that is called _____________ _________________. (pg. 100) 18. When water diffuses out of a plant cell and causes the cell membrane to shrink, that is called _________________________. 19. Define facilitated diffusion: 20. In facilitated diffusion, the movement of molecules across the membrane is assisted by specific proteins called ______________ ________________. 21. List the four steps of facilitated diffusion (Figure 5.5 on page 101). 1. 2. 3. 4. 22. A good example of facilitated diffusion is the transport of ____________. 23. What are ion channels? 24. Ion channels transport ions such as _______________ (Na+), ________________ (K+), ______________ (Ca+), and _______________ (Cl). 25. Each type of ion channel is usually ____________ for one type of ion. For example, ______________ channels only allow _____________ ions to go through, but will not allow _________________ ions of ____________ to enter the cell. 26. Some ion channels are always __________. Others have “________” that open to allow ions to pass or close to stop their passage. 27. List 3 kinds of stimuli that may open or close the gates of ion channels. 1. 2. 3. 28. List the four types of passive transport (as mentioned in the textbook). 1. 2. 3. 4.