6th Grade Unit 1
advertisement

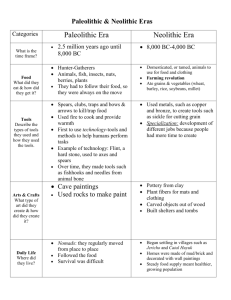
6th GRADE SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT 1: Water World “When the well is dry, we learn the worth of water.” Benjamin Franklin, Poor Richard’s Almanac Unit Product: Report on contemporary issue surrounding water 16 WEEKS: September to December Essential Questions: How did access to bodies of water shape the course of human history? Guiding Questions: What is Social Studies? Why is it important? What makes us human? (the emergence of Homo sapiens) How do we know what we know about early humans? (Paleolithic communities) How did water and ice guide the course of early human history? (Paleolithic communities) What is a community, and why does water make is stronger? (Neolithic communities) How do jobs become specialized in farming communities? (Neolithic communities) How can water make a civilization prosperous? (Mesopotamia, Egypt) How can water be used for trade? (Phoenicians) How can trade lead to cultural diffusion? (China) How can water lead to conflict? (Greece) How can water lead to conquest? (Rome) What technological innovations are associated with water? (Egypt, Rome, Mesopotamia) What is the religious significance of water? (Egypt, China, Greece) What happens to current and ancient civilizations when the water supply is disrupted? (contemporary Earth) 1 NYS Common Core Standards Assessed: Key Ideas and Details RH.6-8.1. Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources. RH.6-8.2. Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of the source distinct from prior knowledge or opinions. RH.6-8.3. Identify key steps in a text’s description of a process related to history/social studies (e.g., how a bill becomes law, how interest rates are raised or lowered). Craft and Structure RH.6-8.4. Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, including vocabulary specific to domains related to history/social studies. RH.6-8.5. Describe how a text presents information (e.g., sequentially, comparatively, causally). RH.6-8.6. Identify aspects of a text that reveal an author’s point of view or purpose (e.g., loaded language, inclusion or avoidance of particular facts). Integration of Knowledge and Ideas RH.6-8.7. Integrate visual information (e.g., in charts, graphs, photographs, videos, or maps) with other information in print and digital texts. RH.6-8.8. Distinguish among fact, opinion, and reasoned judgment in a text. RH.6-8.9. Analyze the relationship between a primary and secondary source on the same topic. Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity RH.6-8.10. By the end of grade 8, read and comprehend history/social studies texts in the grades 6–8 text complexity band independently and proficiently. ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE Diagnostic Assessment Students will complete a baseline skills assessment measuring Social Studies knowledge and skills such as: interpretation of maps, graphs/charts, and timelines; domain-specific vocabulary; knowledge of historical events; and ability to critically analyze and interpret primary source documents. Formative Assessments: Performance Task 1: Letter to Your Ancestors You are an early human during the Neolithic period. Your task is to write a letter to your ancestors who lived during the Paleolithic period. In your letter, describe three ways that life has improved since the time of your ancestors. Use specific facts and details about Paleolithic and Neolithic life to compare and contrast. You may use the summary handout as a reference, as well as your notes. Be sure to: Write from the perspective of a Neolithic person Describe three ways the life has improved since Paleolithic times, comparing and contrasting the two eras 2 of human development using specific facts and details. Use evidence from your resources, including notes, text, and handouts Follow the conventions of standard English including capitalization, punctuation, and spelling Performance Task 2: Job Specialization Catalogue You are a career consultant in ancient Egypt. You help members of your community choose a job based on their skills and interests. Your task is to create a fact and print-rich, illustrated job catalogue of at least six jobs that could be found in ancient Egypt. Be sure to: Summarize six jobs that could be found in Ancient Egypt Integrate relevant facts about each job using complete sentences. Illustrate your jobs with research-based, era-appropriate illustrations such as tools, products, and resources Describe the qualifications and responsibilities of each job using domain-specific vocabulary Follow the conventions of standard English including capitalization, punctuation, and spelling Summative Assessments: Water Issues Students will research one of three contemporary issues concerning water: drought in Southern Africa, hydrofracking in the United States, or the Great Pacific Garbage Patch. Students will write a report integrating information from a variety of sources that answers the question: What is one problem concerning water that faces humans today? What are the causes of this problem? What are some possible solutions to this problem? Be sure to: Write a report on one problem concerning water that faces humans today. Describe the causes of this problem. Describe several possible solutions to this problem. Follow the conventions of standard English including capitalization, punctuation, and spelling 3 TEACHING PLAN Resources Needed: Baseline social studies assessments and activities: Map Scale Activity: https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B9UdPWAE3ZaWNXVGSW9xZTZrYVk Map Scale Activity 2: https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B9UdPWAE3ZaWS2ozdmJObUUxTmc Compass Skills Activity: https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B9UdPWAE3ZaWZGhjcVZNajNLWUU Map Key Activity: https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B9UdPWAE3ZaWeTFJVmo1UDR4bEE Paleolithic Humans: Videos on Neanderthals and Homo sapiens http://www.teachersdomain.org/resource/hew06.sci.life.reg.earlyhumans/ http://www.teachersdomain.org/asset/clim10_vid_evoclimate/ http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/humans/humankind/index.html The Land Bridge Video: http://www.teachersdomain.org/asset/ess05_vid_firstpeople/ Readings: https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B9QcSNvi7up0N0tldXplbk5ReEE Paleolithic Art: https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/16_M5Oxl1W7yCamg2_-hYcQJ6O-nJ1XM6cemE5SXa-L8/edit Neolithic Humans: Agricultural Revolution Readings: https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B9UdPWAE3ZaWNUN4Nlh4RW1tOTQ https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B9UdPWAE3ZaWZlBDSTJEbUViaHM Otzi the Iceman: https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B9QcSNvi7up0alZuaDhNNWZmZjA Early Farming Map: https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B9QcSNvi7up0WENBSHNrams2MkE Comic: https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B9QcSNvi7up0Ql92eldxa3ZiamM Mesopotamia: Farming In Sumeria Activity: http://www.mesopotamia.co.uk/geography/challenge/cha_set.html Job Specialization: http://oi.uchicago.edu/OI/MUS/ED/TRC/MESO/cities_a.pdf Cuneiform: http://oi.uchicago.edu/OI/MUS/ED/TRC/MESO/writing_a.pdf Math and Measurement: http://oi.uchicago.edu/OI/MUS/ED/TRC/MESO/math_a.pdf Ziggurats: http://www.mesopotamia.co.uk/ziggurats/home_set.html Egypt: Introductory Reading: https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B9UdPWAE3ZaWVlpVQS0tZGM2dVU Ancient Greece: Peloponnesian War: http://kidspast.com/world-history/0070-peloponnesian-war.php 4 Week Guiding Questions 1 (2 days) What is Social Studies? Why is it important? WEEKLY CALENDAR Topics/Lessons Assessments Students complete a baseline skills assessment. Key Vocabulary Baseline skills assessment administered Students define and analyze the five components of social studies: culture, history, economics, government, and geography. Social studies, culture, history, economics, government, geography, society Standards Assessed: Week RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.10. Guiding Questions Topics/Lessons Assessments Key Vocabulary 2 What makes us human? Students compare Neanderthals to Homo sapiens. Timeline Homo sapien, Neanderthal, culture, history, economics, government, geography, timeline, BC, CE, latitude, longitude Students create a human history timeline as a classroom display and unit anchor point. Standards Assessed: Graphic organizer comparing Neanderthals and Homo sapiens Materials: Homo sapiens vs. Neanderthals video RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.9., RH.6-8.10. Week Guiding Questions Topics/Lessons Assessments Key Vocabulary 3 (3 days) How do we know what we know about early humans? Students will analyze primary sources on Paleolithic people and hypothesize about the lives of Paleolithic people based on primary sources. Graphic organizer: students make hypotheses based on archeological evidence such as cave paintings and artifacts Paleolithic (literally “old stone”), archeology, artifact, carbon dating, fossil, hunter-gatherer, nomadic Standards Assessed: Week 4 (4 days) Materials: cave paintings, artifacts slideshow RH.6-8.1., RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.10. Guiding Questions Topics/Lessons Assessments Key Vocabulary How did water and ice guide the course of early human history? Students investigate the effect of the last Ice Age on the environment, human development and migration. Students create a land bridge map. Paleolithic, Ice Age, migration, huntergatherer, nomadic Students analyze an ice age map. 5 Standards Assessed: RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.9., RH.6-8.10. Week Guiding Questions What is a community, and why does water make it stronger? 5 Topics/Lessons Assessments Key Vocabulary Students will connect the rise of farming communities to changes in the environment. Graphic organizer comparing Paleolithic and Neolithic humans. Students will compare farming communities with huntergatherer communities. RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.10. Performance Task #1: Letter to Your Ancestors Civilization, natural resource, Neolithic, hunter-gatherer, community, domesticate, livestock, cultivate Week Guiding Questions Topics/Lessons Assessments Key Vocabulary 6 (4 days) How do jobs become specialized in farming communities? Students will analyze the relationship between food surplus and job specialization. Graphic organizer showing job specialization in Neolithic communities job specialization Standards Assessed: Standards Assessed: Week 7 Standards Assessed: Week Students will explore the ways in which communities divide work. Students will hypothesize about how job specialization could lead to more complex and stable civilizations. RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.9., RH.6-8.10. Guiding Questions Topics/Lessons Assessments Key Vocabulary How can water make a civilization prosperous? Students will study how the geography of Mesopotamia, the “land between rivers”, led to its development. Group presentations Cuneiform, city-state, monarchy, scribe, irrigation, social class, barter Students will explore primary sources on Mesopotamian civilization and present in groups. RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.10. Guiding Questions Topics/Lessons Assessments Key Vocabulary 6 8 Standards Assessed: How can water make a civilization prosperous? (CONT’D) Students will study how the Nile River led to Egypt’s development. Performance Task #2: Job Specialization Catalogue Papyrus, obelisk, mummy, pharaoh, pyramid, hieroglyphic, Students will explore primary source evidence on Egyptian job specialization and complete Performance Task #2. RH.6-8.1., RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.10. Week Guiding Questions Topics/Lessons Assessments Key Vocabulary 9 How can water be used for trade? Students will map the trade routes of the Phoenician civilization. Trade route map analysis Trade route, cost/benefit analysis Students will critically discuss contemporary trade, analyzing the costs and benefits of contemporary trade relationships. Standards Assessed: RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.10. Week Guiding Questions Topics/Lessons Assessments Key Vocabulary 10 How can trade lead to cultural diffusion? Students will explore ancient China’s relationship with its neighbors, and study examples of cultural diffusion in East Asia. Graphic organizer showing examples of cultural diffusion in East Asia Cultural diffusion Standards Assessed: RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.10. Week Guiding Questions Assessments Key Vocabulary Topics/Lessons 7 11 How can water lead to conflict? Students will answer, “How did Greece become the dominant power in the Mediterranean Sea?” Written response Naval power Students will answer, “What was the relationship between Athens and Sparta like? What led them to war?” Standards Assessed: RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.9., RH.6-8.10. Week Guiding Questions Topics/Lessons Assessments Key Vocabulary 12 (2 days) How can water lead to conquest? Students will map the growth of the Roman Empire. Written response Empire, conquest Standards Assessed: RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.10. Week Guiding Questions Topics/Lessons Assessments Key Vocabulary 13 What technological innovations are associated with water? (Egypt, Rome, Mesopotamia) Students will study water technologies across civilizations: Shaduf, aquaduct, irrigation, water wheel Students will create models of ancient water technologies. Technology, innovation Standards Assessed: RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.10. Week Guiding Questions Assessments Key Vocabulary Topics/Lessons 8 14 What is the religious significance of water? Students will make connections between the myths of ancient civilizations, including Egypt, Phoenicia, Greece, and China. Graphic organizer Myth, ritual Standards Assessed: RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.10. Week Guiding Questions Topics/Lessons Assessments Key Vocabulary 15 What happens to current and ancient civilizations when the water supply is disrupted? Students will explore how the inhabitants of Tikal in ancient Central America attempted to manage drought through social planning, technology, and ritual. Summative Assessment: Water Issues Drought, social planning, contemporary Key Vocabulary Students will study contemporary issues surrounding water supply. Standards Assessed: RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.10. Week Guiding Questions Topics/Lessons Assessments 16 What happens to current and ancient civilizations when the water supply is disrupted? Students will study contemporary issues surrounding water supply. Summative Assessment: Water Issues Standards Assessed: RH.6-8.2., RH.6-8.4., RH.6-8.5., RH.6-8.7., RH.6-8.10. 9