File - Ms Bonaguro
advertisement

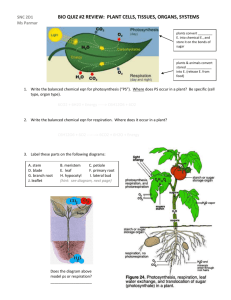
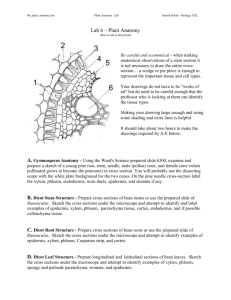
Biology 2012 AOA Plant Structure and Function (For LUOA Seed Lab) Late Nite Labs Name: Date: Note: To answer many of these questions, it is recommended that you also download and review the document “background_for_aoa_plant_stucture_and_function_lab.docx” from msbonaguroluoa.weebly.com. Leaves Save an annotated snapshot of the “Leaf Cross-Section” to your portfolio in Late Nite Labs by clicking the black snapshot button just above the rotating objectives of the microscope. Wait until you see a message that the snapshot has been saved before continuing. (a) Cuticle, phloem channels, with the xylem on top and the phloem on bottom is located in (b) Upper Epidermis the bulging center of the leaf's cross (c) Palisade Mesophyll (neatly arranged section) chlorenchyma cells with chloroplasts) (g) Lower Epidermis (d) Spongy Mesophyll (h) Stoma (e) Air Spaces (i) Guard Cells (f) Vascular bundle with Xylem and Phloem channels (a row of vertical xylem and Save an annotated snapshot of the “Pine Needle Cross-Section.” (a) Epidermis (e) Xylem (b) Mesophyll (f) Phloem (c) Resin Ducts (g) Stoma Pore (d) Endodermis 1. What is the function of the stomata? Why do they appear only on the underside of the leaf? 2. What are the functions of the air spaces near the lower surface of the leaf? 3. List at least three differences between a typical, flat leaf and a pine needle. 4. Why do you think that the basic angiosperm leaf was created to be flat? How did this adaptation come at the expense of another valuable commodity, water? 5. Explain the function of guard cells. 6. How are the guard cells different from other epidermal cells? 7. Describe the general function of xylem and list its cell types. 8. Describe the general function of phloem and list its cell types. Biology 2012 AOA Plant Structure and Function (For LUOA Seed Lab) Late Nite Labs 9. Describe the general functions of parenchyma tissue in stems and leaves. 10. Describe the general function of collenchyma and sclerenchyma tissue. Stems Save an annotated snapshot of the “Monocot Stem Cross-Section” (a) Pith (d) Bundle Sheath (around each xylem and phloem pair) (b) Xylem (e) Epidermis (c) Phloem Save an annotated snapshot of the “Dicot Stem Cross-Section” (a) Pith (d) Vascular Cambium (b) Xylem (e) Cortex (c) Phloem Save an annotated snapshot of the “Pine Stem Cross-Section” (a) Pith (e) Resin ducts in phloem (b) Xylem (in annual rings) (f) Cortex (c) Cambium (separating xylem from (g) Ray (radical line running through xylem phloem) and phloem) (d) Phloem 1. What is the function of the cuticle covering the epidermis of leaves and stems? 2. Where is food stored in the stem? 3. What is the difference between the arrangement of vascular bundles in monocot and dicot stems? Does either arrangement have any impact on the function of the whole stem? 4. Which part of the stem tissue is "wood" made from? 5. What happens to the phloem tissue from year to year of secondary growth? 6. Based on your observations of the woody stem, does xylem or phloem provide structural support for trees? Roots Save an annotated snapshot of the “Monocot Root Cross-Section” (a) Xylem (b) Phloem Biology 2012 AOA Plant Structure and Function (For LUOA Seed Lab) Late Nite Labs (c) Pericycle (between the xylem and (d) Endodermis phloem and the cortex, from which the (e) Cortex root branches grow) (f) Epidermis Save an annotated snapshot of the “Dicot Root Cross-Section” (a) Xylem (b) Phloem (c) Pericycle (between the xylem and phloem and the cortex, from which the root branches grow) 1. What are in the vascular bundles of the roots? (d) Endodermis (e) Cortex (f) Epidermis 2. What is the difference between the arrangement of vascular bundles in monocot and dicot roots? Does either arrangement have any impact on the function of the whole root? 3. Leaf and stem epidermis is covered with a waxy cuticle, but root epidermis is not. Why is the cuticle not required by roots? 4.Where is food stored in roots? 5. What is the purpose of root hairs? 6.Why do we find collenchyma and sclerenchyma cells in stem and leaf tissue but not in roots? 7.Why do root cells require oxygen? 8. What similarities can you observe between the parenchyma cells in the root and in the stem? 9 .How does the function of the parenchyma located in leaves differ from the function of the parenchyma located in roots?