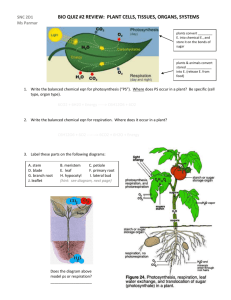
Plant Anatomy
advertisement

06_plant_anatomy.doc Plant Anatomy Lab Henrik Kibak - Biology 242L Lab 6 – Plant Anatomy (Due at end of lab period) Be careful and economical - when making anatomical observations of a stem section it is not necessary to draw the entire cross section… a wedge or pie piece is enough to represent the important tissue and cell types. Your drawings do not have to be "works of art" but do need to be careful enough that the professor who is looking at them can identify the tissue types. Making your drawing large enough and using some shading and extra lines is helpful. It should take about two hours to make the drawings required by A-E below. A. Gymnosperm Anatomy - Using the Ward's Science prepared slide 6300, examine and prepare a sketch of a young pine root, stem, needle, male (pollen) cone, and female cone (when pollinated grows to become the pinecone) in cross section. You will probably use the dissecting scope with the white plate background for the two cones. On the pine needle cross-section label the xylem, phloem, endodermis, resin ducts, epidermis, and stomata if any. B. Dicot Stem Structure - Prepare cross sections of bean stems or use the prepared slide of Ranunculus. Sketch the cross sections under the microscope and attempt to identify and label examples of epidermis, xylem, phloem, parenchyma tissue, cortex, endodermis, and if possible collenchyma tissue. C. Dicot Root Structure - Prepare cross sections of bean roots or use the prepared slide of Ranunculus. Sketch the cross sections under the microscope and attempt to identify examples of epidermis, xylem, phloem, Casparian strip, and cortex. D. Dicot Leaf Structure - Prepare longitudinal and latitudinal sections of bean leaves. Sketch the cross sections under the microscope and attempt to identify examples of xylem, phloem, spongy and palisade parenchyma, stomata, and epidermis. 06_plant_anatomy.doc Plant Anatomy Lab Henrik Kibak - Biology 242L Did not include "E" in spring 09, should include next time. E. Monocot Root Structure - Prepare cross sections of onion roots or use the prepared slide of Lilium. Sketch the cross sections under the microscope and attempt to identify examples of xylem, phloem, endodermis, cortex, epidermis. Need to figure out sectioning for this lab because it did not work well for me. If a carrot can be used, why not a microtome? 2 double edged razors sandwiched around a broken double edged razor might work. Need to develop answers for this lab.