Name - Boyertown Area School District
advertisement

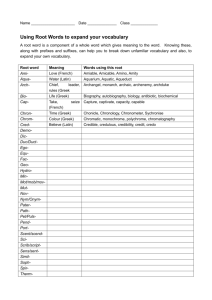
Name: ____Key_______________ Date: _________ Period: ____ Section 1: Greek Art and ArchitectureStudy Prints A. Athens: The Acropolis 1. Why do you think the Greeks build their most important buildings on a hill? - built on a hill for protection (most important places) - built originally for military purposes - temples higher up (closer to the gods) 2. What material was used to make these buildings? - Marble/Bronze Statues 3. Why do think the buildings are in ruins? -earthquakes/erosion- invasion by the Turks -1687- lack of repairs B. Athens: The Parthenon 1. What was the Parthenon? - Temple dedicated to Athena- patron God of Athens ________________________________________________________________________ 2. What type of column was used? - Doric columns ________________________________________________________________________ 3. Describe the Parthenon? - Located on the acropolis of Athens –sacred area to the Athenians - center for religious observances dedicated to Athens C. Athens: The Parthenon (Interior) 1. Whose statue was inside the Parthenon? Athena ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Why do you think the statue held a shield and a spear? Athena was the protector of Athens, symbolic shield and spear ________________________________________________________________________ 3. True or False – The statue was six feet tall. **43 feet tall* 4. In what ways were the insides of the Greek Temples different from churches? Greek temples- lack of windows, simplistic, focal point was Athena’s statue instead of altarlarger 1 D. Aegina: The Temple of Aphaea (dedicated to the local diety Aegina) 1. Is the temple larger or smaller than the Parthenon? ___smaller_____________ 2. What kind of columns can be found in this structure? ___Doric______________ E. Corinth: The Agora 1. What is an agora? Greek market place- gossip, politics, friends and food ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Why do you think there was a covered walkway? - keep rain from interfering - food tent carts set up in the middle of the agora ________________________________________________________________________ F. Delos: A House 1. Was this the home of a poor person or a wealthy person? Explain. Wealthy= size, decorations of house – possibly owned by government officials or very wealthy ________________________________________________________________________ 2. What do you think was the purpose of this room? - residence -government or trade center(would bring many guests) - possible religious shrine ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How was the ceiling of this home different from our homes today? - large doric columns, marble, large statues, no atriums (courtyard) ________________________________________________________________________ 4. TRUE OR FALSE- Columns were only used in Greek Temples. G. The Fortifications (Fort) of Agoesthena 1. Why did the Greeks build walls and forts? - watch tower and defense post - generate community pride -protection from enemies -sense of security ________________________________________________________________________ 2. What were the walls made of? - Stone blocks brick tower ________________________________________________________________________ 2 Name _________________________________ Date ___________ Class _________ 5-1 The Culture of Ancient Greece Directions: Filling in the Blanks Reading the section and completing the sentences below will help you learn more about the culture of Ancient Greece. Refer to your textbook pages 154-163 to fill in the blanks. The Greeks believed in many gods and goddesses who controlled (1) Nature Zeus __________________. Led by (2) _________________, the chief god, the twelve Mt. Olympus most important gods and goddesses lived on (3) __________________. According to Greek myth, the gods were not thought to be (4) __________________, but did have All-powerful Rituals special powers. (5) __________________ were followed in hope of receiving good fortune from the gods. Because the Greeks believed in destiny and prophesy, they often oracle visited a(n) (6) __________________ in order to find out about the future. epics The earliest Greek stories were (7) __________________. The poet (8) Homer __________________ wrote the Iliad and the Odyssey. The Greek people looked on the history epics as real (9) ____________________. Homer's heroes became (10) Role-models ____________________ for Greek boys. Another form of Greek story that taught a lesson fable was the (11) ____________________. Each fable ends with a message, or (12) moral ____________________. Drama (13) ____________________ is a story told by actors who pretend to be characters in the story. A tragedy has an unhappy ending because the character tries to (14) overcome ____________________ difficulties but fails. In a comedy, the story ends (15) happily ____________________. (16) ____________________ Artists in ancient Greece believed in ideas like reason, moderation, balance, and harmony and hoped to inspire people to base their lives on these ideas. pottery Examples of Greek painting can be seen on Greek (17) ____________________. Greek architecture has influenced buildings today in the use of marble (18) columns ____________________, which are common features of churches and government buildings. 3 Greek Theatre Answer these questions using the in-class reading. 1. How did Greek theatre start? Theater grew out of festivals for the God Dionysus. They had a chorus leader who gave a soliloquy. 2. Define soliloquy. A talk in which personal thoughts or feelings are expressed. 3. Describe a Greek tragedy. Stories about suffering that dealt with the past and were relationships between the people and the gods. 4. Describe a Greek comedy. A play in which a happy ending was usually told in the present and made fun of politicians. 5. Why did the Greek actors wear masks? To show gender, age, and mood of the characteralso included a funnel to amplify the voice. ______________________________________________________________________________ 6. True/False: Both men and women acted in Greek theatre. Greek Olympics 1. Do you think the modern day Olympic games are a force of unity in the world. Why or why not. _____Will vary_________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. How did athletes compete in the pancratium? It was a combination of no holds barred boxing/wrestling. You could not bite or gouge eyes. 3. What five events made up the pentathalon? Run, jump, throw discus, wrestle and hurl the javelin- winner was the best overall athlete. 4 Greek Religion Word Unscramble Directions: Look at the letters below. Unscramble each to reveal the name of a Greek god or goddess. Use the clues to help unscramble the letters. 1. S R E A god of war ____ARES_________________________ 2. U E Z S chief god; god of the sky, rain, and lightning _____ZEUS___________________________ 3. M A R T S I E goddess of the hunt and wild animals _____ARTEMIS___________________________ 4. P O O L A L god of the sun and poetry ___APOLLO__________________________ 5. T E S H A I goddess of the home ____HESTIA_________________________ 6. S N P O E I D O god of the sea ___POSEIDON________________________ 7. D E H A S god of the underworld ___HADES_________________________ 8. H S E E M R messenger of the gods ____HERMES________________________ 9. N A H A T E goddess of wisdom ____ATHENA_______________________ 10. T E P H D R I O A goddess of love ____APHRODITE_______________________ 11. R H E A goddess of marriage ____HERA________________________ 12. T R E E D E M goddess of crops ____DEMETER_____________________ 5 Name _______________________________ Date ________________ Class ________ 5-2 Greek Philosophy and History Directions: Outlining Reading the section and completing the outline below will help you learn more about Greek philosophy and history. Refer to your textbook pages 168-173 to fill in the blanks. I. philosophy science Greek _______________ led to the study of history, political science, _______________, and mathematics. A. teachers Many philosophers were _______________ like Pythagoras, who taught that all relationships in the world could expressed be _______________ in numbers. Sophists B. One school of philosophers were the _______________ who traveled from city to city making a living by teaching others. C. sculptor Socrates was an Athenian _______________ whose true love was philosophy. 1. Socratic method Socrates invented the _______________ of teaching, which asks pointed questions to force students to use reason and to see things for themselves. 2. D. rebel Socrates was accused of teaching young Athenians to _______________ against the _______________. State Plato _______________ was a student of Socrates who taught that democracy was not a good system of _______________. government E. II. Americans Aristotle, a student of Plato, influenced the way Europeans and _______________ thought about government. histories Greeks wrote the first real _______________ in Western civilization. A. Herodotus wrote the history of the Persian Wars and tried to separate _______________ from _______________, fact legend but used _______________ and _______________ to explain some events. gods goddesses B. Most historians consider _______________ the greatest historian of the ancient Thucydides world because he saw war and Human beings politics as the activities of _______________ and stressed the importance of having accurate _______________. facts 6 5-3 Alexander the Great: Words to Know Directions: For each of the following terms or place names, indicate which are associated with Philip II and which are associated with Alexander the Great by filling in the number before each term in the correct portion of the Venn diagram. Read pages 174-179 to answer the questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Alexandria- Alexander the great Chaeronea- Phillip II Hellenistic Era- Alexander the great Macedonia- Both Syria- Alexander the great Building Academic Vocabulary achieve, verb achievement, noun Directions: Answer the following questions about the word achieve. You may use your textbook, a dictionary, or Internet resources to help you. 6. What does it mean to "achieve a goal"? Will Vary- a person accomplished something they set out to do 7. What is a goal of yours? Will Vary 8. What were some of the achievements of Philip II and Alexander the Great? 7 Greek Columns: Read page 162 and label the Greek columns. Beneath your label, give one word to describe the look of each column. Name Doric Ionic Corinthian Description Greek Culture-Architecture-TheaterOlympics-Gods Quiz Study Guide Architecture: Agora / Parthenon / Corinthian, Doric, and Ionic columns Theater: Comedy / Tragedy / Soliloquy Olympics: Pentathlon / Pancratium People: Philosopher / Pythagoras/Socrates/Alexander the Great Gods: Athena / Apollo / Aphrodite / Ares / Dionysus / Zeus Short Essay(s): 1. Why did ancient Greek actors wear masks? 2. Why did the ancient Greeks build their most important buildings on the Acropolis? 8