File - Kimberly Gaffney
advertisement

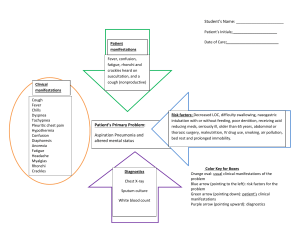
1 CRITICAL THINKING SUMMARY – 3/24/14 Student: Kimberly Gaffney Client Dx: Hepatic encephalopathy Age: 72 Allergies: no known allergies The MEDICAL DIAGNOSIS that brought the client to the hospital is: Hepatic encephalopathy PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of diagnosed disease: (From text) Two major alterations occur with this disease. First hepatic insufficiency because of the inability of the liver to detoxify toxic byproducts of the metabolism. Secondly the Portal –systemic shunting, in which collateral vessels develop as a result of portal hypertension, allows elements of the portal blood to enter systemic circulation (Smeltzer, Bare, Hinkel, & Cheever, 2010). SYMPTOMS typically seen with this diagnosis include (as identified in your text): The signs and symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy asterixis, fetor hepaticus, generalized slowing of ECG, impaired writing and ability to draw figures, minor mental changes and motor disturbances. Other presenting symptoms are confusion, altered mood and sleep pattern, increased deep tendon reflexes, rigidity of extremities. If condition continues to progress it can result in coma (Smeltzer et al., 2010). CLIENT’S SYMPTOMS of the diagnosed disease include: This patient was admitted to the hospital on 3/22/14 with increased abdomen distention, slow speech and walking, difficulty remembering, lethargy, shortness of breath and disorientation. While working with him on 3/24/14, the patient was presenting with jaundice, shortness of breath, increased heart rate, low blood pressure, increased abdomen distention, weakness, lethargy, and an unsteady gait. NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT: Height (actual or estimated): 182.88 cm, 72in Weight (actual or estimated): 108kg, 238.09lbs Estimate Ideal Body Weight (Male: 105lb + 6 lb/inch > 5’. Female: 100lb + 5lb/inch > 5’): 177lb Does this client have characteristics of a well-nourished person? Yes __ No X Explain your answer. The patient has loss total of 15 lbs. in last two months without trying to lose weight. His total protein level was 4.1 and albumin level was 1.46, these are low, which indicates the patient is malnourished. Based on his physical assessment, he was weak in his lower extremities, had moist skin and smooth nails. While caring for this patient he expressed that he would like to eat, this indicated to me that he had a good appetite. Unfortunately he was on a clear liquid diet, but he drank all the ice tea, water, Jell-O and broth he was given. His BMI s 32.3 which indicates he is obese in terms of height to weight ratio. 2 PSYCHOSOCIAL STAGE OF DEVELOPMENT What is the client’s developmental stage? Ego integrity versus despair Has he/she met the necessary accomplishments? Yes X No __ Explain. After meeting the patient for the first time he seemed tired and anxious but friendly. The patient is retired and owns his own home. The ego integrity versus despair stage of psychosocial development requires the older adult to look back on life with pride and no regrets with a positive and enthusiastic attitude (Taylor, Lillis, LeMone & lynn, 2011). When speaking of his family, he was positive, and proud of his children and grandchildren and in what they had accomplished. How is this illness affecting the client’s ability to meet these necessary accomplishments? The patient’s diagnosis is somewhat affecting his ability to meet the necessary accomplishments because he is sick and frequently tired and has been in the hospital for a few days. As a result one can see how these things may affect his ability to meet the necessary accomplishments related to the ego integrity vs. despair stage. However at this point he is remaining optimistic and talks about the past with both family and staff members who enter the room. NURSING DIAGNOSIS/OBJECTIVES/INTERVENTIONS Indicate below the 2 priority nursing diagnoses that are most relevant for your client. #1 NURSING DIAGNOSIS (problem r/t) Chronic pain r/t: liver enlargement DEFINING CHARACTERISTICS (S/S) that support this diagnosis: A patient with chronic pain experiences unpleasant sensory and emotional experiences rising from actual or potential tissue damage (Ladwig & Ackley, 2014). The defining characteristics are patients self –report of 8/10 on a numerical scale and grimacing with movement. OBJECTIVE/CLIENT OUTCOME for this diagnosis: The patient will report being pain free 0/10 using a numerical scale (Ladwig & Ackley, 2014). NURSING INTERVENTIONS that will assist the client to resolve the above identified diagnosis: 1. Assess patient’s pain level, sedation level and respiratory status every four hours (Ladwig & Ackley, 2014). 2. Administer analgesics as prescribed (Ladwig & Ackley, 2014). 3. Encourage the client to plan activities around periods of greatest comfort when possible (Ladwig & Ackley, 2014). #2 NURSING DIAGNOSIS (problem r/t) Fatigue related to cirrhosis and malnutrition 3 DEFINING CHARACTERISTICS (S/S) that support this diagnosis: A patient with fatigue experiences an overwhelming, sustained sense of exhaustion and decreased capacity for physical and mental work at usual level (Ladwig and Ackley, 2014). Respiratory difficulties, disinterest in surroundings, increased drowsiness, increased physical complaints, lethargy, and verbalization of a lack of energy are the defining characteristics associated with fatigue. OBJECTIVE/CLIENT OUTCOME for this diagnosis: The client will be free of fatigue (Ladwig & Ackley, 2011). NURSING INTERVENTIONS that will assist the client to resolve the above identified diagnosis: 1. Evaluate adequacy of nutrition and sleep hygiene: encourage adequate rest, limit naps in afternoon and evening, limit caffeine in afternoon and evening, and use a routine sleep/wake schedule (Ladwig & Ackley, 2014). 2. Collaborate with primary care provider to identify physiological and physiological causes of fatigue: pain, electrolyte imbalance, depression, anemia, medication effects (Ladwig & Ackley, 2014). 3. Encourage client to try complementary and alternative therapy such as guided imagery, massage therapy and acupressure (Ladwig & Ackley, 2014). COMPLICATIONS: If this client’s condition were to worsen, what would be the most likely reason and why? If the client’s condition were to worsen, it would most likely be due bleeding or hemorrhage. With damage done to the liver, the liver cells are not able to use vitamin K to make prothrombin resulting in the gastrointestinal tracts inability to absorb all the vitamin K it is receiving, this results in a decreased production of the clotting factors, with decreased clotting factors the patient is at a high risk of bleeding (Smeltzer et al, 2010). How would you know this is happening? The nurse would know if bleeding was occurring if patient has symptoms of shortness of breath, fatigue, pale mucous membranes, visual bleeding from nose, mouth or wounds, blood was found in urine, sputum or stool, patient had unusual bruising, dizziness or altered level of consciousness and possible if CBC , Hgb, Hct, are decreased. Also if vital signs or diagnostic tests results reflected changes in patient condition (decreased blood pressure increased heart rate and respirations). What will you do if this happens? If this were to happen, the nurse would notify physician, monitor vital signs, if ordered administer vitamin K, hold pressure to site if bleeding is visualized, and administer a blood transfusion. Also monitor the patients’ (CBC, Hgb, Hct) levels for blood loss, effects of mediations administered and an increase of yellowing of the skin. 4 5 PHYSICIAN PRESCRIBED MEDICATIONS AND INTERVENTIONS MEDS/IVs/TX/DIET (Include dose, route, frequency) REASON PRESCRIBED (Drug Classification, What is it treating?) Buspirone 5mg/ 1tab p.o. twice daily Antianxiety agent/ management of anxiety Hydroxyzine 25 mg 1 to 2 capsules Antihistamine -pruritus Ferrous sulfate 325 mg/1 tab p.o. daily Antianemic- GI bleeding and hgb -7.4 Sodium chloride 0.9% at 100ml/hr NURSING IMPLICATIONS FROM TEXT (Checking for adverse reactions, preparation & administration concerns) Dizziness, nervousness, weakness, blurred vision sweating. Drowsiness, ataxia, dry mouth, wheezing, urinary retention, Dizziness, constipation, dark stools, nausea, headache. Administer 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals. Electrolyte replacement- Heart failure, used for electrolyte and pulmonary edema, fluid maintenance. hypernatremia, hypokalemia, hypervolemia- Norco Opioid analgesic –pain (acetaminophen/hydrocodone 10mg/325 1tab p.o.every four hours as needed for pain. Respiratory depression, hypotension, bradycardia, confusion, Piperacillin tazobactam 3.375Gm 50ml IVPB every 6 hours. Seizures, confusion, pseudomemebranous colitis, diarrhea, and pain at IV site. Anti-infective/extended spectrum penicillin- has bacterial infection CLIENT DATA FROM YOUR ASSESSMENT (What data is important to know before & after giving) Limit intake of grape fruit juice it can increase serum levels, assess degree of anxiety before and during therapy. Assess degree of itching and skin involved. Monitor for sedation, or agitation. Assess for constipation and diarrhea, monitor hgb and hct. Monitor I&O, daily weight, edema, lung sounds, hypo and hypernatremia, tachycardia , dry mucous membranes Assess vital signs before and during administration, assess bowel function. Assess pain type, location and intensity Assess for infection (v.s., urine, stool, appearance of wounds). Obtain culture and sensitivity prior to initiating first dose. Observe for anaphylaxis. Monitor WBC, BUN, AST, ALT, electrolytes and 6 Rifaximin 20mg/ml oral suspension 550mg (27.5ml) p.o. twice daily Anti-infective -reduce risk of hepatic encephalopathy symptoms. Dizziness, peripheral edema and pseudomembranous colitis Cholestyramine 4 Gm 1 packet p.o. daily Bile acid sequestrant – decreases pruritus/jaundice Abdominal discomfort, constipation, nausea, tongue irritation and flatulence. Mix with 46oz of water, juice or milk wait 1hour before administration of other medication. Dilaudid 0.5 mg I.V. push every 3 hours for pain Opioid analgesiaabdomen pain Confusion, dizziness, sedation, hypotension, constipation hgb and hct. Assess mental status, monitor bowel function: diarrhea, bloody stool, fever, cramping. Monitor lymphocytes, monocytes and neutrophils. Assess severity of itching and skin integrity. Monitor AST, ALT, phosphorous, chloride, alkaline phosphate, calcium, sodium and potassium and prothrombin time levels. Assess pulse, B.P. and respirations and pain before giving. 7 Analysis of Diagnostic Tests DIRECTIONS: 1. List all diagnostic and laboratory tests pertinent to the patient's medical diagnosis or medical treatments (i.e. medications) and provide the patient values for each test. Explain why they are pertinent for this patient. 2. List any screening diagnostic and laboratory tests that are not within normal limits. Explain why these tests are increased or decreased in relation to your patient's medical condition. Diagnostic/Lab Test sodium Patient Values 134 Analysis of Values Low- hepatic failure potassium 5.4 High- CHF, acute renal injury creatinine 1.91 High-acute renal injury HCO3 19 Low- acute renal injury Hgb 7.4 Low-anemia, cirrhosis, Hct 22.0 Low-anemia, cirrhosis MDRD GFR 35 Low-cirrhosis Glucose level 100 cirrhosis Albumin 1.4 Low- Jaundice, malnutrition, cirrhosis Total protein 4.1 Low- jaundice, cirrhosis malnutrition Bili total 15 High- jaundice, cirrhosis Alk phosphate 156 High- jaundice, cirrhosis and biliary obstruction procalcitonin 8.91 High- Indicative of bacterial infection and risk for sepsis. 8 Urea Nitrogen 29 High- GI bleeding, decreased renal perfusion AST 93 High- jaundice, cirrhosis ALT 37 High-cirrhosis, jaundice Total calcium level 7.6 Low- hypoalbuminemia 9 References Smeltzer, S.C., Bare, B.G., Hinkle, J.L. & Cheever, K.H. (2010). Brunner & Suddarth’s Textbook Medical -Surgical Nursing (12th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Ladwig, G. B. & Ackley, B.J. (2014). Guide to nursing diagnosis (4th ed.). Maryland Heights, MO: Mosby. Taylor, C., Lillis, C., LeMone, P., & Lynn, P. (2011). Fundamentals of Nursing: The Art and Science of Nursing Care (7th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkin.