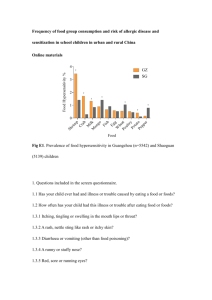
Bean Exercise: Happy Plants Love the Rain…In - pcep
advertisement

Bean Exercise: Happy Plants Love the Rain…In Moderation Grade Level: K-2 CEF reference(s): (K-2Matter.B.2a) Plants and animals (including humans) need water, air, and resources from the land, and they try to live in places that have the things they need. Humans use natural resources for everything they do: for example, they catch fish for food, use soil and water to grow food, and use wood to build shelters, and extract materials such as iron from the Earth to make cooking pans (K-2Life.A.1b) Plants also have different parts (roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits) that help them survive, grow, and produce more plants. Learning Objective(s): Students will be able to name the basic parts of common plants Students will be able to identify the basic needs of plants Students will be able to draw conclusions about how weather affects plant growth Students will be able to state observations and predictions using key vocabulary and compound sentences Students will be able to state the importance of moderation for the survival of living things Activity: Growing Bean Plants Experiment Students work in pairs or triads (threes) to grow bean plants under different conditions. See Growing Bean Plants Experiment handout on page 4. Teachers can ask “Engineering Questions” out loud throughout the exercise to help students think about what is occurring during the experiment. Students can record results, observations about the weather, and predictions in a field journal. See My Bean Plant Journal worksheet on page 9. Suggested Activities Building Background Knowledge Word Wall: Show visual for each key word and post words with visuals on wall. Prediction Practice: Teacher gives each student a sentence frame to state a prediction. Teacher models how to use sentence frame and students vote for the prediction they think is true and fill in their own sentence frame. Whole class sings a song together: Teacher leads a song about plants. Examples below are from http://www.angelfire.com/la/kinderthemes/pfingerplays.html Pacific islands Climate Education Partnership (2012) 1 Do You Know the Parts of Plants? (Tune: Head, Shoulders, Knees, And Toes) Do you know the parts of plants, Parts of plants? Do you know the parts of plants, Parts of plants? All kinds of plants that grow and grow and grow. Do you know the parts of plants, Parts of plants? The roots hold the plant in place, Plant in place. The roots hold the plant in place, Plant in place. The roots store food and water, too. The roots hold the plant in place, Plant in place. The stem move water up the plant, Up the plant. The stem move water up the plant, Up the plant. The stem brings water to the leaves. The stem move water up the plant, Up the plant. The leaves soak up the sun, Soak up the sun. The leaves soak up the sun, Soak up the sun. The sun helps the plant to grow and grow and grow. The leaves soak up the sun, Soak up the sun. Green Plants Need Song (Tune:"Three Blind Mice") Three main things, three main things, Green plants need, green plants need. For plants to grow and plants to thrive, In order to keep green plants alive, What does it take for them to survive? Just three main things. Plants need sun, plants need sun, That's number one, plants need sun. For plants to grow and plants to thrive, In order to keep green plants alive, What does it take for them to survive? Just three main things. Plants need air, plants need air, Be aware, plants need air. For plants to grow and plants to thrive, In order to keep green plants alive, What does it take for them to survive? Just three main things. Plants need water, plants need water, Especially when it's hotter, plants need water. For plants to grow and plants to thrive, In order to keep green plants alive, What does it take for them to survive? Just three main things. The flower grows into a fruit, Into a fruit. The flower grows into a fruit, Into a fruit. Inside the fruit are little tiny seeds. The flower grows into a fruit, Into a fruit. Key Vocabulary and Sentence Frames Key vocabulary: roots, stem, leaf/leaves, grow, water (both a noun and a verb), flood, drought, green, healthy, brown, unhealthy, rain/precipitation, moderation Sentence frames students may use to state observations, results, and predictions: o I think the plant is healthy because the plant is _______. o If plants are given _______water, then they will grow _______. o Today, I observed that the weather is _______. Pacific islands Climate Education Partnership (2012) 2 o I noticed _______. o In a plant’s natural environment, _______. o Compared to yesterday, today is _______. o I predict that the weather tomorrow will be _______. See Teaching Academic Vocabulary online at http://pcep.wikispaces.com/file/view/PCEPlabs_teachingacademicvocab.pdf for more ideas. Formative and Summative Assessment Thumbs up/Thumbs Down to see if students agree with predictions given by teacher during demonstration Teacher checks students’ journal results and predictions for 2-4 weeks Class creates a school bulletin board displaying learning , including predictions and drawings of final results Roll the Ball: Class sits in a circle. Teacher rolls a ball to a student, who then responds. After answering, the student rolls the ball to a classmate. o Students can use sentence frames to answer questions o Teacher has prepared questions about what students observed during the course of the activity and/or what they learned. o Sample Questions: Can you name the different parts of plants? What part of the plant takes in water? What part of the plant takes in energy from the sun? How do we know if a plant is healthy? How do we know if a plant is unhealthy? How does water relate to how a plant will grow? In nature, what process does the watering? What happened when the plants had too much water? What happened when the plants didn’t have enough water? In nature, when would plants receive too much water? In nature, when would plants receive too little water? How are humans affected when plants fail to grow? Extended Activities Students can review weather reports in the newspaper from the previous week and make predictions about how plants will respond to the coming weather. Pacific islands Climate Education Partnership (2012) 3 GROWING BEANS EXPERIMENT Teacher’s Guide Materials 4 CD cases or plastic bags 4 paper towels or newspaper 1 clear cup 1 bag of pinto beans ½ tsp measuring spoon ¼ cup measuring cup Set Up Bean Experiment Label the CD cases: “no rainfall,” “low rainfall,” “medium rainfall,” and “high rainfall.” Fold each paper towel to fit into the CD case. Place one folded paper towel into each CD case. Place four beans into each paper towel. Space the beans approximately one inch apart and one inch from the sides of the CD case. Engineering Questions a. Why are we placing the beans on paper towels? The paper towels absorb the water to keep a moist environment around the beans and keep beans in the same position, similar to soil. b. Why are we spacing the beans? To give the beans enough space to grow without touching each other and the CD case sides Set Up ‘Flooded’ Beans Fill the clear cup with enough water to fully submerge beans and label it “Flood”. Drop four beans into the cup and set aside. The purpose of this set of beans is to show students how an extreme amount of water can damage the plant and stunt its growth. It is expected that there will be no growth in these beans and that the beans will deteriorate. Pacific islands Climate Education Partnership (2012) 4 Water Your Beans Place the clear cup and the CD cases in a sunny place, not in direct sunlight. CD cases should be placed bean side up. Water the beans accordingly for one week: No Water: Do not water. This set of beans is not expected to grow. Its purpose is to show that water is necessary for growth. Low Rainfall: Pour ½ tsp of water onto the middle of the paper towel every other day. The purpose of this set of beans is to show how a low amount of rainfall leads to slow plant growth. Medium Rainfall: Pour ½ tsp of water onto the middle of the paper towel once a day at around the same time of day. With this set of beans, students can compare the amount of growth to that of low and high rainfall bean sets. High Rainfall: Pour ¼ cup of water onto the middle of the paper towel once a day at around the same time of day. The purpose of this set of beans is to show students how high rainfall leads to much faster growth. Close each CD case after watering. Engineering Questions c. What will happen to each set of beans over the week? See above. Older students may emphasize that the difference in growth among the sets of beans is related to the different amounts of water. d. Why do we close the CD case after watering? To keep the water from evaporating e. Why do we pour the water in the middle of the paper towel? To simulate rain; the water should soak and spread through the paper towel. Sample Results (after 1 week) High Rainfall Medium rainfall Low Rainfall Flood Engineering Questions f. Do your beans look similar to the results above? Why or why not? g. How does the amount of rain affect the way plants grow? Rainfall affects plants growth—too much or too little water limits growth. Link experiment to recent drought or rainfall events. Pacific islands Climate Education Partnership (2012) 5 GROWING BEANS EXPERIMENT Student Version Materials 4 CD cases or plastic bags 4 paper towels or newspaper 1 clear cup 1 bag of pinto beans ½ tsp measuring spoon ¼ cup measuring cup Set Up Bean Experiment Label the CD cases: “no rainfall,” “low rainfall,” “medium rainfall,” and “high rainfall.” Fold each paper towel to fit into the CD case. Place one folded paper towel into each CD case. Place four beans into each paper towel. Space the beans approximately one inch apart and one inch from the sides of the CD case. Engineering Questions a. Why are we placing the beans on paper towels? b. Why are we spacing the beans? Set Up ‘Flooded’ Beans Fill the clear cup with enough water to fully submerge beans and label it “Flood”. Drop four beans into the cup and set aside. Pacific islands Climate Education Partnership (2012) 6 Water Your Beans Place the clear cup and the CD cases in a sunny place, not in direct sunlight. CD cases should be placed bean side up. Water the beans accordingly for one week: No Water: Do not water. Low Rainfall: Pour ½ tsp of water onto the middle of the paper towel every other day. Medium Rainfall: Pour ½ tsp of water onto the middle of the paper towel once a day at around the same time of day. High Rainfall: Pour ¼ cup of water onto the middle of the paper towel once a day at around the same time of day. Close each CD case after watering. Engineering Questions c. What will happen to each set of beans over the week? d. Why do we close the CD case after watering? e. Why do we pour the water in the middle of the paper towel? Sample Results (after 1 week) Flood High Rainfall Medium rainfall Low Rainfall Engineering Questions f. Do your beans look similar to the results above? Why or why not? g. How does the amount of rain affect the way plants grow? Pacific islands Climate Education Partnership (2012) 7 My Bean Plant Journal GROWING BEANS EXPERIMENT Engineering Questions a. Why are we placing the beans on paper towels? b. Why are we spacing the beans? c. What will happen to each set of beans over the week? d. Why do we close the CD case after watering? e. Why do we pour the water in the middle of the paper towel? f. Do your beans look similar to the results above? Why or why not? g. How does the amount of rain affect the way plants grow? Pacific islands Climate Education Partnership (2012) 8 My Bean Plant Journal Name: ____________________________________ Today is ___________________________________ How does rainfall affect how plants grow? High Rainfall Medium Rainfall Flood Low Rainfall No Water Observations: Record what you actually see and do during the investigation Today, I observed that ___________________. I noticed that _____________________. Compared to yesterday, today ___________________________. Predictions: State what you think will happen and give a reason or explanation. I predict that _________ set of beans will ___________. This is because ____________. I think _______________ because ______________________. If ____________, then ___________________. Pacific islands Climate Education Partnership (2012) 9