How are Floods Caused
advertisement

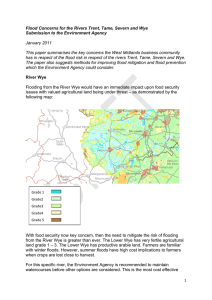
How are Floods Caused? Although Australia is the second driest continent (after Antarctica), flooding is a major problem with a potential to produce a disaster of national importance. A flood is caused when water inundates land which is normally dry – throughout this module, you will see a number of different flood scenes. The experience for people caught in a flood may vary according to a number of factors: the time of year the flood comes the time of day when the worst flooding occurs how quickly the flood arrives and how quickly the water rises how long the flood lasts the depth of water and speed at which it flows how well prepared people are for a flood the amount of outside help that is available for rescue and relief operations Floods can occur as a result of a variety of causes. These include: dam bursts coastal flooding by tidal waves, tsunamis and storm surges very heavy thunderstorm activity for a short period of time rapid snowmelt However, the most common cause of flooding is an excessive amount of rain in the area that supplies water to a river (called the catchment area or drainage basin of that river). This causes the river to overflow its banks further downstream. In order to better understand how this type of flooding occurs we need to consider the river and the area through which it flows as part of a system called the water cycle. Precipitation (rain, snow, hail and sleet) forms the input into the system. When it falls to the land in the catchment area of a river a number of things may happen: Water may return to the atmosphere through evaporation from the ground surface and through transpiration from plants, which together form an output from the system called evapotranspiration. If water gathers on the ground infiltration may occur. This is when the soil soaks up water. The speed of infiltration is called the infiltration rate. Once in the soil the water moves quite slowly, either near the surface as throughflow or much deeper as groundwater flow. The upper surface of the groundwater zone is the watertable. Any water that does not infiltrate moves rapidly downhill on the ground surface and is called runoff. Too much runoff is the most common cause of rivers overflowing their banks and causing floods. TASK 5.1 (Extension) Flood Simulation: visit the Virtual River website linked below and attempt to complete the two river flooding simulation exercises. They require considerable time and patience but are most worthwhile. If you need to pause halfway through the exercise you can bookmark the page you are up to and return to it later. Geology Labs Online Virtual River Simulations http://64.239.9.13/VirtualRiver/ If you persevere and collect your certificate, forward a copy to your teacher for bonus recognition.