oligo - IUBio Archive for Biology
advertisement

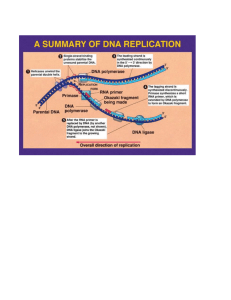
OligoMutantMaker (version 1.0) Copyright 1987 Kevin Beadles, David Canter, Arnold Berk ("readme.doc" added 8/26/88, 2/24/89 by Spencer Yeh) INTRODUCTION OligoMutantMaker simplifies the designing and screening of oligonucleotide-directed single amino acid substitution experiments by searching for nucleotide sequences which introduce a restriction endonuclease recognition sequence into the codon substitution site of the mutant. The program utilizes the redundancy of the genetic code to generate all possible nucleotide sequences for a given amino acid substitution (including nucleotide sequences in which silent mutations are introduced into the 5' and/or 3' codons immediately adjacent to the substitution site) and determines whether any restriction endonuclease recognition sequences are present. Any nucleotide sequence containing a restriction site is displayed/printed along with relevant information about the site such as its restriction enzyme(s), the random frequency of the enzyme's recognition sequence(s), the prototype of the enzyme, isoschizomers of the enzyme, and the unit cost of the enzyme from various biochemical suppliers. CONTACT ADDRESS For questions about the program or suggestions for future improvements please contact: Kevin Beadles 1044 1/2 Shrader St. San Francisco, CA 94117 tel.: (415) 759-0148 (Kevin will call you back collect if he must return your call.) SYSTEMS SUPPORTED An IBM compatible computer running MS-DOS is needed. AVAILABILITY OligoMutantMaker is available from the BIONET Lending Library. Please send a stamped, self-addressed return envelope along with a formatted diskette (specify capacity) with your request to: BIONET Administrator BIONET/ IntelliGenetics 700 East El Camino Real, Suite 300 Mountain View, CA 94040 tel.: (415) 962-7337 PROGRAM FILES before de-ARCing README.DOC BWMUTANT.COM CMUTANT.COM CUTTERS.DAT CODONID.DAT [ENZYME.TXT] (BIONET diskette version) This documentation file Executable file for monochrome monitors Executable file for color monitors Binary database of enzyme cleavage and availability data Standard genetic code This file is created everytime the program is run. It contains a copy of the results of the last analysis. PROGRAM FILES before de-ARCing (BIONET downloadable version) README.DOC This documentation file. OLIGO.UUE Archived and uuencoded file for both monochrome and color executable versions, and associated data files. (234 Kb). PROGRAM FILES after de-ARCing (Approx. 350 Kb total) README.DOC BWMUTANT.COM CMUTANT.COM CUTTERS.DAT CODONID.DAT [ENZYME.TXT] This documentation file Executable file for monochrome monitors Executable file for color monitors Binary database of enzyme cleavage and availability data Standard genetic code This file is created everytime the program is run. It contains a copy of the results of the last analysis. DOCUMENTATION The program is internally documented with help messages. STARTING THE PROGRAM On the BIONET diskette version, the program files are not compressed, whereas the ".uue" files in the downloadable version require both the UUDECODE program and an "ARC"-compatible dearchiving program such as PKUNPAK to restore the executable file. ".UUE" files: First decode the ".uue" file: >UUDECODE oligo.uue Then dearchive the resulting ".arc" file to an appropriate directory by using PKUNPAK (or compatible program): >PKUNPAK oligo.arc c:\oligo Once installed, CD to the appropriate directory and then start the program by typing its name at the MS-DOS prompt: or >BWMUTANT (for monochrome monitors) >CMUTANT (for color monitors) It is recommended that the user copy the program files to hard disk so that more disk space will be available to the program. SAMPLE PROGRAM OUTPUT The following is abreviated output from a sample run to give an idea of how the program works: OligoMutantMaker requires the entry of nine codons (27 nucleotides) from the "sense"--or mRNA-homologous--strand of DNA. The codons are are numbered "-4" through "+4" (upstream-to-downstream or 5'-to-3') where codon #0 is the codon to be substituted. The codons must be entered individually using standard one letter nucleotide abbreviations (A, C, G, T or U) as they are requested. (The user enters the 27 nucleotide fragment at this point) Nucleotide # 1 4 7 Nucleotide Sqn GGG GGG GGG GGG GGG GGG GGG GGG GGG Codon # -4 Amino Acid Sqn GLY GLY GLY GLY GLY GLY GLY GLY GLY -3 -2 10 -1 13 0 16 1 19 2 22 3 25 4 (Once the fragment is entered, the user picks an amino acid replacement for the central codon) 1) ALA 9) HIS 17) THR 2) ARG 10) ILE 18) TRP 3) ASN 11) LEU 19) TYR 4) ASP 12) LYS 20) VAL 5) CYS 13) MET 21) STP 6) GLN 14) PHE 7) GLU 15) PRO 8) GLY 16) SER Please enter the number of the amino acid that you want to insert at codon #0: 14 <D>isplay <P>rint <R>estart (The results are then displayed. Lowercase letters indicate altered base pairs. In the description of the recognition sequence, the "/"'s indicate where the enzyme cuts on each of the strands.) GGG GGG GGG GGa ttc GGG GGG GGG GGG -- the recognition sequence is GANTC -- --Hinf I 5' G/ANT C 3' C TNA/G random site frequency: 1/256 isoschizomers: FnuA I, Hha II, Nca I, Nov II, NsiH I, Hine I BMB: 4.4c/u 1000u $44 BRL: 4c/u 1000u $40 NEB: 1.1c/u 5000u $55 USBC: 3.5c/u 1000u $35 <D>isplay <P>rint <R>estart ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ABOUT THE PROGRAM Restriction Site Location: OligoMutantMaker searches for restriction sequences which have at least one nucleotide in codon #0 (i.e. the codon to be substituted). Since the longest recognition sequence (GGCCNNNNNGGCC--Sfl I) spans thirteen nucleotides, it is necessary to enter 27 nucleotides (twelve nucleotides on either side of the three nucleotides which comprise codon #0) into the program in order for it to function. "Silent" Mutations: The program utilizes the redundancy of the genetic code to generate all possible nucleotide sequences for the given amino acid substitution in codon #0 (i.e. the codon to be substituted). In addition to searching for restriction sites which match these nucleotides sequences, the program also examines those nucleotide sequences in which "silent" mutations have been introduced into codon #-1 and codon #+1 (i.e. the codons immediately upstream--or 5'--and downstream--or 3'--from codon #0, respectively) and determines whether any additional restriction sites are created. Only those "silent" mutations which can be created by a single substitution in the nucleotide closest to codon #0 (i.e. the third--or "wobble"-nucleotide of codon #-1 and the first nucleotide of codon #+1) are examined. Therefore, only five nucleotides (centered upon the middle nucleotide of codon #0) are subject to substitution. Abbreviations used in OligoMutantMaker: standard three letter amino acid abbreviations STP: stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) standard one letter nucleotide abbreviations N: any nucleotide m: methylated nucleotide /: cleavage site standard restriction endonuclease abbreviations BMB: Boehringer Mannheim Biochemicals BRL: Bethesda Research Laboratories NEB: New England Biolabs USBC: United States Biochemical Corperation u: unit(s) c/u: cents/unit Miscellaneous Notes: OligoMutantMaker recognizes 164 different restriction sites which are are cleaved by 126 different restriction enzymes. Price comparisons are based upon the smallest low concentration order available from each supplier. OligoMutantMaker does not search for cleavage specificities generated by methylating DNA with a selected restriction endonuclease (see NEB 1986/87 Catalog p32 & p123 for further details). OligoMutantMaker does not note enzyme specificities resulting from star activity (NEB 1986/87 Catalog p86 & p121). Bibliography: Boehringer Mannheim Biochemicals, 1987/88 (Catalog) Bethesda Research Laboratories, Catalog & Reference Guide (1985) New England Biolabs, Catalog 1986/87 United States Biochemical Corporation, Enzymes & Reagents for Molecular Biology 1987