Chapter 21: Financial Statement Analysis
Assignment 21-2
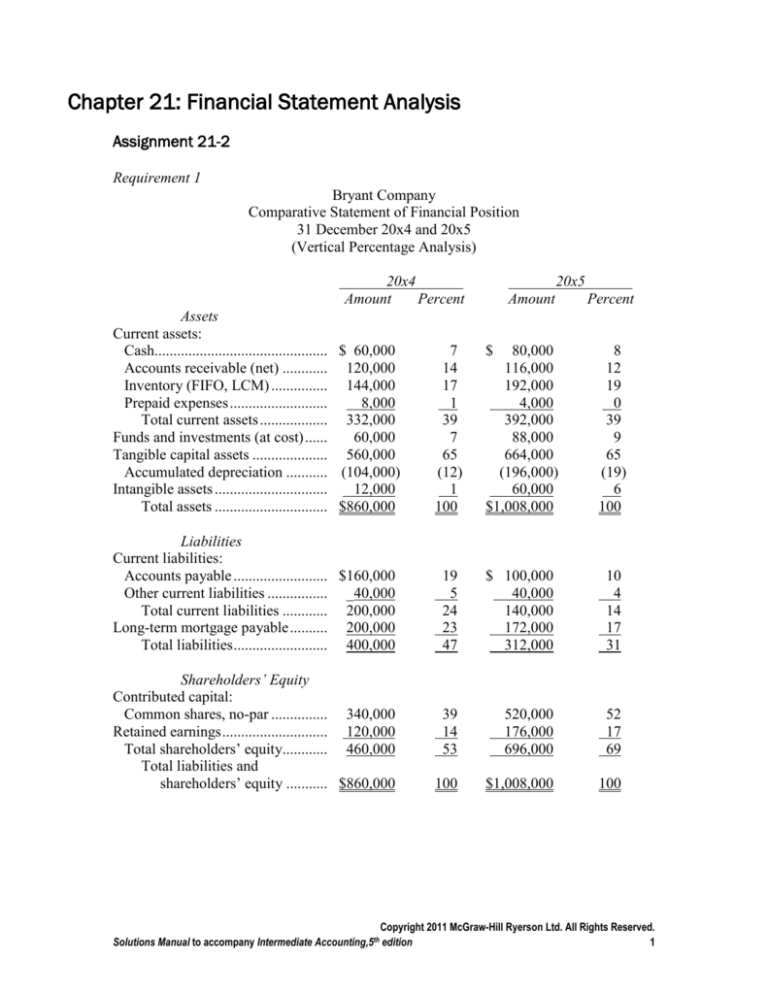
Requirement 1
Bryant Company
Comparative Statement of Financial Position
31 December 20x4 and 20x5
(Vertical Percentage Analysis)
20x4
Amount
Percent
Assets
Current assets:
Cash.............................................. $ 60,000
Accounts receivable (net) ............ 120,000
Inventory (FIFO, LCM) ............... 144,000
Prepaid expenses ..........................
8,000
Total current assets .................. 332,000
Funds and investments (at cost) ......
60,000
Tangible capital assets .................... 560,000
Accumulated depreciation ........... (104,000)
Intangible assets ..............................
12,000
Total assets .............................. $860,000
7
14
17
1
39
7
65
(12)
1
100
Liabilities
Current liabilities:
Accounts payable ......................... $160,000
Other current liabilities ................ _40,000
Total current liabilities ............ 200,000
Long-term mortgage payable .......... 200,000
Total liabilities ......................... 400,000
Shareholders’ Equity
Contributed capital:
Common shares, no-par ............... 340,000
Retained earnings ............................ 120,000
Total shareholders’ equity............ 460,000
Total liabilities and
shareholders’ equity ........... $860,000
20x5
Amount
$
Percent
80,000
116,000
192,000
4,000
392,000
88,000
664,000
(196,000)
60,000
$1,008,000
8
12
19
0
39
9
65
(19)
6
100
19
5
24
23
47
$ 100,000
40,000
140,000
172,000
312,000
10
4
14
17
31
39
14
53
520,000
176,000
696,000
52
17
69
100
$1,008,000
100
Copyright 2011 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Solutions Manual to accompany Intermediate Accounting,5th edition
1
Requirement 2
Bryant Company
Comparative Statement of Financial Position
31 December 20x4 and 20x5
(Horizontal Analysis)
20x4
Assets
Current assets:
Cash..............................................
Accounts receivable (net) ............
Inventory (FIFO, LCM) ...............
Prepaid expenses ..........................
Funds and investments (at cost) ......
Tangible capital assets ....................
Accumulated depreciation ...........
Intangible assets ..............................
Total assets .............................
Liabilities
Current liabilities
Accounts payable .........................
Other current liabilities ................
Long-term mortgage payable ..........
Total liabilities .......................
Shareholders’ Equity
Contributed capital:
Common shares, no-par ...............
Retained earnings ............................
Total shareholders’ equity............
Total liabilities and
shareholders’ equity ...............
20x5
100%
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
133
97
133
50
147
119
188
500
117
100
100
100
100
63
100
86
78
100
100
100
153
147
151
100
117
Copyright 2011 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Solutions Manual to accompany Intermediate Accounting,5th edition
2
Copyright 2011 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Solutions Manual to accompany Intermediate Accounting,5th edition
3
Assignment 21-10
(a) Ratios that measure profitability
Return on long-term capital
(after tax)
Income + Interest exp. on
long-term capital, net of tax
Average LT Debt + Equity
$28 + ($4(1–.40))
$167
= .18
(or 18%)
Return on long-term capital
investment, excluding current
liabilities.
Return on assets (after tax)
Income +
Interest exp.,net of tax
Average total assets
Income – Pref dividends
Average common owners’
equity
$28 + ($4(1–.40))
$185
= .16
(or 16%)
Rate of return earned on all
assets employed
$28
$124
= .23
(or 23%)
Rate of return earned on assets
provided by owners
$28 + $4 + $20
$157
= .33
(or 33%)
Profit margin earned on each
dollar of sales
$28 + $4 + $20 + $8 = .28
(($184 + $29) +
(or 28%)
($186 + $37)) ÷ 2)
Return on invested capital
exclusive of return of capital
(depreciation)
Return on common owners’
equity
Operating margin (before tax)
Return on gross assets
(before tax)
Income + interest + income tax
Total revenue
EBIT + Depreciation
Average total assets (net) +
Average accumulated
depreciation
Solutions Manual to accompany Intermediate Accounting,5th edition
Copyright 2011 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
4
(b) Ratios that measure efficiency:
1.
Asset turnover
Total revenue
Total assets (average)
$157
$185
= .85 times
Efficiency of asset utilization
2.
Accounts receivable
turnover
Credit sales
Average trade receivables
$51
$21
= 2.4 times
Efficiency of collection of
accounts receivable
3.
Average collection period
of accounts receivable
365 (days)
Receivable turnover
365
2.4
= 152 days
Average number of days to
collect receivables
4.
Inventory turnover
Cost of goods sold
Average inventory
$70
$34
= 2.1 times
Number of times average
inventory was sold
Solutions Manual to accompany Intermediate Accounting,5th edition
Copyright 2011 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
5
(c) Ratios that measure solvency:
1.
Debt:equity
Total liabilities
Total owners’ equity
2.
Debt: total capitalization
3.
Debt: capital employed
4.
Debt: total assets
5.
Times-interest-earned
Income + interest + tax
Interest expense
$28 + $20 + $4
$4
= 13
Income available to cover
interest
6.
Times-debt-service-earned
Cash flow from
ops + interest + tax
Interest + projected debt
service costs ÷ (1 – t)
$22 + $20 + $4
$4
= 11.5
Ability to co. to service debt
charges
Long-term debt
Long-term debt + owners’
equity
Long-term debt + current liabilities
Long-term debt + current liabilities –
(liquid) current assets + equity
Total liabilities
Total assets
Solutions Manual to accompany Intermediate Accounting,5th edition
$57
$129
= .44
(or 44%)
Compares resources provided
by creditors versus owners
$45
$45 + $129
= .26
(or 26%)
Proportion of long-term capital
financed by debt
$45 + $12
$45 + $12 –
($20 + $4 + $19)
+ $129
= .40
(or 40%)
Debt burden with liquid current
assets netted out.
$57
$186
= .31
(or 31%)
Proportion of resources
provided by creditors
Copyright 2011 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
6
(d) Ratios that measure liquidity:
1.
Current ratio
2.
Quick ratio
3.
Defensive interval
Current assets
Current liabilities
$83
$12
= 6.9
Ability to pay liabilities with
current assets
Monetary current assets
Monetary current liabilities
$43
$12
= 3.6
Ability to pay liabilities with
liquid current assets
Monetary current assets *
Projected daily operating
expenditures
$43 = 1,427 days
11÷365
Average number of days the
company can operate with the
currently available liquid assets
* Interest + administrative expense – depreciation
Solutions Manual to accompany Intermediate Accounting,5th edition
Copyright 2011 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
7
Assignment 21-18
Requirement 1 (EPS calculations in thousands)
a. Basic EPS: ($898 – $401) ÷ [(380 × 1/12) + (420 × 11/12)] = $2.06
1
Preferred shares are cumulative
b. Diluted EPS: [$898 + $98(1–.30)] ÷ [417* + 401 + 502 + $403] = $1.81
* From basic calculation
Dilution tests:
1
Pref. shares $40/40=$1; dilutive
2
$98(1–.30) = $68.60; dilutive
3
Options: 40K shares issued and (40 × $16) ÷ $20 = 32 retired
c. Debt: equity: ($2,190 + $833 + $619) ÷ ($500 + $166 + $2,150 + $2,461) = 0.69
Note: deferred income tax might be classified differently: assumptions must be stated!
d. Inventory turnover : $7,620 ÷ [($2,575 + $2,110) ÷ 2] = 3.25
e. Quick: ($1,720 + $1,150 + $450) ÷ $2,190 = 1.52
f. Return on assets: (after tax) [$898 + $98(1–.30)] ÷ [($8,919 + $7,401)/2] = 11.8%
g. Return on common shareholders’ equity: ($898 – $401) ÷ $4,1802 = 20.5%
1
2
Preferred shares are cumulative.
[($2,150 + $2,461 + $166) + ($1,700 + $1,716 + $166)] ÷ 2 = $4,180
h. Accounts receivable turnover: $10,450 ÷ [($1,150 + $1,170) ÷ 2] = 9
i. Asset turnover: $10,450 ÷ [($8,919 + $7,401) ÷ 2] = 1.28
j. Return on long-term capital, after tax:
[$898 + $98(1–.30)] ÷ {[($8,919 – $2,190) + ($7,401 – $1,900)] ÷ 2} = 15.8%
k. Operating margin: ($898 + $98 + $385) ÷ $10,450 = 13.2%
Copyright 2011 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Solutions Manual to accompany Intermediate Accounting, 5th edition
8






