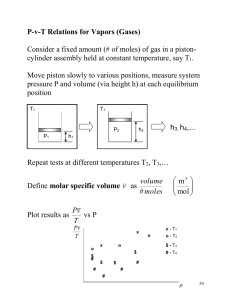
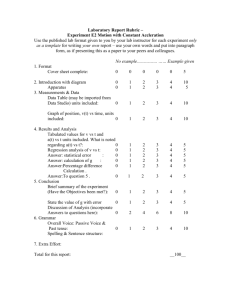
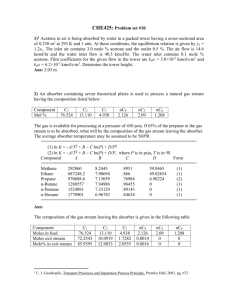
Seminar 9: Batch rectification
advertisement
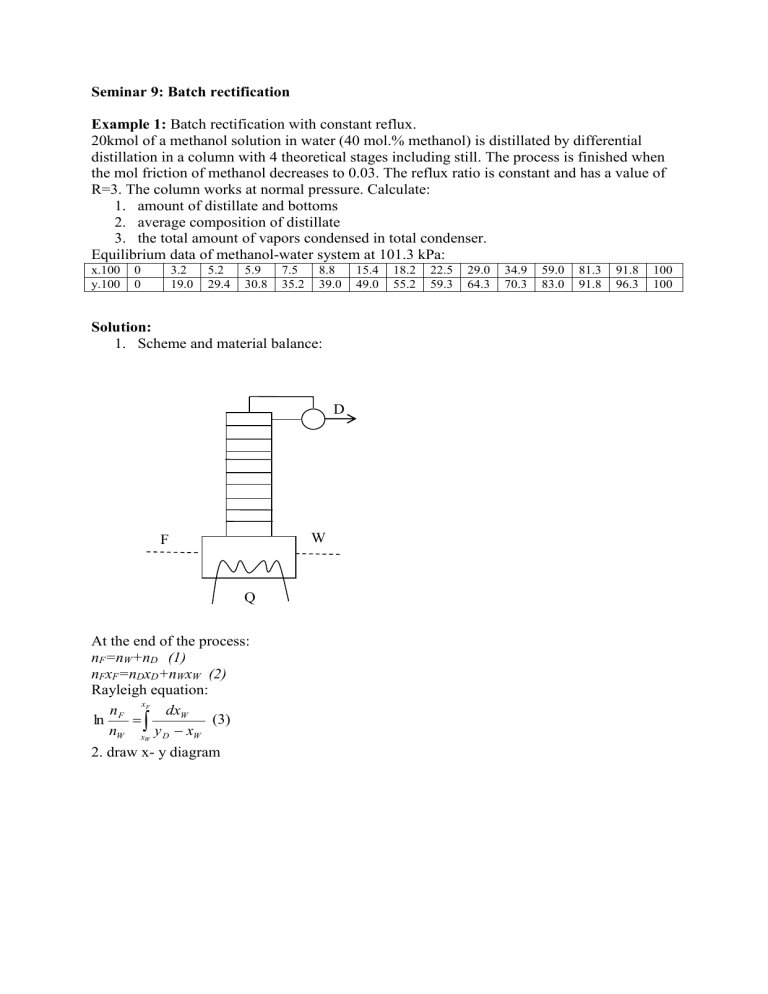
Seminar 9: Batch rectification Example 1: Batch rectification with constant reflux. 20kmol of a methanol solution in water (40 mol.% methanol) is distillated by differential distillation in a column with 4 theoretical stages including still. The process is finished when the mol friction of methanol decreases to 0.03. The reflux ratio is constant and has a value of R=3. The column works at normal pressure. Calculate: 1. amount of distillate and bottoms 2. average composition of distillate 3. the total amount of vapors condensed in total condenser. Equilibrium data of methanol-water system at 101.3 kPa: x.100 y.100 0 0 3.2 19.0 5.2 29.4 5.9 30.8 7.5 35.2 8.8 39.0 Solution: 1. Scheme and material balance: D W F Q At the end of the process: nF=nW+nD (1) nFxF=nDxD+nWxW (2) Rayleigh equation: x n F F dxW (3) ln nW xW y D xW 2. draw x- y diagram 15.4 49.0 18.2 55.2 22.5 59.3 29.0 64.3 34.9 70.3 59.0 83.0 81.3 91.8 91.8 96.3 100 100 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 2. Choose different composition of distillate 3. Calculate xD/R+1 for each xD 4. Draw operating line than 4 steps between the equilibrium curve and operating line starting from xD 5. Take of the corresponding xw 100 95 90 85 80 75 70 65 60 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 Example for xD=0.90 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 xD xD/R+1 Received xW 1/xD-xW 0.6 0.15 0.03 0.75 0.1875 0.036 0.80 0.2 0.045 0.90 0.225 0.1 0.92 0.230 0.140 0.94 0.235 0.230 0.96 0.240 0.400 1.75 1.4 1.33 1.25 1.28 1.408 1.79 6. Calculate the right side of equation 3 using a numerical or graphical method. 2 1.8 1.6 1/xD-xW 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 J=0.536 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 xW For example using trapezium rule xF f ( x) i 1 f ( x) i dxW xi 1 xi =0.563 x y D xW = i 2 W 7. calculation of nW, nD, xD, and nV n ln F 0.563 nW nF 1.702 nW 11.75kmol nW n D n F nW 8.25kmol n F x F nW xW 0.927 nD nV =nD(R+1) = 33 kmol xD 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 Example 2: Batch rectification with constant distillate composition A mixture of benzene and toluene in an amount of 1200 kg and mass friction of benzene 0.317 is distillated by differential rectification into a distillate with 93 wt% of benzene (During the process the distillate composition is constant). The rectification is finished when the friction of benzene in the reboiler decreases under 3.4 wt.%. At this composition of the bottoms the R/Rmin =2. and average efficiency of the column is 70 %. The pressure is 101.3 kPa. Calculate: 1. The amounts of distillate and bottom 2. The Number of real stages in the column 3. Cooling water requirement in total condenser, if its temperature is changed by 38 oC. 4. Requirement of vapor with a pressure of 0.2 Mpa. Equilibrium data: x. y. t/oC 0 0 110.6 0.1 0.208 106.1 0.2 0.372 102.2 0.3 0.507 98.6 0.397 0.618 95.2 Heats of evaporation of pure components: t/oC 20 60 ΔvhB [kJ/kg] 435.3 408.1 ΔvhT [kJ/kg] 407.3 388.5 0.489 0.710 92.1 0.592 0.789 89.4 0.7 0.853 86.8 100 378.8 368.4 Solution: Scheme and material balance: D W F Q At the end of the process: mF=mW+mD mFwF=mDwD+mWwW m ( w wW ) mD F F 379kg wD wW mW mF mD 821kg Conversion of mass basis parameters to mol basis parameters: 0.803 0.914 84.4 0.903 0.957 82.3 0.95 0.979 81.2 140 345.8 343.7 1 1 80.2 x FA wFA MA 0.354 , by the same way xDA= 0.940, and xWA=0.04 wFA wFB MA MB nD mD mD 4.80kmol M D M A xD A M B xD B M A 78kg / kmol M B 92kg / kmol nF mF mF 13.79kmol M F M A xF A M B xF B nW nF nD 8.99kmol Calculation of Rmin: - Draw x-y diagram - Draw the operating line for Rmin and xD at the end of the process 1 0.95 0.9 0.85 0.8 0.75 0.7 0.65 0.6 y 0.55 0.5 0.45 0.4 0.35 0.3 0.25 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 x From the picture above xD Rmin 1 0.05 0.55 0.6 0.65 0.7 0.75 0.8 0.85 0.9 0.95 1 xD 1 17.8 0.05 Calculation of R: R 2.Rmin 35.6 Rmin xD 0.026 R 1 Draw the operating line for R and xD at the end of the process Draw steps between operating line and equilibrium curve. The operating line section on axis y is 1 0.95 0.9 0.85 0.8 0.75 0.7 0.65 0.6 y 0.55 0.5 0.45 0.4 0.35 0.3 0.25 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 0.55 0.6 x The number of steps=7.8 NTS=7.8-1=6.8 Number of real stages NTS NRS 10 Calculation of total amount of vapor produced in the still: xF R 1 dx (1) nV n F x D x F n 1 2 xw x D x n 1 Calculation steps: x 1. choose a number of R , D , respectively. R 1 xD 2. Calculate , R respectively. R 1 0.65 0.7 0.75 0.8 0.85 0.9 0.95 1 3. For each R, draw the calculated number of steps between the equilibrium curve and operating line (in our case it is 8 steps) and determine xn+1 R 1 , for each R 4. Calculate the under integral function xD xn1 2 5. Using numerical integration (for example trapezium method ) calculate the integral xF R 1 x xD xn1 2 dxn1 w 6. calculate nV in equation (1) 1 0.026 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.3 2 xD R 1 R 35.6 8.4 5.25 3.69 2.13 3 xn+1 0.04 0.105 0.158 0.212 0.331 45.2 13.5 10.2 8.85 8.44 R 1 4 xD xn1 2 50 45 R+1/(xD-xn+1) 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 xn+1 xF 5. J= xw R 1 xD xn1 2 dxn 1 = 3.82 xF 6. nV n F x D x F xw R 1 x D xn1 2 dxn1 = 30.87 kmol. Calculation of cooling water requirement: 0.25 0.3 0.35 Assuming only the condensation of vapor in condenser and negligible heat losses the condenser heat duty can be calculated by: Qc nV v hD The distillate temperature can be obtained from the t-x,y diagram tD=81.5 oC. Graf The condensation heat of individual components at this temperature are: v h A =392.35 kJ/kg =30 600 kJ/ kmol v h B =377.7 kJ/kg=34750 kJ/kmol v hD v h A x A v hB x B =30850 kJ/kmol Qc nV v hD =952308 kJ=952.3 MJ cooling water requirement mwater: Qc m water =5995.4 kg. t water c p water Steam requirement calculation: Assuming only the condensation of steam in reboiler and negligible heat losses, the heat duty of reboiler can be calculated by: QW nV v hW Assuming that nv is constant and perfect thermal insulation: Qw=Qc Than for steam requirement we can write: Qc 0.2 Mpa =432.44 kg., v hsteam =2202.2 kJ/kg. msteam v hsteam