unused - Strive Studios
advertisement

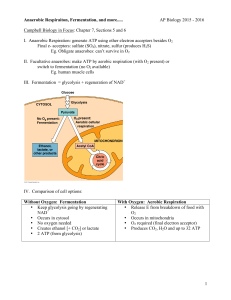
Chapter 8 Student: _________________________________________________________ 1. Some bacteria are strict aerobes and others are strict anaerobes. Some bacteria, however, are facultative anaerobes and can live with or without oxygen. If given the choice of using oxygen or not, which should a facultative anaerobe perform? A. Use oxygen since aerobic metabolism provides more ATP per molecule of carbohydrate broken down than anaerobic metabolism. B. Not use oxygen since it is a facultative anaerobe, it doesn't tolerate oxygen well. C. Use oxygen because aerobic metabolism is easier. D. It doesn't matter; both process will produce the same results. 2. Which of the following molecules can enter the citric acid cycle? A. proteins B. amino acids C. fatty acids D. pyruvate E. all of the choices are correct 3. Which of the following molecules is NOT oxidized during the citric acid cycle? A. NADH B. CO2 C. FADH2 D. none of these are oxidized during the citric acid cycle 4. Which of these processes occurs in the cytosol? A. the citric acid cycle B. glycolysis C. the electron transport system D. the transition reaction 6. The prepartory reaction breaks A. glucose into pyruvates. B. pyruvates into glucose. C. pyruvates into acetyl-CoA and carbon dioxide. D. pyruvates into acetyl-CoA and water. E. acetyl CoA into pyruvates and carbon dioxide. 8. Cellular respiration yields about ____ of the energy of glucose in ATP molecules. A. 2% B. 15% C. 28% D. 39% 9. The process based on the Greek root words for "sugar" and "lysis" is A. metabolism. B. glycolysis. C. phosphorylation. D. fermentation. E. chemiosmosis. 10. The first process in breaking down glucose is A. the citric acid cycle. B. glycolysis. C. the electron transport system. D. fermentation. E. the preparatory reaction. 11. Which process produces both NADH and FADH2? A. the citric acid cycle B. glycolysis C. the electron transport system D. fermentation E. the preparatory reaction 12. Which process produces alcohol or lactate? A. the citric acid cycle B. glycolysis C. the electron transport system D. fermentation E. the preparatory reaction 13. Which process reduces molecular oxygen to water? A. the citric acid cycle B. glycolysis C. the electron transport system D. fermentation E. the preparatory reaction 14. Which process involves chemiosmotic phosphorylation? A. the citric acid cycle B. glycolysis C. the electron transport system D. fermentation E. the preparatory reaction 15. Which connects glycolysis with the final stages of the aerobic pathways? A. the citric acid cycle B. glycolysis C. the electron transport system D. fermentation E. the preparatory reaction 16. Some desert beetles can live out their life without ever drinking liquid water. They survive on "metabolic water," which A. was produced as water in the organisms they eat. B. is absorbed from the air along with respiratory oxygen. C. is a breakdown product of pyruvate, along with carbon dioxide inside the mitochondria. D. is a breakdown product from glycolysis in the cytoplasm. E. is an original storehouse of water that is never allowed to pass out the cell membrane. 17. The large number of ATPs produced are A. embedded in the cristae membranes and diffuse both directions. B. inside the mitochondria matrix and diffuse out through the membrane. C. inside the mitochondria matrix and leave through a channel protein. D. outside the mitochondria and diffuse in through the membrane. E. outside the mitochondria and enter through a channel protein. 18. The enzymes of the electron transport chain are bound to the surface of the cristae. The cristae are folded inward in order to A. decrease the intermembrane space. B. increase diffusion surface for glycolysis. C. separate the products from the substrate in the citric acid cycle. D. form battery-like "cells" for the electron transport chain. E. reduce the distance the FADH2 and NADH has to travel, and place the products of one reaction near the enzymes for the next reaction. 19. Compared with other cell components (organelles, cell membrane or nucleus), the mitochondria would be the only fraction that would A. form an electrochemical gradient across a membrane. B. use significant amounts of oxygen. C. use a chemiosmotic complex to produce ATP. D. produce ATP via glycolysis. E. release protons (H+). 20. One turn of the citric acid cycle produces A. 2 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 ATP. B. 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 1 ATP. C. 1 NADH, 3 FADH2, 2 ATP. D. 3 NADH, 2 FADH2, 1 ATP. E. 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 2 ATP. 21. Acetyl-CoA is produced from A. pyruvate and a coenzyme. B. citric acid and a coenzyme. C. ATP and pyruvate. D. CO2 and pyruvate. E. citric acid and CO2. 22. The carbon dioxide we exhale is produced in A. glycolysis. B. the electron transport system. C. lactate fermentation. D. the citric acid cycle. 23. The primary energy carrier between the citric acid cycle and the electron transport system is A. NADH. B. ADP. C. FADH2. D. H2O. E. CO2. 24. About _____ of the energy in the glucose molecule is captured in ATP through the reactions of cellular respiration. A. 12% B. 26% C. 39% D. 57% E. 84% 25. Which process must occur before fermentation? A. the citric acid cycle B. glycolysis C. the electron transport system D. fermentation E. the preparatory reaction 26. Why would an organism utilize fermentation if it was wasteful of the energy in food molecules and posed the threat of killing itself with high levels of toxic alcohol? A. The organism can survive short spells of anaerobic conditions and maintain growth and reproduction. B. If glucose levels are not high, there may be time to disperse the alcohol "waste." C. Fermentation can provide a rapid burst of ATP since it does not have to go through the full breakdown cycle. D. All of the choices are advantages. E. None of the choices is an advantage; anaerobes only survive where aerobes cannot. 27. The critical factor driving yeasts to use fermentation to metabolize sugar is A. inability to carry on glycolysis. B. lack of oxygen. C. lack of any enzymes. D. that yeast is intolerant to alcohol. E. that yeasts can secure 38 ATP molecules from fermentation. 28. Which of these pairs of processes are anaerobic? A. fermentation and glycolysis B. fermentation and the citric acid cycle C. glycolysis and the citric acid cycle D. the citric acid cycle and the electron transport system E. glycolysis and the electron transport system 29. The energy stored in 36 ATP molecules produced by aerobic respiration is 39 percent of the energy available in a six-carbon glucose and the other 61% of the glucose bond energy is lost. The respiration of an 18carbon fatty acid produces 216 ATP. We can expect that A. the degradation of a fatty acid is totally unrelated to the citric acid cycle. B. six times as much energy was stored in this molecule but also a similar proportion is lost. C. because the molecules are so large, fats are an inefficient form of stored energy. D. this respiration pathway must occur in some cell organelle besides the mitochondrion. 30. Degradative reactions A. cause death. B. can drive anabolism. C. tend to be endergonic. D. include the buildup of products such as complex proteins and nucleic acids. E. All of the choices are true. 31. For fatty acids to be able to enter the pathways of cellular respiration, they must be A. deaminated. B. combined with glycerol. C. combined with ATP. D. broken into acetyl groups. E. be converted into five-carbon sugars. 32. Adult humans cannot synthesize _____ out of _____ amino acids. A. eleven, twenty B. nine, eleven C. nine, twenty D. any, twenty E. half, all 33. The amino acids we cannot synthesize are called _____ because we _____ . A. unnecessary, therefore do not need them B. limiting, must include them in our diet C. anabolic, must use alternative amino acids D. essential, must include them in our diet. E. superfluous, must survive without them. 34. The end products of eukaryotic cellular aerobic respiration include(s) A. carbon dioxide. B. water. C. ATP. D. All of the choices are correct. 35. The correct sequence for aerobic metabolic breakdown of glucose is A. glycolysis—preparatory reaction--cirtric acid cycle--electron transport system B. preparatory reaction --glycolysis---electron transport--citric acid cycle C. electron transport system--citric acid cycle--- preparatory reaction --glycolysis D. None of the choices are correct. 36. Of the following processes which does NOT requrie oxygen to occur? A. electron transport system B. preparatory C. glycolysis D. citric acid cycle 37. The end product of glycolysis A. is pyruvate in aerobic respiration. B. can form alcohol and/or lactate if fermentation occurs. C. nets the cell 2 ATP. D. All of the choices are correct. 38. For aerobic respiration to occur A. pyruvate must be transported to the mitochondrion. B. oxygen must be available to the mitochondrion. C. hydrogen ions released from the breakdown of pyruvate must be carried to the electron transport system. D. All of the choices are correct. 39. The citric acid cycle A. must occur twice for each glucose molecule metabolized. B. produces 2 ATP directly from the cycle intermediates. C. produces 4 carbon dioxide molecules per glucose molecule. D. All of the choices are correct. 40. The electron transport system produces ______ATP from each NADH and/or _________ATP from each flavin mononucleotide entering the system. A. 4; 2 B. 3; 2 C. 2: 4 D. 2; 3 41. Organisms that can undergo aerobic metabolism and fermentation have more enzymes than those organisms that cannot undergo fermentation. True False 42. The preparatory reaction involves the oxidation of pyruvate and the reduction of NAD+. True False 43. Active cells must continually produce ATP. True False 44. The most efficient pathway for ATP production in animal cells is by glycolysis. True False 45. Metabolism of fats produces more ATP molecules per gram than metabolism of carbohydrates or proteins. True False 46. The final electron acceptor in glycolysis is oxygen. True False 47. The carrier molecules of the electron transport system are located in the cytosol. True False 48. Glycolysis is linked to the citric acid cycle when oxygen is not available. True False 49. Fermentation follows glycolysis in some cells when oxygen is not available. True False 50. The highest concentration of hydrogen ions in the mitochondria is in the intermembrane space. True False 51. Because NAD+ and FAD are critical coenzymes in cellular respiration, huge quantities must be synthesized in the cell to ensure there is no shortage. True False 52. Each molecule of NADH produced in the mitochondria provides the energy for two ATP molecules. True False 53. The breakdown of glucose in cellular respiration is a catabolic reaction. True False 54. All of the molecules available for biosynthesis constitute the metabolic pool. True False 55. Fermentation is the process that produces bubbles of carbon dioxide that makes bread dough rise. True False 56. Glycolysis and fermentation are thought to be older processes than the electron transport system and the citric acid cycle. True False 57. Fermentation is the process that causes your muscles to be sore after a long, strenuous workout. True False 58. The final electron acceptor in the electron transport system is oxygen. True False 59. Photosynthesis is the most abundant form of anabolic metabolism in life. True False 60. The totality of metabolism in humans must include both anabolism and catabolism. True False 61. Explain why the process of glycolysis and cellular respiration releases the energy of glucose in small quantities rather than all at once. 62. A little knowledge is sometimes a dangerous thing. For instance, the overall equation for cellular respiration of sugar is essentially the same as for taking a match and burning a sugar cube! Some people believe "spontaneous human combustion" is a simple runaway of normal cell processes. From your study of both cellular respiration, and the tissue environment of cells, why would scientists question the existence of "spontaneous human combustion" and not even consider the idea that it is linked to cellular respiration? 63. Describe how the processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration are linked, and what aspects they have in common. 64. List and describe the four processes in the oxidation of glucose to carbon dioxide and water. 65. Discuss the differences in actions, locations, products, and energy yield of anaerobic and aerobic breakdown of glucose. 66. Describe what fermentation is and how it is different in animals versus yeast. 67. Explain how fermentation is useful in humans, and why most of the body's glucose breakdown is done using the aerobic pathway. 68. Discuss what the metabolic pool is and its links to cellular respiration and biosynthesis. Chapter 8 KEY 1. A 2. E 3. B 4. B 5. D 6. C 7. C 8. D 9. B 10. B 11. A 12. D 13. C 14. C 15. E 16. C 17. C 18. E 19. B 20. B 21. A 22. D 23. A 24. C 25. B 26. D 27. B 28. A 29. B 30. B 31. D 32. C 33. D 34. D 35. A 36. C 37. D 38. D 39. D 40. B 41. TRUE 42. TRUE 43. TRUE 44. FALSE 45. TRUE 46. FALSE 47. FALSE 48. FALSE 49. TRUE 50. TRUE 51. FALSE 52. FALSE 53. TRUE 54. TRUE 55. TRUE 56. TRUE 57. TRUE 58. TRUE 59. TRUE 60. TRUE 61. Answers will vary. 62. Answers will vary. 63. Answers will vary. 64. Answers will vary. 65. Answers will vary. 66. Answers will vary. 67. Answers will vary. 68. Answers will vary.