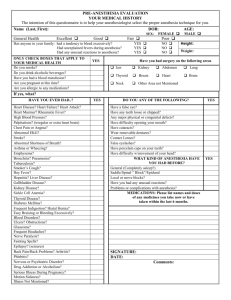
Module 1. Propedeutics of surgical dentistry Text test tasks What
advertisement

Module 1. Propedeutics of surgical dentistry Text test tasks 1. What concentration of chlorhexidine bigluconate solution is used for processing surgery’s hands? A. * 0.5% B. 1% C. 2% D. 3% E. 1% 2. The surgeon handles hand 96 % solution of alcohol for 10 sec, which is a way of processing the hands he used? A. Method Furbringer B. Method Alfred C. Method Spasokukotskyy-Kochergin D. * Method Bruno E. Scrubbing hibitanom 3. How many minutes should boil surgical instruments in the sterilizer? A. 20 minutes. B. 30 min C. 40 min D. 50 minutes. E. * 60 min 4. What is determined by ortolidic testing? A. * The presence of residual blood B. The presence of corrosion C. Sterility of instruments D. The presence of residues of detergents E. The presence of microflora 5. What is the regulatory area set to one dental chair, dental clinics II category? A. 18 m2 B. 20 m2 C. * 14 m2 D. 25 m2 E. 23 m2 6. What are the methods of antiseptics? A. Mechanical B. Physical C. Biological D. Chemical E. * All of the above 7. What form of dental care is the most accessible to the public? A. * State budget B. Private C. Cooperative D. Self-supporting E. All of the above 8. On which day is opened an unworkable paper to the patient with home injury when after 12 hours after injury he was find out in the blood of 0,15 % ethanol? A. From the first day after injury B. On the third day after injury C. * Does not seem at all D. On the sixth day after injury E. On the sixth day after treatment in the medical institution 9. What part of dental patients require the hospital treatment? A. 0.5-1 % B. * 1-1.5 % C. 1.5-2 % D. 2-2.5 % E. 2.5-3 % 10. What concentration of iodopirone solution is used for treatment of surgery’s hands? A. 0.5 % B. * 1% C. 2 % D. 4 % E. 3 % 11. What is the sanitary standard of operating area for 1 dental chair (operating table) in dental clinic 1 category? A. 14 m2 B. 16 m2 C. 20 m2 D. * 23 m2 E. 27 m2 12. How many medical positions in the clinic V category? A. 5.7 B. 7.11 C. * 10-14 D. 12-15 E. 14-17 13. What is the main structural link dental units? A. * Dentist B. Dental office C. Dental clinic D. Dental hospital E. Dental clinic 14. Which are the operations named below related to the planned intervention? A. Operation tooth B. Operation disclosure phlegmon C. Splinting at the turn of the jaw D. * Resection of the root apex E. Reduction of dislocation of the mandible 15. What is finded out by the phenolphthalein testing? A. Sterility of instruments B. The presence of corrosion C. * The presence of residues of detergents D. The presence of residual blood E. The presence of microflora 16. On which day is opened an unworkable temporary paper to the patient with home injury, if he is not found alcohol intoxicated? A. From the first day after injury B. On the third day after injury C. On the sixth day after injury D. * On the sixth day from the date of application in medical facility E. Not seem at all 17. What method is to perform for sterilization of gloves? A. Autoclaving B. Boiling C. Machining under running water D. Processing 2% chloramines E. * All of these methods 18. What is the alcohol concentration of the solution used for skin treatments of the surgical field? A. 96% B. 50% C. 40% D. * 70% E. 80% 19. What is the optimal concentration of hydrogen peroxide solution used for treatment of oral cavity before extraction of the tooth? A. * 3% B. 2% C. 0.5% D. 1% E. 4% 20. What is the minimum area of operating room on the one operation table? A. 22-28 m2 B. 26-32 m2 C. 32-34 m2 D. 36-40 m2 E. * 36-48 m2 21. How is provided sterilization of cutting forcepss? A. * Chemical treatment of 96 % alcohol B. Boiling C. Autoclaving D. Processing in dry-heat closet E. The method of roasting 22. How many medical positions in the clinic III category? A. 11 – 14 B. 14-17 C. 17-20 D. * 20-24 E. 24-28 23. At what time is helded the general cleaning of the surgical department? A. At least 2 times a week B. * At least 1 time a week C. At least 3 times a week D. Everyday E. Two times a day 24. Surgeon washed his hands with warm soapy water, wiped them dry with a sterile towel and within 2-3 min wipe alcohol chlorhexidine solution. What is a way to handle hand applied by the surgeon? A. Method Furbringer B. Method Alfred C. Method Spasokukotskyy-Kochergin D. Method Bruno E. * Process hands hibitan 25. What is the optimal concentration of potassium permanganate solution to handle oral cavity before extraction of the tooth? A. 1/500 B. * 1/1000 C. 1/5000 D. 1/10000 E. 1/20000 26. What are the criteria for assessing the health of sterilization of dental clinics? A. Bacteriological control B. These accounting journal sterilization C. These visual control of sterilization D. Determination of disinfectant solutions E. * All answers are correct 27. The wound was washed with 0.06% chlorhexidine solution bigluconate and put it in a rubber graduate. What kinds of antiseptics were used in the patient? A. Physical B. * Physical and chemical C. Biological and chemical D. Physical and biochemical E. Chemical and biological 28. On which day letter issued disability fractures of the mandible in the area of articular process if the injury received in the workplace? A. * On the 1st day B. On the 3rd day C. On the 2nd day D. With the 6-day E. Not seem at all 29. What applies to chemical methods of sterilization and disinfection? A. High temperature B. Ultrasound C. Boiling D. * Compounds of inorganic and organic origin E. Antibiotics 30. What solutions are approved for use in the antiseptic treatment of operating in the face? A. Solution of ascorbic acid B. 96% solution of ethanol C. 5% solution of iodine D. 6% solution of hydrogen peroxide E. * Iodonat 31. The presence of what statistical documents is mandatory for clinical patient? A. * Form number 037 B. Form number Form number 043 + 030 C. Form number 030 D. Form number 039 E. Form number 043 32. By what statistical document can evaluate a doctor for a month? A. Form number 037 B. Form number 049 C. Form number 043 D. * Form number 039 E. Form number 030 33. Arrange a new dental clinic 1-category. How many staff units Surgeons - Dentists provided in this clinic? A. 5.4 staff units B. * 3.2 staff units C. 4.3 staff units D. 2.1 staff units E. 6.5 staff units 34. The clinic, which employs 20 dentists who perform planned and unplanned operations have fixed operating days. How many posts of doctors - anesthetists provided in this clinic? A. 2 posts B. 3 posts C. 4 posts D. * 1 post E. Over 4 posts 35. What is the method of examination in which the conduct tap the tooth tip or tweezers? A. Palpation B. Thermodiagnosis C. *Percussion D. Electroodontodiagnosis E. Radiography 36. Which of the following is one of the additional methods of examination? A. * Radiography, biomicroscopy B. Definition of bite C. Depth measurement vestibulum of the mouth D. Determining the degree of mobility E. All answers are correct 37. What is the X-ray examination in which you can get images of a certain layer of bone? A. Stereoroentgenography B. * Tomography C. Panoramic radiography D. Radioscopy E. Radioviziography 38. What is the method for studying the circulation, based on the detection of the optical density of the tissues? A. Sample Kulazhenko B. Fluorescent diagnostics C. * Photopletismography D. Electroodontodiagnosis E. There is no right answer 39. What is the method of studying tissue oxygen balance? A. Rheography B. Fluorescent diagnostics C. Sample Kulazhenko D. * Polarography E. Photopletismography 40. What method of diagnosis is carried out using the apparatus pulptestera? A. Photopletismography B. Luminescent diagnosis C. Sample Kulazhenko D. * Electroodontodiagnosis E. Polarography 41. What is included in the standard set for oral examination? A. Mirror, trowel B. Probe, Forceps C. * Mirror, probe, tweezers D. Spatula, probe, mirror E. There is no right answer 42. On what basis is based subjective test? A. Data given local B. * Patient complaints C. Additional methods of examination D. Results intraoral examination E. All answers are correct 43. What is the method of touching the organ or its individual parts? A. Percussion B. Biomicroscopy C. * Palpation D. Radiography E. Probe 44. What is a fluorescent diagnostics? A. The method of studying blood flow, based on the detection of optical density tissue B. * The method is based on the ability of tissues to emit light when exposed to ultraviolet rays C. The method is based on the rate of formation of hematoma D. Method of studying the oxygen balance of periodontal tissue E. There is no right answer 45. What is the method of in vivo blood flow, based on the detection pulse oscillation? A. * Rheography B. Fluorescent diagnostics C. Sample Kulazhenko D. Electroodontodiagnosis E. Polarography 46. Indicate by International Classification symbols of permanent teeth: the first upper right premolars, the second lower left molar: A. 37, 24 B. 41, 37 C. C.28, 15 D. 34, 37 E. * 14, 37 47. What is the document form 037? A. Ambulatory patient card B. Leaf for the monthly report of C. * Leaf daily examination of patients D. Leaf accounting of physician podiatrist E. There is no right answer 48. Why take a swab or scraping? A. Biomicroscopic research B. * Microbiological studies C. X-ray study D. Fluorescent diagnostics E. There is no right answer 49. From all osteomyelitis of maxillofacial area acute osteomyelitis (odontogenic) is: A. 15-33% B. 30-45% C. 45-60% D. * 60-65% E. 65-70% 50. Of all the inflammatory processes in maxillofacial area osteomyelitis in children is: A. 10-15% B. * 15-33% C. 25-43% D. 45-63% E. 65-83% 51. Differential diagnosis of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis should be carried out: A. . Odontogenic osteomyelitis B. Ewing sarcoma C. Abscesses of soft tissue D. Acute parotitis E. * All answers are correct 52. 52. With detoxification aim pour: A. Isotonic solution B. Glucose C. Neokompensan D. Rheopolyglucin E. * All answers are correct 53. Chronic odontogenic osteomyelitis often occurs in the mandible in children: A. 2-4 years B. 4-6 years C. * 5-10 years D. 8-11 years E. 9-13 years 54. What are the changes in the blood during hematogenous osteomyelitis: A. * Leukocytosis B. Offset formula right C. Reducing ESR D. Albuminosis E. There is no correct answer 55. When the affected upper jaw (acute osteomyelitis) due to inflammation of the tissue of the orbit observed: A. Exophthalmos B. Conjunctiva chemosis C. Eye closed D. * All answers are correct E. There is no correct answer 56. Medium and large sequestra are formed by: A. 1-2 weeks B. * 2-3 weeks C. 3-4 weeks D. 4-5 weeks E. 5-6 weeks 57. Over the course of the disease osteomyelitis are: A. Acute B. Primary chronic C. Chronic as a result of acute D. Chronic under increasing E. * All answers are correct 58. Nonodontogenic osteomyelitis is divided into: A. Vascular B. Stomatogenic C. Posttraumatic D. Contact E. * All answers are correct 59. Gravity flow hematogenous osteomyelitis causes: A. * Septic background disease B. Age of child C. Preferably damage maxilla D. The destructive nature of the process E. destructive, destructive - productive and hyperplastic forms of chronic osteomyelitis 60. What is the result of osteomyelitis of the jaw bones is a feature of childhood: A. Aedentia B. Formation of bone defect C. * Delayed growth of the jaw D. Pathological fracture of the jaw E. There is no correct answer 61. Length of rehabilitation period for patients with hematogenous osteomyelitis: A. Until clinical recovery B. Lasting remission for a year C. By the period of formation of milk occlusion D. * Until the growth of the jaw bones E. There is no correct answer 62. The first radiographic signs of degradation of the jaws in children with osteomyelitis are: A. At 4-5 days B. For 6-8 days C. * In 10-12 days D. After 3 weeks E. After 4 weeks 63. Depending on the type of infection osteomyelitis classified as follows: A. Vascular, stomatogenic B. Productive, hyperplastic C. * Specific, nonspecific D. Posttraumatic, contact E. Focal, generalized 64. When shown the first radiological signs of destructive odontogenic osteomyelitis? A. At 1-2nd day B. At the 3-4-th day C. * As of 15-20-th day D. In the 30-40th day E. On the 50th day 65. What is the cause of traumatic osteomyelitis? A. Age of the patient B. Acute lymphadenitis C. Trauma poorly manufactured prosthesis D. * A tooth or tooth root in the line of fracture E. There is no right answer 66. What is the cause of traumatic osteomyelitis of the jaws? A. Age of the patient B. Acute lymphadenitis C. * Infection fracture line D. Trauma poorly manufactured prosthesis E. There is no right answer 67. What is the cause of traumatic osteomyelitis of the jaws? A. Age of the patient B. Acute lymphadenitis C. Trauma poorly manufactured prosthesis D. * Inadequate reposition and immobilization of fragments E. There is no right answer 68. What is the method of prevention of posttraumatic osteomyelitis of the jaws? A. Physiotherapy B. Temporary immobilization of fragments C. Deferred immobilization fragments D. * Removal of tooth or tooth root from the line of fracture E. There is no right answer 69. Early acute odontogenic osteomyelitis preceding: A. * Infectious disease paraallergic reactions, allergic diseases; B. Chronic disease of the gastrointestinal tract; C. Violation of cardiovascular activity; D. Violation of nervous activity; E. There is no right answer. 70. In the acute stage of odontogenic osteomyelitis of the mandible is characterized by: A. Aching pain in the causal tooth that increase with beatting; B. Intense pain in jaw radiating along the branches of the trigeminal nerve; C. * Lower lip paresthesia, pain when swallowing, chewing, painful swelling of the soft tissues, difficulty opening the mouth, chewing dysfunction and pronunciation; D. Flatulence alveolar bone on both sides; E. Difficulty opening the mouth. 71. Tactics treatment of acute odontogenic osteomyelitis: A. * Remove tooth, reduce "stress" tissue inflammation and drain, set anti-inflammatory treatment; B. Prevent the development of infection and formation of necrosis on the periphery of the inflammatory foci; C. Reduce vascular permeability and the formation of vasoactive substances; D. Reduce total intoxication, reduce neurohumoral shifts; E. A symptomatic treatment 72. The therapeutic odontogenic osteomyelitis during the formation of sequestra: A. * Infection control in inflammation, prevent the formation of new necrosis (storage microcirculation in peripheral inflammatory focus), decreased vascular permeability and intensity neurohumoral shifts; B. Appointment hamaglobulin, antistaphylococcal plasma; C. Conducting sequestrectomy; D. Antibiotic therapy; E. Appointment of infusion therapy. 73. Tactics odontogenic osteomyelitis treatment in a phase of stabilization of the inflammatory process: A. * Sequestrectomy, improving nonspecific immunity, creating favorable conditions for the flow of reparative regeneration in the jaw bones; B. Timely dental prosthetics, dental health and the bow of the throat; C. Intensive detoxification treatment; D. Antibiotic therapy; E. Appointment of infusion therapy. 74. Pathognomonic symptoms of acute odontogenic osteomyelitis of the maxilla in children: A. Isolation of pus from the outer ear; B. Abscesses in the cheeks; C. * Development of infiltrates, abscesses, fistulas on alveolar process of the upper jaw or palate; D. High body temperature; E. There is no right answer. 75. Before the sequestrectomy on the upper jaw with osteomyelitis in the molars in the elderly, which apparatus necessary to make? : A. Tire Vankevych; B. Capua, which increases bite; C. * Protective plate; D. Tire Weber E. Tihershtedt tire. 76. Indications for routine tooth extraction: A. Acute suppurative periodontitis; B. Aggravated chronic periodontitis; C. * Chronic periodontitis; D. Chronic pulpitis; E. Catarrhal gingivitis 77. After what period after myocardial infarction can already conduct routine tooth extraction: A. After 1 week; B. After 3-4 weeks; C. After 1-2 months; D. * After 3-6 months; E. After 1-2 years 78. What are the stages of pregnancy can cause temporary contraindications for tooth extraction: A. * The 1-2 and 8-9 months; B. At 2-3 and 6-7 month; C. In 3-4 months; D. In 5-6 months E. In 7-8 months 79. If the forceps is cheeks spikes, they are designed to remove: A. The upper incisors; B. Upper premolars; C. The upper molars; D. Lower incisors; E. * Lower molars 80. When you remove the upper tooth doctor is: A. To the left and in front of the patient; B. * Case and ahead of the patient; C. In front and on the side, which corresponds extracted teeth; D. Arbitrary (any) provision doctor; E. Behind the patient. 81. When you remove the lower front teeth doctor is: A. Case and behind the patient; B. Left and posteriorly from the patient; C. C. * Case and slightly ahead of the patient; D. D. Arbitrary (any) provision doctor E. E. Behind the patient 82. When you remove the lower right molars and premolars doctor is: A. * From the right and posteriorly from the patient B. From the right and in front of the patient; C. To the left and in front of the patient; D. Arbitrary (any) provision doctor E. Behind the patient 83. When you remove the left lower molars and premolars doctor is: A. Left and posteriorly from the patient; B. * Left and somewhat ahead of the patient; C. From the right and posteriorly from the patient; D. Arbitrary (any) provision doctor E. Behind the patient 84. The correct sequence of techniques extractions forceps: A. Promotion, blending closing cheeks, luxate and tooth extraction; B. * Overlay, promotion, closing cheeks, luxate and tooth extraction; C. Overlay, closing, moving cheeks, luxate and tooth extraction; D. Closing, blending promotion cheeks, luxate and tooth extraction E. Promotion, luxate, traction. 85. First swinging motion when removing the teeth of the upper jaw do: A. Medially than removing the sixth tooth; B. Medially than removing molars; C. Medially than removing premolars and molars; D. * Outside, in addition to removing the sixth tooth; E. Outside, in addition to removal of molars; 86. First swinging motion when removing the teeth on the lower jaw do: A. * Outside, in addition to removing the second and third molars; B. Outside, in addition to removal of molars; C. Outside, in addition to removal of premolars and molars; D. Medially than removing the second and third molars; E. Medially than removing molars; 87. Epithelialization holes one root of teeth going on that day after removal? A. 10.12 days; B. 12-16 days; C. * 16-18 days; D. D. 20-22 days; E. E. 24-30 days 88. Epithelialization holes permanent teeth occurs on any day after the removal? : A. 14-18 day; B. * 19-23 day; C. 24-28 day; D. 29-32 day E. 12 day 89. In the presence of inflammation holes in the teeth of one root delay epithelialization observed on: A. * 1 week later; B. 2 weeks later; C. 3 weeks later; D. Do not delay observed E. 5 days 90. In the presence of inflammation in the multi-hole teeth delayed epithelialization observed on: A. 1 week later; B. * 2 weeks later; C. 3 weeks later; D. Do not delay observed E. 5 days 91. Which day after tooth extraction hole completely filled with granulation tissue? A. 3-4 days; B. 7-8 days; C. * After 2 weeks; D. After 3 weeks; E. After 4 weeks 92. In what time frame after tooth extraction hole begins to fill small glomerular spongy bone? : A. For 14 days; B. * At 21 days; C. By the end of the first month; D. By the middle of the second month; E. By the end of the second month; 93. . In what terms fossa radiographically different from the surrounding tissue (with uncomplicated healing)? A. By the end of the first month; B. At 2-4 month; C. * 4-6 months; D. At 7-8 months; E. At 8-9 months 94. In reaction to (alveoli) in what time frame hole radiographically different from the surrounding bone tissue? : A. By 2-4 months; B. By 4-6 months; C. By 6-8 months; D. * Up to 8-10 months; E. Up to 10-12 months 95. When should extract the tooth push in soft tissue? : A. Not earlier than 1 week; B. * As previously; C. Not earlier than 3 weeks; D. Not earlier than 4 weeks E. Not earlier than 5 days 96. Can tampon hole iodoform swab if during tooth extraction complications arose - the disclosure of the maxillary sinus floor? : A. * You can; B. Possible only when there postextraction bleeding; C. You can only purulent inflammation of the maxillary sinus; D. Possible in all cases E. Possible only if push root in maxilla bosom. 97. When perforation of the maxillary sinus, which took place during tooth extraction complicated by acute sinusitis (without tooth root in maxillary sinus) is shown: A. Urgent holding maxillary sinusotomy with plastic commonostium; B. Scheduled holding maxillary sinusotomy with plastic commonostium; C. * Rinsing sinuses antiseptic solutions (to relieve inflammation) of plastic commonostium; D. Spot wash maxillary sinus, maxillary sinusotomy with plastic fistula in postoperative sinus rinse repeatedly (through rinostomy) antiseptic solutions; E. Conducting local plastic commonostium without maxillary sinusotomy; 98. What method should be carried out removal of the tooth root, push in the maxillary sinus? : A. The method Pichler; B. * The method maxillary sinusotomy with local plasticity commonostium; C. Maxillary sinusotomy method without local plastic commonostium; D. Leave root maxillary sinus to the appearance of clinical symptoms of sinusitis; E. Local plastic commonostium, holding rinostomy and washout push root 99. Life expectancy platelets: A. 1-2 days; B. 3-6 days; C. * 7-12 days; D. 15-30 days; E. 1-2 months; 100. How is bleeding that occurs after surgery? : A. Idiopathic; B. * Iatrogenic; C. Symptomatic; D. Rhinogenous E. Spontaneous 101. Through what time Aminocaproic acid is completely eliminated from the body? : A. 15 minutes; B. 30 minutes; C. One hour; D. * Four hours; E. Six hours; 102. Daily dose of aminocaproic acid (dry matter) for an adult is: A. 2.0 grams; B. 4.0 grams; C. 5,0-8,0 grams; D. * 10,0-15,0 grams; E. 20,0-30,0 grams 103. Percentage ethamsilate sodium solution (in capsules) used for intramuscular or intravenous administration to stop the bleeding: A. 1% solution; B. 2% solution; C. 5.5% solution; D. 7.5% solution; E. * 12.5% solution; 104. 107. When hypoprothrombinaemia to stop bleeding should be: A. Aminocaproic acid or amben (pamba); B. Rutin or askorutin; C. * Fitomenadion or vikasol; D. Clonidine, Raunatin E. Ascorbic acid 105. To stop the bleeding with increasing fibrinolytic activity of blood should be used: A. * Aminocaproic acid or amben (pamba); B. Rutin or askorutin; C. Fitomenadion or vikasol; D. Clonidine, raunatin E. Ascorbic acid 106. To stop the bleeding with increased permeability of blood vessels to assign: A. Aminocaproic acid or amben (pamba); B. * Rutin or askorutin; C. Fitomenadion or vikasol; D. Ascorbic acid E. Clonidine, raunatin 107. To stop the bleeding with high blood pressure are used: A. Aminocaproic acid or amben (pamba); B. Rutin or askorutin; C. Fitomenadion or vikasol; D. * Clonidine, Raunatin E. Ascorbic acid 108. Hemophilia - a group of common hemorrhagic diathesis due to hereditary platelets: A. * Deficiency of factor VIII or IX; B. Increased fibrinolytic activity of blood; C. Increase in blood pressure; D. Low content of calcium in the blood; E. Reduced vitamin K in the body; 109. Call inhibitors of fibrinolysis: A. Prednisolone, hydrocortisone; B. Cryoprecipitate; C. * Kontrikal, gordoks; D. Eritromassa; E. Albumin, globulins 110. If alveolitis occurs in the form of "dry holes", it is shown: A. Coagulation walls and floor holes; B. * Loose tamponade fossa iodoform swab; C. Turundas with Vishnevskyy ointment; D. Mechanotherapy E. Tamponade dry swab 111. After the tooth extraction is not recommended to: A. Intense antiseptic mouthwash no earlier than 2 hours after the operation; B. * Use of hot food or coffee within 2 hours after the operation; C. Antiseptic baths are contraindicated intense rinse the mouth; D. Significant physical exertion; E. UHF therapy in thermal dose 112. In what forms can occur alveolitis? : A. * In the form of "dry holes" or osteomyelitis fossa; B. Just as "dry holes"; C. In the form of acute, chronic and recurrent; D. Only in the form of osteomyelitis fossa E. There is no right answer 113. For the treatment of alveolitis or you can use turundas treated with antiseptic ointment? : A. You always; B. * You can, if used hydrophilic ointment; C. You can not use; D. You can, but in combination with drainage devices E. It's any ointments 114. When you remove 46 teeth due to improper use of the elevator was dislocated intact tooth 45. Your actions in this situation. A. *Reduce tooth and fix his tire. B. Remove 45 tooth. C. Hold endodontic treatment and resection top of 45 tooth. D. Seal the channel of 45 tooth. E. Admit a patient to the hospital for examination and to further treatment. 115. When you remove the 28 tooth in the patient was cast tuber maxilla. Your actions in this case. A. * Remove mound, wound edges mobilize and stitched wound tightly B. Run radical maxillary sinusotomy with plastic closure Oro-antral communication. C. Remove mound and tamponage iodoform wound swab. D. Hold fixation of maxilla E. Remove mound and wound drain pipe drainage. 116. In surgical dental office appealed patient complaining of the presence of roots destroyed 37 tooth. What forcepss can be used to remove roots 37 tooth? A. * Beak forceps, converging, side elevators. B. Beak forceps that do not converge, direct elevator. C. Forceps bent in the plane, side elevators. D. Bagnetlikes forceps, straight grain elevator. E. S-shaped forceps, straight and side elevators. 117. What is the position of the left hand of the physician in removing the teeth of the mandible left? A. Left hand turns his head to the right patient and keeps it in that position B. Returns the head of the patient to the doctor and forefinger assigns cheek C. The index finger of his left hand removes the medial tongue patient D. Left hand presses the front teeth and chin E. * The index and thumb left hand covers the alveolar bone of the mandible in the area of the tooth is removed, and all the other covers the edge of the mandible. 118. After what period does begin the phase of regeneration and wound epithelialization after extraction? A. After 48-72 hours B. After 3-4 days C. After 6-7 days D. * After 12-14 days E. After 3-4 weeks. 119. What is the position of the head of the patient when removing front teeth mandible? A. The patient sits on a chair with maximally lowered head thrown B. Chairman of the patient is at the level of the shoulder girdle doctor and returned to the right C. Chairman of the patient is at the elbow and returned to the left D. The patient sits on the most elevated chair with head down. E. * Chairman of the patient is at the elbow in front of doctor 120. What is the position of the head of the patient in removing teeth of the upper jaw on the left? A. Chairman of the patient should be on the level as the raised chair and look straight B. * Chairman of the patient should be at the level of the shoulder girdle and some returned to the doctor C. Chairman of the patient should be at the level of the elbow joint doctor and returned to the left D. Chairman of the patient should be possible to cast the proper height E. Chairman of the patient should be at the level of the elbow joint doctor and returned to the doctor. 121. Terms doctor left hand while removing the teeth of the upper jaw on the left? A. Maintains the patient's head, hand on the left malar area B. The index finger of his left hand removes cheek out C. Left hand helps keep the patient's mouth in the open state D. * Includes index finger outside, and a large part of the palatal alveolar bone in the area of the tooth, which removes E. Left hand presses on the forehead of the patient. 122. What is the position of the head of the patient when removing front teeth of the upper jaw? A. Chairman of the patient should be returned to the doctor B. Chairman of the patient should be returned to the doctor and cast C. * Chairman of the patient should be at the level of the shoulder girdle and look straight D. Chairman of the patient should be returned to the left E. Chairman of the patient should be tilted. 123. At what level should be at the head of the patient in removing teeth on the upper jaw? A. At the level of the head doctor who removes teeth B. At the level of the elbow joint doctor C. * The level of the shoulder girdle doctor D. At the level of the maximum dredged up chairs E. At the level of the chest. 124. At what level should be at the head of the patient in removing teeth on the lower jaw? A. At the level of the maximum lowered seat B. At the level of the head doctor C. At the level of the shoulder girdle doctor D. * At the level of the elbow joint doctor E. At the level of the waist. 125. How to prevent damage to the gums and mucosa alveolar process recommended? A. * Hold syndesmotomy B. Blend forceps on language and buccal surface of teeth C. Deeply push cheeks forceps under clear D. Firmly grabbing alveolar outgrowth fingers of the left hand E. Avoid sudden rotational movements and luxation forceps. 126. What should be used to prevent root fracture during removal of the lower incisors? A. * Luxation in vestibular-oral direction B. Rotation C. Rotation and luxation in a lingual direction D. Rotation and luxation in the vestibular direction E. Luxation the media-lateral direction. 127. What movements are performed with forceps when removing premolars of the upper jaw? A. Rotation B. Rotation and luxation in palatal direction C. * Luxation in vestibular-oral direction D. Luxation in the vestibular direction and rotation E. Luxation in media-distal direction. 128. What forceps do you choose to remove the 26 tooth? A. Direct forceps B. S-shaped forceps with smooth cheeks C. * S-like pincers with spikes on the right cheek D. S-shaped forceps with spike on the left cheek E. Nipper, bent by plane. 129. What luxation movements should be used when removing the first premolars on the upper jaw to prevent fracture of the tooth root? A. * Luxation, mainly in the vestibular side B. Luxation, mainly in the oral side C. The combination of rotary and luxation D. E. 130. A. B. C. D. E. 131. A. B. C. D. E. 132. A. B. C. D. E. 133. A. B. C. D. E. 134. A. B. C. D. E. 135. A. B. C. D. E. 136. A. B. C. D. E. The combination of rotary and traction Rotary. What forceps do you need to use to remove the tooth 34 with the destroyed crown? *Ribbanted forceps with cheeks that connect with each other Ribbanted forceps with cheeks that do not connect with each other Ribbanted forceps spiked Circling bent by plane Bayonets forceps. What signs have forceps to remove the upper incisors? S-shaped forceps with cheeks that do not merge. S-shaped forceps, one of which is cheeks spike. Direct with spikes on both cheeks * Direct with rounded cheeks that do not merge. Direct forceps, which merge cheeks. What signs does have forceps to remove the upper wisdom teeth? Bayonets forceps with narrow cheeks that do not merge Straight forceps with broad cheeks that do not merge S-shaped forceps with broad cheeks with stud * Bayonets forceps with broad cheeks, which are barrel shape, not merge and do not have spines S-shaped forceps with broad cheeks, which are spikes. What signs does have forceps for removing the lower wisdom teeth? Forceps with broad cheeks, which are bent on the edge Forceps with broad cheeks, which merge Forceps with broad cheeks, one of which is a thorn * Circling bent on a plane with wide cheeks that do not merge and have a spike on each cheek Circling bent on a plane with broad cheeks, which merge and have one spike. What signs does have forceps to remove the lower canines and premolars? Beak forceps with broad cheeks with spikes Beak forceps with narrow cheeks to merge * Beak forceps cheeks with medium width without spines that do not merge Direct forceps cheeks with medium width to merge Beak forceps cheeks with medium width to merge 138. What signs does have forceps to remove the lower incisors? Straight forceps with narrow cheeks to merge Beak forceps with spike from the outside Beak forceps with narrow cheeks to merge * Beak forceps with narrow cheeks that do not merge Beak forceps with broad cheeks with spikes on both cheeks. What signs does have forceps to remove premolars of the upper jaw? Direct, cheeks that do not merge S-shaped forceps with cheeks that merge * S-like pincers on cheeks without spikes that do not merge Bayonets forceps with narrow cheeks Straight forceps with broad cheeks to merge. 137. What instruments are used to removed deeply fractured medial root of 47 tooth? A. Direct elevator B. * Right elevator angle C. Left elevator angle D. Elevators Lekluse E. Chisel and hammer. 138. What instruments are used to remove deeply fractured distal root of tooth 47? A. Direct elevator B. Right elevator angle C. * Left elevator angle D. Elevators Lekluse E. Chisel and hammer. 139. How is correct to recognize the left elevator angle? A. Cheeks bent down working plane cheeks case B. * Cheeks bent down working plane left cheeks C. Cheeks bent to the left, the working plane cheeks case D. Cheeks bent upwards, working plane left cheeks E. Working part connected with the handle perpendicular to the elevator. 140. How is correct to recognize the right elevator angle? A. Cheeks bent down working plane left cheeks B. * Cheeks bent down working plane cheeks case C. Cheeks bent to the left, above the working plane cheeks D. Cheeks bent upwards, working plane cheeks case E. Working part connected with the handle perpendicular to the elevator. 141. What instruments are used to remove the deeply fractured medial root of 46 tooth? A. Direct elevator B. Left elevator angle C. * Right elevator angle D. Elevators Lekluse E. Chisel and hammer. 142. Which forceps should be applied to remove the 24 tooth for orthodontic reasons: A. * S-like forceps B. Straight forceps with cheeks that do not converge C. Bayonet forceps D. Straight forceps with cheeks that converge E. S-shaped forceps right? 143. A patient diagnosed with pericoronitis 38 tooth small mouth opening limitation. Select the appropriate anesthesia and instruments for tooth extraction: A. Torusal anesthesia, straight and corner elevator B. * Torusal anesthesia, direct elevator, forceps, bent on plane C. Mandibular anesthesia direct elevator D. Anesthesia for Bershe-Dubov, direct elevator horyzontal forceps E. Mandibular anesthesia beak forceps with spikes on the cheeks. 144. Elevator Lekluse for removal of teeth is used for: A. * Lower eight teeth B. Upper large molar teeth C. D. E. 145. A. B. C. D. E. 146. A. B. C. D. E. 147. A. B. C. D. E. 148. A. B. C. D. E. 149. A. B. C. D. E. 150. A. B. C. D. E. 151. A. B. C. D. E. 152. Lower incisors Upper small molar teeth Lower small molar teeth? Which forceps should be used to remove the medial root of the tooth 36: Direct elevator Elevator corner "to itself" * Elevator corner "from itselfs" Beak forceps with spikes Elevator Lekluse? What forceps should you use when removing 14 tooth with destroyed crown: Direct S-shaped S-shaped law S-like * Bayonet? Please remove tooth 15. Crown of the tooth is preserved. Which forceps should be used: Bayonet forceps Direct forceps * S-like forceps S-shaped forceps left S-shaped forceps right? Select forceps for removing 12 teeth: S-shaped with a spike on the left cheek S-shaped with a spike on the right cheek S-shaped forceps Bayonet * Direct. Which forceps should be applied during the removal of 24 teeth for orthodontic reasons: * S-like forceps Straight forceps with cheeks that do not converge Bayonet forceps Straight forceps with cheeks that converge S-shaped forceps right? Select forceps, what do you need to remove 11 teeth: Bayonet * Direct S-like S-shaped with a spike on the right cheek S-shaped with a spike on the left cheek. Select forceps, which in ample allotment to 36 tooth: Bent on a plane Beak with cheeks that do not converge Beak with cheeks that converge * Beak with spikes on cheeks Bayonet. Select forceps which hold ample to remove the roots of 47 teeth: A. * Beak with cheeks that connect B. Beak with cheeks that do not connect C. Beak with spikes on cheeks D. Bent on a plane E. Bayonet. 153. What are forceps used to remove 47 teeth with preserved coronal part: A. Bayonet forceps B. Beak forceps with cheeks that are connect. C. * Beak forceps with spikes on both cheeks D. S-shaped forceps E. Beak forceps with cheeks that are not connect? 154. What forceps should you use to remove the 27 tooth: A. * S-similar to spike right B. S-shaped spike on the left C. Bagnetlikes crowns forceps D. S-shaped forceps E. Bagnetlikes root forceps? 155. What forcepss should be used to remove the medial root of the tooth 36: A. Elevator corner "to itself" B. * Elevator corner "from itselfs" C. Direct elevator D. Beak forceps with spikes E. Elevator Lekluse? 156. On what grounds forceps to remove the teeth on the upper jaw differ from forceps for removing teeth on the lower jaw: A. * For an angle B. For sideways C. Justify cheeks D. By bending handles E. By climbing cheeks? 157. Patients is showed to removal of 36 teeth. Where should be the doctor: A. Behind and centered on the patient B. To the left and behind the patient C. Ahead and to the left of the patient D. * The front and right of the patient E. Right and slightly back from patient? 158. What forceps should be used when removing the 14 tooth with crown destroyed: A. Direct forceps B. S-shaped forceps C. S-shaped forceps right D. S-shaped forceps left E. * Bayonet forceps? 159. Please remove tooth 15. Crown of the tooth is preserved. What forceps should be used: A. Bayonet forceps B. Direct forceps. C. * S-like forceps D. E. 160. A. B. C. D. E. 161. A. B. C. D. E. 162. A. B. C. D. E. 163. A. B. C. D. E. 164. A. B. C. D. E. 165. A. B. C. D. E. 166. A. B. C. S-shaped forceps left S-shaped forceps right? What is the coronaro-radicular separation? Removing the root while preserving the tooth crown Removing the root together with part of the tooth crown * Dissection of the tooth into two parts in the bifurcation Removing a tooth filling channel and return it in the hole Resection of jaw In which of these processes is shown resection of the root apex of the tooth? Pathological tooth mobility In acute or aggravated form of chronic periodontitis * In the presence of granulomas in the projection of the root apex When there are periodontal disease Acute periostitis What is the deal hemisection of the tooth? Autopsy crown of the tooth and its removal Remove the top after opening its borders to bifurcation * Autopsy crown of the tooth to the bifurcation and removing parts of it together with the root Remove multi-tooth section it into two parts and transplanting part of the tooth in its alveolus Tooth extraction What is a tooth root amputation? Removing the root together with the adjacent coronal tooth Autopsy crown to the bifurcation of the root removal and revision pathological focus * Autopsy root on the verge neck of the tooth and its removal Autopsy root and remove its apical part Remove the top half What is the replantation of the tooth? Removing the root and keeping his artificial tooth alveoli Autopsy coronal tooth to its bifurcation Tooth, cutting off the root apex and the introduction of the tooth alveoli intervention and resection of the root apex There is no right answer * Tooth and putting in his own alveoli after endodontic intervention Which teeth can perform the operation hemisection of the root? At any tooth * The molars of the upper and lower jaw In the teeth during dental bridges In premolars upper and lower jaws In mandibular incisors What is periodontitis? The inflammatory process that affects the bone hole tooth * The inflammatory process that affects the periodontal tissues and spread to adjacent bone structures The inflammatory process that affects the gum tissue in the area of causal tooth D. E. 167. A. B. C. D. E. 168. A. B. C. D. E. 169. A. B. C. D. E. 170. A. B. C. D. E. 171. A. B. C. D. E. 172. A. B. C. D. E. 173. A. B. C. D. E. 174. A. The inflammatory process that affects the tooth pulp The inflammatory process that affects the jaw bone What is the width periodontitis cracks on the upper jaw is normal? 0,5-0,12 mm. 0,8-0,16 mm. * 0,15-0,20 mm. 0,20-0,25 mm. 0.25-0.30 mm. What is the width periodontal gap in the mandible is normal? * 0,15-0,22 mm. 0,18-0,20 mm. 0,20-0,25 mm. 0,22-0,28 mm. 0.28-0.34 mm. What provides cushioning function periodontal? Pie ligament * Collagen, reticular and elastic fibers, blood and lymphatic vessels Cementoblasts and osteoblasts Blood and lymph vessels The vessels and nerves What fabric structures does provide trophic function of periodontal? Blood and lymph vessels Collagen fibers * The vessels and nerves Pie ligament Cementoblasts and osteoblasts What fabric structures does provide periodontal retaining function? Blood and lymph vessels * Ligaments Cement tooth Bone wells Cementoblasts and osteoblasts Which of the following below applies to general anesthesia? Application and infiltration anesthesia * Anesthesia and neuroleptanalgesia Method creeping infiltration Vishnevskyy . Regional anesthesia Infiltration anesthesia On which types the anesthesia is divided? Physical and chemical Application and instillation Central and peripheral * Inhaled and non-inhaled Local and conductor Which of the following drugs used for inhalation anesthesia? Hexenal B. Lidocaine C. Ketamine D. Septanest E. * Nitrous Oxide 175. How is called the anesthesia by which injected a mixture of neuroleptic analgesic? A. Ataralheziya B. Audioanesteziya C. * Neuroleptanalgesia D. Acupuncture anesthesia E. Instilation anesthesia 176. Which of the following drugs used for anesthesia non-inhaled? A. Ether B. * Ketamine C. Nitrous Oxide D. Ftorotan E. Hexenal 177. What listed below is general anesthesia? A. * Intravenous anesthesia B. Stem anesthesia C. Spinal anesthesia D. Perirenal blockade E. Epidural anesthesia 178. The patient suffers from epilepsy. Under what kind of anesthesia is necessary to the operation? A. * Under endotracheal anesthesia B. . Under anesthesia mask C. . Under anesthesia naso-pharyngeal D. . Under infiltration anesthesia E. Under anesthesia 179. What method of anesthesia is the most safe and have enough effectiveness in outpatient dental practice for the treatment of patients who undergo treatment fear of the dentist? A. Audioanesthesia B. Neuroleptanalgesia C. * Ataralgesia D. Endotracheal anesthesia E. Hypnosis 180. Which drug is used in outpatient dental practice, during intravenous anesthetic thiopental sodium solution to avoid or prevent laryngo-and bronchospasm? A. Diphenhydramine B. Dyprazin C. Adrenalin D. Fentanyl E. * Atropine 181. What are the different types of anesthesia? A. * Inhaled, non-inhaled, neuroleptanalgesia B. Inhaled, mask, endotracheal C. D. E. 182. A. B. C. D. E. 183. A. B. C. D. E. 184. A. B. C. D. E. 185. A. B. C. D. E. 186. A. B. C. D. E. 187. A. B. C. D. E. 188. A. B. C. D. E. 189. Inhaled, non-inhaled, endotracheal Endotracheal, mask, neuroleptanalgesia Neuroleptanalgesia, mask, inhalation In how many steps performed premedication? One-step In two stages * The three stages In four stages In the five stages What is the show for anesthesia in a dental clinic? Acute respiratory infection Acute inflammation Endocrine pathology * Diseases of the CNS Cardiovascular disease What is the contraindications for anesthesia in a dental clinic? Fear of the treatment and removal of teeth Lactose anesthetics Pathology of CNS Asthma * Acute respiratory infection What doctor’s things are used in anesthesia mask? Propanidid and sodium hydroxybutyrate Viadryl and altezyn Hexenal * Chloroform and ether Trichlorethylene and Methoxyflurane Which of complications is not related to anesthesia complications? Spasm of the larynx Swelling of the larynx * Angioedema Apnea Aspiration of vomit What are the ways to maintain the anesthesia? * Half-closed, half open and closed Indoor and outdoor Indoor, outdoor and semiClosed, open and half-open Half-open, half-closed and open In which of these injuries is not indicated general anesthesia? Fractures of the upper jaw and the type Lefort 2 Lefort 3 Fractures of the mandible with damage to the tongue Fractures of the mandible with damage to the pharynx and larynx * Fractures of the nose Fractures of the mandible with muscle damage floor of the mouth What medicines are used in non-inhaled anesthesia? A. Droperidol, fentanyl, diazepam B. * Viadryl, hexenal, thiopental sodium C. Ether, ftorotan, nitrous oxide D. Trichlorethylene Methoxyflurane E. Cyclopropane, chloroform 190. How many stages are of clinical anesthesia? A. Two B. Three C. Four D. * Five E. Six 191. What medicines are used in neuroleptanalgesia? A. Viadryl, hexenal, thiopental sodium B. Ether, ftorotan, nitrous oxide C. Trichlorethylene Methoxyflurane, chloroform D. Sodium hydroxybutyrate, propanidid E. * Droperidol, fentanyl, diazepam 192. What is the contraindications for anesthesia in a dental clinic? A. * Severe anemia B. Asthma C. Fear of the treatment and removal of teeth D. Lactose anesthetics E. Pathology of CNS 193. What is the show for anesthesia in a dental clinic? A. Acute respiratory infection B. Acute inflammation C. * Lactose anesthetics D. Severe anemia E. Endocrine pathology 194. What type of anesthesia is indicated for revealing severe phlegmon of maxillofacial area? A. Neuroleptanalgesia B. * Mask anesthesia C. Endotracheal anesthesia D. Non-inhaled anesthesia E. Local anesthesia 195. What is the contraindications for anesthesia in a dental clinic? A. Pathology of CNS B. Fear of the treatment and removal of teeth C. Lactose anesthetics D. * Violations clotting E. Asthma 196. Which medicines can be used for premedication before extraction of the teeth? A. Trimecaine B. * Trioksazyn C. Timalin D. Cocaine E. Dikain 197. What is the narcotic effect of the application of to vein anesthesia by sombrevin? A. * Within 3-5 minutes. B. Within 6-8 minutes. C. For 9-12 min. D. Within 13-15 minutes. E. Within 17-20 minutes. 198. Coagulation theory is: A. Solubility of drugs in lipid cellules membranes B. Change of boundary tension between the membrane and the liquid C. * Reverse coagulation of protoplasm of nerve cells D. Lock regulation of redox processes E. Formation of stable water crystals 199. In patients 6 years cleft hard and soft palate. What method of general anesthesia are used during surgery - uranostafiloplastic? A. Intravenous B. Rectal C. * Endotracheal through the oral cavity D. Intra-muscular E. Mask 200. Requirements for general anesthesia in the clinic (by Bazhanov) A. Anesthesia should be absolutely safe B. Awakening Fast C. The patient must independently go home D. No side effects after anesthesia E. * All answers are correct 201. When conducting the second phase of sedation? A. The evening before surgery B. Over 5 hours before surgery C. For 4 hours before surgery D. * By 1,5-2 hours before surgery E. There is no right answer 202. What is the substance of these should be used to suppress fear and internal stress in the patient before visiting the dentist? A. * Diazepam B. Extract Valerian C. Droperidol D. Chlorpromazine E. Sodium bromide 203. What drugs are used for classical neuroleptanalgesia? A. Chlorpromazine with droperidolom B. Omnopon with chlorpromazine C. Diazepam with pipolfenom D. * Fentanyl with droperidolom E. Thiopental sodium suprastin 204. What method of anesthesia is the most safe and effective enough in ambulatory stomatological practice for the treatment of a patient who is undergoing treatment in fear of the dentist? A. Audioanesthesia B. Neuroleptanalgesia C. * Ataralgesia D. Endotracheal anesthesia E. Hypnosis 205. What kind of anesthesia is appropriated to the patient with hypersensitivity to local anesthetics for tooth extraction? A. Intravenous anesthesia B. * Endotracheal anesthesia C. Anesthesia D. Electrophoresis with novocaine E. Application anesthesia 206. What kind of anesthesia is advisable to apply a patient with Parkinson's disease for tooth extraction? A. Application anesthesia B. Infiltration anesthesia C. Anesthesia D. inhalation anesthesia mask E. * Intravenous anesthesia 207. What kind of anesthesia should be applied to patients with epilepsy tooth extraction? A. Application anesthesia B. Mask anesthesia C. * Intravenous anesthesia D. Infiltration anesthesia E. Anesthesia 208. What kind of anesthesia should be applied to the patient spastic paralysis for tooth extraction? A. Application anesthesia B. Infiltration anesthesia C. Anesthesia D. Electrophoresis with novocaine E. * Intravenous anesthesia 209. What is the show for anesthesia in a dental clinic? A. Acute respiratory infection B. Acute inflammation C. Severe anemia D. * Fear of the treatment and removal of teeth E. Cardiovascular disease 210. Through what anatomical formation is transmitted the pain? A. Hill maxilla B. The body of the mandible C. * Thalamus D. Pituitary E. Epiphysis 211. Pain - a kind of human condition, defined set of physiological processes in the central nervous system caused by the stimulus. This definition includes: A. Timofeev B. Danilevsky C. Hotsku D. * Anokhin E. Hotyu 212. At what time in the literature appear first information about anesthesia in dental practice? A. In the twentieth century B. * Since the nineteenth century C. From the thirteenth century D. From the twelfth century E. From the eleventh century 213. In what year and who first used ether anesthesia in removing tooth? A. * 1842., Long B. 1844., Wells C. 1846r., Morton D. 1847., Inozemtsev E. 1847., Pirogov 214. Who first used nitrous oxide anesthesia in dentistry? A. Inozemtsev B. Pirogov C. * Wells D. Long E. Morton 215. What date is considered the discovery of ether anesthesia? A. * October 16, 1846 B. October 16, 1848 C. October 16, 1849 D. January 16, 1847 E. October 15, 1845 216. Who first publicly demonstrated ether anesthesia? A. Inozemtsev B. Pirogov C. * Wells D. Long E. Morton 217. Who was the first and in what year who used ether anesthesia? A. 1842., Long B. 1844., Wells C. 1846r., Morton D. * 1847., Inozemtsev E. 1847., Pirogov 218. Who is the author of the first monograph of anesthesia? A. Inozemtsev B. C. D. E. 219. A. B. C. D. E. 220. A. B. C. D. E. 221. A. B. C. D. E. 222. A. B. C. D. E. 223. A. B. C. D. E. 224. A. B. C. D. E. 225. A. B. C. D. E. * Pies * Wells Long Morton What did in 1847, John Snow? Publicly demonstrated ether anesthesia First held ether anesthesia First held nitrous oxide anesthesia * First described 5 stages of anesthesia Posted monograph from anesthesia In what year was established the first union anesthesiologists? 1,894 1,895 * 1893 1,793 1,993 As the first in 1904, started applying Fedorov and Kravtsov? Inhalation anesthesia Mask anesthesia Intramuscular anesthesia * Intravenous anesthesia Rectal anesthesia Lipoid theory of narcosis is: * Solubility of drugs in lipid cellulare membranes Change of boundary tension between the membrane and the liquid Contact coagulation of protoplasm of nerve cells ock regulation of redox processes Formation of stable water crystals The theory of boundary tension is: Formation of stable water crystals Contact coagulation of protoplasm of nerve cells * Change the boundary tension between the membrane and the liquid Solubility of drugs in lipid cellulare membranes Lock regulation of redox processes Theory breach of redox processes is: Formation of stable water crystals Contact coagulation of protoplasm of nerve cells Change of boundary tension between the membrane and the liquid Solubility of drugs in lipid cellulare membranes * Lock the regulation of redox processes Theory of water microcrystals is: * Formed stable water crystals Contact coagulation of protoplasm of nerve cells Change of boundary tension between the membrane and the liquid Solubility of drugs in lipid cellulare membranes Lock regulation of redox processes 226. A. B. C. D. E. 227. A. B. C. D. E. 228. A. B. C. D. E. 229. A. B. C. D. E. 230. A. B. C. D. E. 231. A. B. C. D. E. 232. A. B. C. D. E. 233. A. B. C. Who is the author of lipoid theory? * Herman Traube Fervorn Bernard Pauling What theory belongs Traube? Lipoid * Of boundary tension Violation of redox processes Coagulation WATER microcrystals Who is the author of the theory of breach of redox processes Herman Traube * Fervorn Bernard Pauling Which theory was put forward in 1931, Bancroft and Richter? Lipoid Of boundary tension Violation of redox processes * Coagulation WATER microcrystals What kind of anesthesia theory proposed in 1961 Pauling? Lipoid Of boundary tension Violation of redox processes Coagulation * Water microcrystals The fourth stage of ether anesthesia by Hvedelom this: Analgesia Excitation Surgical * Agonal Awakening The fourth stage of ether anesthesia by Zhorov this: Analgesia Excitation Surgical Agonal * Awakening How many stages lasts ethereal mononarcosis? 5 6 *4 D. 7 E. 8 234. Through what organs non-inhaled anesthetics are excreted? A. Liver B. Heart C. * Kidneys D. Lights E. Stomach 235. Way withdrawal of inhaled drugs is through: A. Liver B. Heart C. Kidneys D. * Lungs E. Stomach 236. What is the average threshold of excitability pulp electroodontotometria in patients with neuritis of the facial nerve? A. * 3.1 Ma B. 10.5 Ma C. 15-20 Ma D. 25-30 Ma E. 35-40 Ma 237. 288. What method is evaluated condition near apex tissues? A. Review B. Palpation C. Test Kulazhenko D. * D.Elektroodonometriya E. Poll 238. What medical documentation should maintain dental surgeon? A. Medical Book B. Procedural leaf C. Journal of Accounting D. Journal of preventive examinations E. * The history of the disease and leaf daily accounting work 239. What research should be conducted in the presence of a history of infectious hepatitis? A. Clinical analysis of blood B. Electrolytes Blood C. Cholesterol levels D. * Bilirubin Blood E. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 240. What research should be conducted in the presence of a history of infectious hepatitis? A. Clinical analysis of blood B. Electrolytes Blood C. Cholesterol levels D. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate E. * Australian antigen blood 241. What can we diagnosed by benzydyn testing ? A. Sterility of instruments B. The presence of corrosion C. * The presence of residual blood D. The presence of residues of detergents E. The presence of microflora 242. How many doctors dental clinic provides anesthesiologist? A. At 10 B. At 15 C. * At 20 D. At 25 E. At 5 243. How long does it sterilize dental mirror in 6% solution or hydrogen peroxide at room temperature? A. 30 minutes. B. 60 minutes. C. 120 minutes. D. * 180 minutes E. 240 minutes. 244. 295. How many beds are allocated one operating table in the dental hospital? A. 10-20 B. 20-30 C. * 30-40 D. 40-50 E. 50-60 245. 296. How many categories are distinguished dental clinics? A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 5 E. * 6 246. 297. Which operations related to unplanned interventions? A. Replantation B. Resection of the root apex C. * C. Tooth extraction D. Sequestrectomy E. The surgical treatment of periodontal diseases 247. 298. What part of dental patients require outpatient treatment? A. 75-88% B. 84-90% C. 91-95% D. 93-97% E. * 98-99% 248. What is the mode of transmission, in which the infection is transmitted through the suture material or other materials that remain in the wound? A. Contact direct B. Contact indirect C. D. E. 249. A. B. C. D. E. 250. A. B. C. D. E. 251. A. B. C. D. E. 252. A. B. C. D. E. 253. A. B. C. D. E. 254. A. B. C. D. E. 255. A. B. C. D. E. 256. * Implantation Airborne Dust What is the 3rd stage of general anesthesia? excitation * Surgical agonal awakening analgesia What is the 4-th stage of general anesthesia? * Wake excitation analgesia surgical sedation Mask anesthesia relates to: noninhalation conduction anesthesia infiltration anesthesia central pain * Inhalation Endotracheal anesthesia relates to: conduction anesthesia central pain inhalation noninhalation * Infiltration What is the most common scheme of sedation? by Bruno * For Mukovozovy by cervical by Pirogov by Morton The most common scheme for sedation: * Mukovozovym Nick Pirogov Morton Bruno Mukovozov suggested: * scheme sedation mask inhalation anesthesia endotracheal anesthesia neuroleptanalhezia ataralhezia As suggested Mukovozov? A. ataralhezia B. mask inhalation anesthesia C. endotracheal anesthesia D. * Scheme sedation E. neuroleptanalgesia 257. How many hours break in eating patients is mandatory before surgeony? A. 1 B. 3 C. 2 D. 1.5 E. * 6 258. What drug is injected under sedation, which weakens the vagus reaction of the heart, blocking the innervation of the striated muscles of the larynx and prevents laryngospasm? A. analgin B. dimedrol C. * Atropine D. loratydyn E. promedol 259. The drug used for sedation, which reduces vagus reaction blocks innervation of striated muscels larynx and prevents laryngospasm: A. promedol B. loratydyn C. diphenhydramine D. analgin E. * Atropine 260. For neuroleptanalgesia use: A. propanidid B. thiopental sodium C. geksenal D. * Talamonal E. ketolonh 261. What drug is used for neuroleptanalgesia? A. * Talamonal B. thiopental sodium C. ketolonh D. geksenal E. propanidid 262. Which established ongoing preparations used for ataranalgesia? A. * Tramadol B. geksenal C. thiopental sodium D. propanidid E. talamonal 263. For ataranalgesia use: A. geksenal B. propanidid C. D. E. 264. A. B. C. D. E. 265. A. B. C. D. E. 266. A. B. C. D. E. 267. A. B. C. D. E. 268. A. B. C. D. E. 269. A. B. C. D. E. 270. A. B. C. D. E. 271. thiopental sodium * Tramadol talamonal Ketolonh used for: inhalation anesthesia neuroleptanalgesia infiltration anesthesia * Ataranalgesia central pain Why use ketolonh? infiltration anesthesia neuroleptanalgesia * Ataranalgesia central pain inhalation anesthesia Talamonal used for: infiltration anesthesia conduction anesthesia *neuroleptanalgesia inhalation anesthesia central pain Why talamonal is used? * Neuroleptanalgesia inhalation anesthesia ataranalgesia central pain applique anesthesia Thiopental sodium is used for: * Noninhalation anesthesia ataranalgesia neuroleptanalgesia central pain Application anesthesia Why use sodium thiopental? Application anesthesia central pain neuroleptanalgesia ataranalgesia * Noninhalation anesthesia Ftorotanom used for: Application anesthesia conduction anesthesia * Inhalation anesthesia noninhalation anesthesia ataranalgesia Why use ftorotan? A. B. C. D. E. 272. A. B. C. D. E. 273. A. B. C. D. E. 274. A. B. C. D. E. 275. A. B. C. D. E. 276. A. B. C. D. E. 277. A. B. C. D. E. 278. A. B. C. D. ataranalgesia noninhalation anesthesia infiltration anesthesia * Inhalation anesthesia neuroleptanalgesia Nitrogen oxide is used for: neuroleptanalgesia noninhalation anesthesia ataranalgesia * Inhalation anesthesia infiltration anesthesia Nitrous oxide-narcotic substance used for: * Inhalation anesthesia ataranalgesia neuroleptanalgesia noninhalation anesthesia applique anesthesia Why use nitrous oxide? applique anesthesia neuroleptanalgesia ataranalgesia noninhalation anesthesia * Inhalation anesthesia Hexenal used for: applique anesthesia neuroleptanalgesia ataranalgesia * Noninhalation anesthesia inhalation anesthesia Why use geksenal? * Noninhalation anesthesia inhalation anesthesia ataranalgesia neuroleptanalgesia applique anesthesia Propanidid used for: * Noninhalation anesthesia ataranalgesia neuroleptanalgesia inhalation anesthesia applique anesthesia Ketamine hydrochloride is used for: inhalation anesthesia ataranalgesia neuroleptanalgesia * Noninhalation anesthesia E. 279. A. B. C. D. E. 280. A. B. C. D. E. 281. A. B. C. D. E. 282. A. B. C. D. E. 283. A. B. C. D. E. 284. A. B. C. D. E. 285. A. B. C. D. E. 286. A. B. applique anesthesia Why use ketamine hydrochloride? applique anesthesia * Noninhalation anesthesia ataranalgesia neuroleptanalgesia applique anesthesia Etomidate is used for: * Noninhalation anesthesia neuroleptanalgesia ataranalgesia applique anesthesia inhalation anesthesia Why use Etomidate? inhalation anesthesia ataranalgesia neuroleptanalgesia applique anesthesia * Noninhalation anesthesia Diprofol used for: * Noninhalation anesthesia central pain conduction anesthesia infiltration anesthesia ataranalgesia Reason for use diprofol? ataranalgesia * Noninhalation anesthesia central pain conduction anesthesia neuroleptanalgesia Midazolam used for: neuroleptanalgesia central pain Application anesthesia conduction anesthesia * Noninhalation anesthesia Reason for using midazolam? * Noninhalation anesthesia applique anesthesia inhalation anesthesia conduction anesthesia ataranalgesia Sibazon used for: neuroleptanalgesia * Ataranalgesia C. applique anesthesia D. conduction anesthesia E. noninhalation anesthesia 287. Reason for use Sibazon? A. neuroleptanalgesia B. noninhalation anesthesia C. * Ataranalgesia D. infiltration anesthesia E. Application anesthesia 288. What dose before the operation at night for sedation for Mukovozovy give phenobarbital? A. * 0.1 g B. 1 g C. 1.5 g D. 2.5 g E. 0.0001 g 289. Product ketolonha: A. bottle B. * Ampoule C. karpula D. powder E. granules 290. To improve myocardial contractility patients after anesthesia 2-3 days injected polarization mixture: A. Pirogov B. Bershe C. * Lyabori D. Gaucher E. Dodsworth 291. Polarization mixture activates ion transport: A. * Sodium and potassium B. Calcium C. sodium D. potassium E. calcium and fluoride 292. Multi-balanced anesthesia, which is based on the use benzodiazepamy that exhibit tranquilizing effect in combination with analgesics, relaxants to enhance adaptation homeostatic mechanisms in the body: A. neuroleptanalgesia B. * Ataranalgazy C. inhalation anesthesia D. noninhalation anesthesia E. infiltration anesthesia 293. Combination drug for neuroleptanalgesia: A. droperidol B. B. fentanyl C. * Talamonal D. validol E. Sibazon 294. What antiseptics and what concentration should be used to prevent the transfer of infection at work doctor surgeon-dentist in rubber gloves? A. 0.1% "novosept" B. 0.5% "novosept" C. * 1.0% "novosept" D. 1.5% "novosept" E. 3% hydrogen peroxide 295. What antiseptics and what concentration should be used to prevent the transfer of infection at work doctor surgeon-dentist in rubber gloves? A. 0.1% chloramine B. * 0.5% chloramine C. 1.0% chloramine D. 1.5% chloramine E. 2.0% chloramine 296. Which population should assist a dentist in public institutions? A. 2-2.5 thousand B. * 4-4.5 thousand C. 6-6.5 thousand D. 7-8 thousand E. 8-9 thousand 297. How many dental surgeons allocated one position nurse? A. At 0.5 positions dentist-surgeon B. * At 1 post dental surgeon C. By 1.5 positions dentist-surgeon D. At 2 posts dentist-surgeon E. At 3 positions dentist-surgeon 298. How many posts dentists allocated one position nurses? A. 0.25 positions B. 0.5 positions C. * 1 post D. 1.5 positions E. 2 posts 299. How to be dentists, surgeons for surgical department of the organization? A. 3 B. * 6 C. 4 D. 7 E. 8 300. What are the components of the clinical examination of the patient? A. With patient complaints and history of life B. From the history of life and disease C. * From the subjective and objective examination D. From examination of the oral cavity and additional methods of examination E. Since radiography and palpation 301. Which part of the survey include general and local examination? A. The subjective test B. To the history of the disease C. In the history of life D. * The physical examination E. There is no right answer 302. Which part of the survey include medical history and life? A. * The subjective test B. By physical examination C. By local survey D. Additional methods of examination E. There is no right answer 303. What are the components of the local examination of the patient? A. Inspection and palpation of the oral cavity B. Palpation of soft tissue facial C. * Extraoral and intraoral examination D. Intraoral examination E. There is no right answer 304. What is the optimal concentration for the prevention of infection at work surgeon-dentist in rubber gloves? A. * 0.5% chlorhexidine B. 1.0% chlorhexidine C. 1.5% chlorhexidine D. 2.0% chlorhexidine E. 2.5% chlorhexidine 305. What antiseptics and what concentration should be used for prevent transfer infection while working as a dental surgeon in rubber gloves? A. * 2.4% solution pervomur B. 0.5% solution pervomur C. 1.0% solution pervomur D. 1.5% solution pervomur E. 3.0% solution pervomur 306. What antiseptics and what concentration should be used to prevent the transfer of infection while working as a dental surgeon in rubber gloves? A. 1:1000 dyocidy B. 1:2000 dyocidy C. 1:3000 dyocidy D. * 1:5000 dyocidy E. 1:10000 dyocidy 307. Physician dental surgeon must make a report of clinical work per month. Which document shall complete? A. Form 043 B. Form 037 C. * Form 039 D. Form 049 E. There is no right answer 308. What antiseptics and what concentration should be used to prevent the transfer of infection in the absence of opportunities in surgeon dental work in rubber gloves? A. 1% chloramine B. * 2% solution of chlorine bleach C. 0.5% dyocidy D. 3% pervomur E. 5.0% pervomuru 309. What antiseptics and what concentration should be used to prevent the transfer of infection in the absence of opportunities in surgeon dental work in rubber gloves? A. 3.0% hydrogen peroxide B. 5.0% potassium iodide C. 1.0% ammonia D. 1.0% chloramine E. * 2.0% chloramine 310. What antiseptics and what concentration should be used to prevent the transfer of infection in the absence of opportunities in surgeon dental work in rubber gloves? A. 0.1% rn "novoseptu" B. 3.0% rn "novoseptu" C. * 2.4% Mr. pervomuru D. 3% solution pervomuru E. 1.0% Mr. chloramine 311. What refers to special methods of examination used oral surgeon? A. Poll B. Review C. Palpation D. Percussion E. * Cytology 312. What refers to a special survey methods that use oral surgeon? A. Poll B. Review C. Palpation D. * Radiography E. Percussion 313. Which research method should be used to assess the function of chewing? A. Radiography B. Thermometry C. Tomography D. * Mastykatiogarphy E. Thermography 314. What method assess round apical tissues? A. Review B. Palpation C. Test Kulazhenko D. Poll E. * Rentgenography 315. Which method of research should be conducted to evaluate the contractile function of masticatory muscles? A. Rentgenography B. * Gnatodynamometry C. Tomography D. Thermometry E. Thermography 316. What a contrast agent used in sialography? A. 10.0% calcium chloride B. Barium sulfate C. Kseroform D. Iodoform E. * 30.0% iodolipoll 317. What a contrast agent used in sialography? A. * 10.0% Mr. etiotrast B. Barium sulfate C. Kseroform D. Iodoform E. 10.0% Mr. calcium chloride 318. What is the average threshold of excitability pulp electroodontometry in patients with periodontitis? A. 20-30 mA B. 40-50 mA C. 60-70 mA D. 80-90 mA E. * 100-150 mA 319. What is the average threshold of excitability pulp electroodontometry in patients with neuritis of the facial nerve? A. * 3.1 mA B. 5.10 mA C. 15-20 mA D. 25-30 mA E. 35-40 mA 320. What method is evaluated condition round apical tissues? A. Review B. Palpation C. Test Kulazhenko D. * Electroodontometry E. Poll 321. What medical documentation should maintain dental surgeon? A. Medical Book B. Procedural leaf C. Journal of Accounting D. Journal of preventive examinations E. * Medical Card and leaf daily accounting work 322. What research should be conducted in the presence of a history carieted infectious hepatitis? A. Clinical analysis of blood B. Electrolytes Blood C. Cholesterol levels D. * Bilirubin Blood E. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 323. What research should be conducted in the presence of a history carieted infectious hepatitis? A. Clinical analysis of blood B. Electrolytes Blood C. Cholesterol levels D. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate E. * Australian antigen blood 324. What find out by benzidiny sample? A. Sterility of instruments B. The presence of corrosion C. * The presence of residual blood D. The presence of residues of detergents E. The presence of microflora 325. How many doctors dental clinic provides anesthesiologist? A. At 10 B. At 15 C. * At 20 D. At 25 E. At 5 326. How long does it sterilize dental mirror in 6% solution or hydrogen peroxide at room temperature? A. 30 minutes. B. 60 minutes. C. 120 minutes. D. * 180 min. E. 240 minutes. 327. How many beds are allocated one operating table in the dental hospital? A. 10-20 B. 20-30 C. * 30-40 D. 40-50 E. 50-60 328. How many categories are distinguished dental clinics? A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 5 E. * 6 329. Which following below operations related to unplanned interventions? A. Replantation B. Resection of the root apex C. * Operation tooth D. Sequestrectomy E. . The surgical treatment of periodontal diseases 330. What part of dental patients require outpatient treatment? A. 75-88% B. 84-90% C. 91-95% D. 93-97% E. * 98-99% 331. What is the mode of transmission, in which the infection is transmitted through the suture material or other materials that remain in the wound? A. Contact direct B. Contact indirect C. * Implantation D. Airborne E. Dust 332. What form of dental care the most accessible to the public? A. * State budget B. Private C. Cooperative D. Self-supporting E. All of the above 333. What concentration district chlorhexidine bigluconate used for processing surgeon’s hand? A. * 0.5% B. 1% C. 2% D. 3% E. 1% 334. The surgeon handles hand 96% p-m alcohol for 10 min. Which method of treatment arms he used? A. Method Fyurbrinhera B. Method Alfred C. Method Spasokukotsky-Kochergina D. * Method Bruno E. Scrubbing hibitanom 335. How many minutes should boil surgical instruments in the sterilizer? A. 20 minutes. B. 30 minutes. C. 40 minutes. D. 50 minutes. E. * 60 min. 336. As determined by ortolidic sample? A. * The presence of residual blood B. The presence of corrosion C. Sterility of instruments D. The presence of residues of detergents E. The presence of microflora 337. What regulatory area set for operating one dental chair dental clinics II category? A. 18 m2 B. 20 m2 C. * 14 m2 D. 25 m2 E. 23 m2 338. What are the methods of antiseptics? A. Mechanical B. Physical C. Biological D. Chemical E. * All of the above 339. On which day the patient home with a leaf injury sick if it after 12 after injury in the blood of 0.15% ethanol? A. From the first day after injury B. On the third day after injury C. . * Does not seem at all D. D. On the sixth day after injury E. On the sixth day after treatment in the medical institution 340. What part of dental patients require hospital treatment? A. 0.5-1% B. * 1-1.5% C. 1.5-2% D. 2-2.5% E. 2.5-3% 341. What concentration district iodopyrony used for treatment of hand surgeony? A. 0.5% B. * 1% C. 2% D. 4% E. 3% 342. How many medical positions in the clinic V category? A. 5.7 B. 7.11 C. * 10-14 D. 12-15 E. 14-17 343. What sanitary standard operating area for 1 dental chair (operating table) in the dental clinic 1 category? A. 14m2 B. 16m2 C. 20m2 D. * 23m2 E. 27m2 344. What is the main structural link dental units? A. * Dentist B. Dental office C. Dental clinic D. Dental hospital E. Dental clinic 345. Which following below operations related to the planned intervention? A. Operation tooth B. Operation disclosure phlegmon C. Splinting at the turn of the jaw D. * Resection of the root apex E. Reduction of dislocation of the mandible 346. Surgeon wash your hands with warm running water and soap for a minute, then disinfection in 0.5% sodium amonii acid for 3 min. in the two basins. Then drained them sterile towel and processed the alcohol for 5 minutes. What a way to handle hands employed doctor? A. Method Fyurbrinhera B. Method Alfred C. * Method Spasokukotsky-Kochergina D. Method Bruno E. Scrubbing hibitanom 347. What is using phenolphthalein sample? A. Sterility of instruments B. The presence of corrosion C. * The presence of residues of detergents D. The presence of residual blood E. The presence of microflora 348. What method perform sterilization gloves? A. Autoclaving B. Boiling C. Machining under running water D. Processing 2% chloramine E. * All of these methods 349. On which day the patient home with a leaf injury temporary disability, if he is not found intoxicated? A. From the first day after injury B. On the third day after injury C. On the sixth day after injury D. * On the sixth day from the date of application in medical facility E. Not seem at all 350. What is the alcohol concentration of the solution used for skin treatments surgical field? A. 96% B. 50% C. 40% D. * 70% E. 80% 351. What is the optimal concentration hydrogen peroxide for treatment of oral cavity before removing a tooth? A. * 1. 3% B. 2. 2% C. 3. 0.5% D. 4. 1% E. 5 .4% 352. What is the minimum area of operating on the same table? A. 22-28 m2 B. 26-32 m2 C. 32-34 m2 D. 36-40 m2 E. * 36-48 m2 353. How is sterilization of cutting forcepss? A. * Chemical treatment of 96% alcohol B. Boiling C. Autoclaving D. Processing in dry-heat closet E. The method of roasting 354. Patient asked with complaining of painful ulcers presence left cheek. Diagnosed squamous cell carcinoma of the face, the second stage. What documents are required? A. * Message Form 090 / O B. Protocol Forms 0242 / O C. Sending in CCCs D. Control card 6 / O E. Sending in EDB 355. How many medical positions in the clinic III category? A. 11 – 14 B. 14-17 C. 17-20 D. * 20-24 E. 24-28 356. At that time held general cleaning surgical department? A. At least 2 times a week B. * At least 1 time a week C. At least 3 times a week D. Everyday E. Two times a day 357. The surgeon thoroughly wash hands, forearms undernail spaces and within 10 minutes the two sterile toothbrushes and soap. Hands thoroughly drained sterile cloth, then for 5 minutes handles 96% alcohol. What a way to handle hand applied surgeon? A. Method Fyurbrinhera B. * Method Alfeld C. Method Spasokukotsky-Kochergina D. Method Bruno E. Scrubbing hibitanom 358. What is the optimal concentration district potassium permanganate to handle oral befor extraction tooth? A. 1/500 B. * 1/1000 C. 1/5000 D. 1/10000 E. 1/20000 359. What are the criteria for assessing the health of sterilization of dental clinics? A. Bacteriological control B. These accounting journal sterilization C. These visual control of sterilization D. Determination of disinfectant solutions E. * All answers are correct 360. The wound was washed with 0.06% chlorhexidine solution bigluconate and put it in a rubber graduate. What kinds of antiseptics used in the patient? A. Physical B. * Physical and chemical C. Biological and chemical D. Physical and biochemical E. Chemical and biological 361. On which day letter issued disability fractures of the mandible in the area of articular process if the injury received in the workplace? A. * On the 1st day B. On the 3rd day C. On the 2nd day D. With the 6-day E. Not seem at all 362. On admission to the dentist-surgeon turned victim with limited thermal burns skin face III degree. Determine where treatment must be given affected. A. Hospitalized in the casualty department B. Out in the dentist-surgeon C. * Admitted to the burn center (branch) D. Ambulatory surgical department clinics E. Ambulatory emergency station in the place of residence 363. In patients with deep burns of the face and trunk on the affected area for more than 10% originated burn shock. In which department should be hospitalized victim? A. In therapy department B. * In the intensive care unit at the burn center C. In the surgical ward D. In the maxillofacial department E. In the casualty department 364. In the dental clinic turned sick. After physical examination oral surgeon clinics were diagnosed abscess of the right submandibular region. What should be further tactics of the doctor? A. Hold punction removal of purulent exudate B. Assign medication and physiotherapy C. Assign medication with dynamic observation D. Conduct section phlegmon in the clinic E. * Immediately send the patient to a specialized health care facilities 365. What applies to chemical methods of sterilization and disinfection? A. Boiling B. High temperature C. Ultrasound D. * Compounds of inorganic and organic origin E. Antibiotics 366. What solutions are approved for use in the antiseptic treatment of operating in the face? A. ascorbic acid B. 96% ethanol C. 5% iodine D. 6% hydrogen peroxide E. * Iodonate 367. Dentist after the internship gets a job in a specialized institution providing care to HIVinfected and AIDS patients. What order should he carefully processed for organizing dental care these patients? A. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CAREC of Ukraine № 302 of 27.12.1999, the B. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CAREC Ukraine № 405 vid13.112001 was C. * MINISTRY OF HEALTH CAREC of Ukraine № 120 from 25.05.2000, the D. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CAREC Ukraine № 566 of 23.11.2004, the E. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CAREC of Ukraine № 305 of 22.11.2000, the 368. Dentist at the end of the work shift must complete a diary account of the dentist. In what order MINISTRY OF HEALTH CAREC Ukraine it can read the instructions for completing this accounting and statistical form? A. * № 181 of 15.05.2001r. B. № 455 from 13.11.2001r. C. № 344 from 15.12.2000r. D. № 302 from 27.12.1999r. E. № 305 from 22.11.2000r. 369. The presence of statistical documents is mandatory for clinical patient? A. * Form number 037 B. Form number Form number 043 + 030 C. Form number 030 D. Form number 039 E. Form number 043 370. By what statistical document can evaluate a doctor for a month? A. Form number 037 B. Form number 049 C. Form number 043 D. * Form number 039 E. Form number 030 371. What is the method of examination in which the conduct tap the tooth tip or tweezers? A. Palpation B. Thermodiagnostic C. * Percussion D. Electroodontodiagnosis E. Radiography 372. Arrange a new dental clinic 1-category. How many staff units Surgeons - Dentists provided in this clinic? A. 5.4 staff units B. * 3.2 staff units C. 4.3 staff units D. 2.1 staff units E. 6.5 staff units 373. The clinic, which employs 20 dentists who perform planned and unplanned operations have fixed operating days. How many posts of doctors - anesthetist provided in this clinic? A. 2 posts B. 3 posts C. 4 posts D. * 1 post E. Over 4 posts 374. Which of the following is one of the additional methods of examination? A. * Radiography, biomicroscopy B. Definition of bite C. Depth measurement vestubulum mouth D. Determining the degree of mobility E. All answers are correct 375. . What is the X-ray examination in which you can get images of a certain layer of bone? A. Stereorentgenography B. * Tomography C. Panoramic radiography D. Radioscopy E. Radioviziography 376. What is the method for studying the circulation, based on the detection of the optical density of the tissues? A. Sample Kulazhenko B. Fluorescent diagnostics C. * Photopletizmography D. Electroodontodiagnosis E. There is no right answer 377. What is the method of studying tissue oxygen balance? A. Rheography B. Fluorescent diagnostics C. Sample Kulazhenko D. * Polarography E. Photopletizmography 378. What method of diagnosis is carried out using the apparatus pulptesting? A. Photopletizmorgaphy B. C. D. E. 379. A. B. C. D. E. 380. A. B. C. D. E. 381. A. B. C. D. E. 382. A. B. Fluorescent diagnostics Sample Kulazhenko * Electroodontodiagnosis Polarography What is included in the standard set for oral examination? Mirror, trowel Probe, Forceps * Mirror, probe, tweezers Spatula, probe, mirror There is no right answer On what basis is based subjective test? Data given local * Patient complaints Additional methods of examination Results intraoral examination All answers are correct What is the method of feeling the body or its individual parts? Percussion Biomicroscopy * Palpation Radiography Probe What is a fluorescent diagnostics? The method of studying blood flow, based on the detection of optical density tissue * The method is based on the ability of tissues to emit light when exposed to ultraviolet rays C. The method is based on the rate of formation of hematoma D. Method of studying the oxygen balance of periodontal tissue E. There is no right answer 383. What is the method of in vivo blood flow, based on the detection pulse oscillation? A. * Rheography B. Fluorescent diagnostics C. Electroodontodiagnosis D. Polarography 384. Indicate by International Classification symbols of permanent teeth: the first upper right preolars, the second lower left molar: A. 37, 24 B. 41, 37 C. 28, 15 D. 34, 37 E. * 14, 37 385. What document form 037? A. Ambulatory patient card B. Leaf for the monthly report of C. * Leaf daily examination of patients D. Leaf accounting of physician podiatrist E. 386. A. B. C. D. E. 387. A. B. C. D. E. 388. A. B. C. D. E. 389. A. B. C. D. E. 390. A. B. C. D. E. 391. A. B. C. D. E. 392. A. B. C. D. E. 393. A. B. There is no right answer What are scraping? * Biomicroscopy research Microbiological studies X-ray study Fluorescent diagnostics There is no right answer What are the tongs to remove the canines of the upper jaw? S-shaped with a thorn * Direct Rostral root Bent on a plane Rib bented What are the tongs to remove the third molars of the upper jaw? Direct S-shaped with a thorn S-shaped with cheeks that converge * Bayonet with rounded cheeks that do not converge Rostral What is the forceps for removal of third molars of the upper jaw? Direct curling * Bayonet crowns curling S-shaped forceps with spike Rib bented with cheeks that converge Bent on a plane What are the tongs to remove the roots of maxillary incisors? Rostral * Straight from the cheeks, converging S-shaped with cheeks that converge S-shaped with a spike right Bent on a plane What is the forceps to remove the roots of mandibular incisors? * Rib bented Rib bented forceps with spike S-shaped tongs with cheeks that converge S-shaped tongs with cheeks that do not converge S-shaped with a spike right What are the tongs to remove the roots of mandibular incisors? * Rib bented with cheeks that converge Rib bented with cheeks that do not converge S-shaped forceps with spike Bayonet tongs with cheeks that converge Rib bented forceps with spike What are the tongs to remove the canine mandible? Rib bented with cheeks that converge S-shaped forceps with spike C. D. E. 394. A. B. C. D. E. 395. A. B. C. D. E. 396. A. B. C. D. E. 397. A. B. C. D. E. 398. A. B. C. D. E. 399. A. B. C. D. E. 400. A. B. C. D. E. 401. * Rib bented with cheeks that do not converge Horizontal Bore Bayonet tongs with cheeks that converge What are the tongs to remove the mandibular premolars? Rib bented with cheeks that converge S-shaped forceps with spike * Rib bented with cheeks that do not converge Bayonet tongs with cheeks that converge S-shaped with a spike right What are the tongs to remove the 1st and 2nd mandibular molars? Rib bented with cheeks that converge S-shaped forceps with spike Horizontal Bore * Rib bented with cheeks that do not connect and studs Bayonet tongs with cheeks that converge What are the tongs to remove the 3rd mandibular molar? Rib bented with cheeks that converge S-shaped forceps with spike * Horizontal Bore Rib bented with cheeks that do not converge Bayonet tongs with cheeks that converge Which instrument remove the lower third molar? Direct forceps Crochet Limberg S-shaped forceps * Direct elevator S-shaped forceps with spike What is the forceps to remove the roots of the teeth of the mandible? Trowel Direct curling * Rib bented with cheeks that converge Rib bented forceps with spike Horizontal Bore What is the forceps to remove the roots of the teeth of the mandible? Direct curling Needle Holders Rib bented forceps with spike Horizontal crown forceps * Rib bented with cheeks that converge Which forceps is required to remove fracture roots of the lower teeth and upper jaw? * Direct elevator Direct curling Needle Holders Hook Limberg Horizontal Bore curling Which instrument remove the lower third molar? A. B. C. D. E. 402. A. B. C. D. E. 403. A. B. C. D. E. 404. A. B. C. D. E. 405. A. B. C. D. E. 406. A. B. C. D. E. 407. A. B. C. D. E. 408. A. B. C. D. Direct forceps S-shaped forceps Crochet Limberg * bent on a plane Rib bented with cheeks that converge Which instrument remove the lower third molar? Direct forceps Crochet Limberg Elevators Volkova * Direct elevator S-shaped forceps How to call tongs to remove the 1-st and 2-nd left maxillary molars? S-shaped: With cheeks that converge From left spike With cheeks that do not converge * with spine right With two studs What are the tongs to remove the maxillary incisors? Direct root * Straight Bore Rib bented root Curved on a plane S-shaped tongs What are the tongs to remove the roots of maxillary incisors? Bayonet with cheeks that converge Rib bented root Bent on a plane S-shaped with cheeks that do not converge * Direct forceps What are the tongs to remove the roots of maxillary premolars? * S-similar to the cheeks, converging S-shaped with a thorn Rostral root Bent on a plane Direct root What are the tongs to remove premolars of the upper jaw? Bayonet Direct root S-shaped with a thorn Rostral root * S-similar to the cheeks that do not converge How to call tongs to remove the 1-st and 2-nd right maxillary molars? With cheeks that converge * The spike left With cheeks that do not converge With thorn case E. 409. A. B. C. D. E. 410. A. B. C. D. E. 411. A. B. C. D. E. 412. A. B. C. D. E. 413. A. B. C. D. E. 414. A. B. C. D. E. 415. A. B. C. D. E. 416. A. B. Direct Crowns What are the tongs to remove the roots of maxillary incisors? * Direct root Rostral root Bent on a plane S-shaped with cheeks that do not converge S-shaped with a thorn Which teeth are removed with forceps straight? Molars Premolars Wisdom Teeth * Maxillary incisors Cutters mandible Which teeth removed S-shaped forceps? The roots of teeth Mandibular molars Molars of the upper jaw * Premolars of the upper jaw Cuspid of the maxilla Which teeth removed S-shaped forceps with spike? Cutters 3rd molars * Molars of the upper jaw Premolars of the upper jaw Cuspid of the maxilla Which teeth are removed with forceps rib bented with cheeks that converge? Cutters mandible Mandibular molars Premolars of the upper jaw * The roots of the teeth of the mandible Cuspid of the maxilla What are the teeth on the lower jaw is removed with forceps rib bented cheeks not agree? * Cutters First molar The roots of teeth Second molar Third molar When you remove the roots of the teeth used corner elevator? Cuspid Cutters Premolars The roots of teeth * The roots of molars 169. What signs have tongs to remove the upper wisdom teeth? Bayonet forceps with narrow cheeks that do not merge Direct tongs, with broad cheeks with stud C. D. E. 417. A. B. C. D. E. 418. A. B. C. D. E. 419. A. B. C. D. E. 420. A. B. C. D. E. 421. A. B. C. D. E. 422. A. B. C. D. E. 423. A. B. C. D. E. Direct tongs, with broad cheeks that do not merge * Bayonet tongs, with broad cheeks, which are barrel shape, and have no spines S-shaped tongs What signs have tongs for removing the lower wisdom teeth? Forceps with broad cheeks, which are bent on the edge Forceps with broad cheeks, one of which is a thorn Pinch, bent on a plane with wide cheeks that do not merge and have a spike on each forceps S-shaped tongs * Pinch bent on a plane with wide cheeks that do not merge and have one spike What signs have tongs to remove the lower molars? Rib bented with wide cheeks that are bent on a plane Rib bented forceps with broad cheeks, one of which is a thorn * Rib bented , with wide cheeks that do not merge and have a spike on both cheeks Forceps, curved on the edge, with cheeks of medium width, not merge S-shaped tongs What signs have tongs to remove the lower canines and premolars? Rib bented forceps with broad cheeks with spikes * Rib bented with cheeks middle without spikes that do not merge Rib bented with narrow cheeks to merge Direct tongs, with medium cheeks, that connect S-shaped tongs What signs have tongs to remove the lower incisors? Rib bented forceps with broad cheeks with spikes on both cheeks Rib bented forceps with spike from the outside * Rib bented with narrow cheeks that that do not connect Rib bented with narrow cheeks to merge S-shaped tongs What signs have tongs to remove premolars upper jaw? Direct forceps, whose cheeks that do not connect * S-like pincers on cheeks without spikes that do not merge Bayonet forceps with narrow cheeks Straight forceps with broad cheeks, which merge Rib bented forceps with spike from the outside What are the signs of forceps to remove the roots of the mandible? Rib bented cheeks with medium width * Rib bented with narrow cheeks to merge Rib bented with narrow cheeks that do not merge Rib bented , bent on a plane Rib bented forceps with spike from the outside How to recognize the left elevator angle? Cheeks bent down working plane cheeks case * Cheeks bent down working plane left cheeks Cheeks bent to the left, above the working plane cheeks Cheeks bent upwards, working plane left cheeks Cheek goes straight 424. How to recognize the right elevator angle? A. * Cheeks bent down working plane cheeks case B. Cheeks bent down working plane left cheeks C. Cheeks bent to the left, the working plane cheeks from the top D. Cheeks curved top, working plane cheeks case E. Cheek goes straight 425. Why use the elevator Leklyza? A. To remove the upper molars B. To remedy zygomatic arch fracture and bone C. To remove the lower molars D. * To remove the 8 and 8 teeth of the mandible E. To remove the maxillary incisors 426. What are the roots of the teeth and can be removed by direct elevator? A. The roots of one root tooth B. * All teeth and their roots C. Molars of the upper jaw D. The roots of the teeth of the upper jaw E. Maxillary incisors 427. What movements performed with forceps when removing premolars of the upper jaw? A. Rotation B. Rotation and luxate in palatal direction C. * Luxate in vestibular-oral direction D. Luxate in the vestibular direction and rotation E. Rotation and traction 428. What movements forceps performed at extracted lower cuspid? A. Rotation B. * Rotation and luxate C. Luxate in vestibular-oral direction D. Luxate in media-distal and vestibular-oral direction E. Traction 429. What movements performed with forceps when removing cutters and cuspid of a upper jaw? A. Impose forceps and loosen the tooth in the palatal and vestibular direction B. * Impose tongs, fix, luxate in vestibular-oral direction, combining with rotary movements C. Apply tongs, fix them, and do rotation D. Apply tongs, hold, and abruptly down to remove tooth E. Apply and pull the tooth down 430. When removing a tooth on the upper jaw most likely perforated maxillary sinus floor? A. * First molar B. Lateral incisors C. Cuspid D. First premolars E. Second premolars 431. What sequence to be followed when removing 37 tooth forceps? A. Overlay, promotion, luxate inward and outward traction B. Overlay, promotion, closing, luxate, rotation, traction C. * Overlay, promotion, closing, luxate inward and outward traction D. Overlay, promotion, closing, luxate outside and inside, traction E. Overlay, luxate, traction 432. Which techniques to use when removing 16 tooth forceps? A. Overlay, promotion, closing, luxate, rotation, traction B. Overlay, closing, luxate inward and outward traction C. * Overlay, promotion, closing, luxate inward and outward traction D. Overlay, promotion, closing, luxate outside and inside, traction E. Overlay, luxate, traction 433. At what level should be at the head of the patient when removing the teeth on the lower jaw? A. At the level of the maximum lowered seat B. At the level of the shoulder girdle doctor C. * At the level of the elbow joint doctor D. At the waist doctor E. At the level of the head doctor 434. At what level should be at the head of the patient when removing the teeth on the upper jaw? A. At the level of the head doctor who removes teeth B. At the level of the elbow joint doctor C. At the level of the chest physician D. * At the level of the shoulder girdle doctor E. At the waist doctor 435. What is the position of the head of the patient, when you remove the front teeth of the upper jaw? A. Chairman of the patient should be returned to the doctor B. Chairman of the patient should be returned to the doctor and cast C. * Chairman of the patient should be at the level of the shoulder girdle and see a doctor straight D. Chairman of the patient should be returned to the left E. Chairman of the patient should be returned to the doctor and lowered 436. What is the position of the head of the patient when removing the teeth of the upper jaw on the left? A. * Chairman of the patient should be at the level of the shoulder girdle doctor and just returned to him B. Chairman of the patient should be at the level of the elbow joint doctor and returned to the left C. Chairman of the patient should be as abandoned due to the altitude D. Chairman of the patient should be at the level of the elbow joint doctor and returned to him E. Chairman of the patient should be returned to the doctor and cast 437. What is the position of the head of the patient in removing the teeth of the mandible? A. * Chairman of the patient should be at the level of the elbow joint and see a doctor straight B. Chairman of the patient should be at the level of the shoulder girdle doctor and returned to the left C. Chairman of the patient should located at elbow joint doctor and returned to the right D. Chairman of the patient should be level with the face of the doctor and returned to him E. Chairman of the patient should be returned to the doctor and cast 438. What is the position of the head of the patient when removing front teeth of the mandible? A. The patient sits on a chair with maximally lowered head thrown B. Chairman of the patient at the level of the shoulder girdle and the doctor turned to the left C. Chairman of the patient is at elbow joint doctor and returned to the left D. * Chairman of the patient is at the elbow joint doctor and returned to the left E. Chairman of the patient should be level with the face of the doctor and returned to him 439. What is the position of the left hand of the physician in removing the teeth of the mandible on the left? A. Left hand turns his head to the right and hold her in that position B. Returns the head of the patient to the doctor and forefinger assigns cheek C. The index finger of his left hand removes the medial tongue patient D. * The index and thumb left hand covers the alveolar bone of the mandible, in the area where deletes, and all other covers margin of the low jaw E. Keep the lower jaw of the patient 440. What is the position of the left hand of the physician in removing teeth of the upper jaw on the left? A. Holds the head of the patient hand on the left zygomatic area B. * Includes index finger outside, and a large part of the palatal alveolar bone in the area of the tooth that removes C. The index finger of his left hand removes cheek out D. Left hand helps hold patient's mouth in the open state E. Keep the lower jaw of the patient 441. What are the stages of the operation consists tooth extraction? A. With medical preparation of the patient, forceps and tooth extraction B. * Forceps, promotion, fixation, or luxate rotation and traction C. From the psychological and emotional preparation of the patient, forceps and tooth extraction D. With antiseptic preparation of the oral cavity, forceps and tooth extraction E. There is no right answer 442. What are ways to remove the teeth? A. Using forceps B. Using forceps and elevator C. * The typical and atypical D. With elevator and drill E. One-step and two-step 443. What are the roots of the teeth and can be removed by direct elevator? A. The roots of one root tooth B. Molars of the upper jaw C. * All teeth and their roots D. The roots of the teeth of the upper jaw E. Premolars of the upper jaw 444. A. B. C. D. E. 445. A. B. C. D. E. 446. A. B. C. D. E. 447. A. B. C. D. E. 448. A. B. C. D. E. 449. A. B. C. D. E. 450. A. B. C. D. E. 451. A. B. C. What is the most expedient forceps while removing fragment distal root of tooth 46? * Left elevator . Right elevator Direct elevator Rib bented with cheeks that converge Elevator Leklyza Which forceps to use when removing 21 teeth? Direct elevator * Direct curling Beak pliers Circling bent on plane Elevator Leklyza What forcepss needed to remove the 16 tooth? Direct elevator and bayonet tongs with cheeks that converge Direct elevator and S-shaped tongs with cheeks that converge * Direct elevator and bayonet tongs with cheeks that do not converge Direct elevator and S-shaped tongs with spines on vestibular Corner elevator Which forceps to use when removing roots 17 tooth? S-shaped tongs Dextral Straight forceps with cheeks that converge Direct forceps with cheeks that do not converge * Bayonet Forceps Elevator Leklyza Which forceps you choose to remove the 17 tooth? * Bayonet crowns curling Bayonet root curling S-shaped tongs Direct curling Elevator Leklyza With the help of forceps can remove the root of the tooth 28? * Bayonet Forceps Beak pliers Tongs for eight upper teeth Direct curling Elevator Leklyza What instruments are removed deeply broken medial root of 47 tooth? Direct elevator * Right angled elevator Left corner elevator Elevators Leklyza Diret forceps What tongs remove roots mandibular molars? S-shaped forceps, whose cheeks merge * Bayonet forceps, whose cheeks merge Bayonet forceps, cheeks that do not merge D. Direct forceps, whose cheeks merge E. Bented on a plane 452. What tongs remove roots front group of teeth of the upper jaw? A. S-shaped forceps with spike on one forceps B. Direct forceps with narrow cheeks that do not merge C. * Bayonet forceps with narrow cheeks that merge D. Direct forceps with broad cheeks that do not merge E. Bayonet forceps with cheeks that do not merge 453. What to do when the bottom perforation maxillary sinus after tooth extraction and the absence of inflammation in it? A. Hold maxilla sinustomy B. Dynamic observation C. Rinse sinus antiseptic D. * Close perforation hole flap of cheek E. Do Nothing 454. What is a direct complication during removal of the 3rd lower molar? A. Trismus B. * Bleeding C. Paresis of facial nerve D. Osteomyelitis of the mandible E. Alveolitis 455. What are the teeth on the lower jaw removed Leklyza elevator? A. Fangs B. Cutters C. Premolars D. * The third molars E. 1-st and 2-nd molars 456. How to enroll with an intact tooth, which accidentally dislocate when removing damaged roots nearby? A. Discarded and did not speak to the patient B. Soothe patient and tooth paste to their place in the alveoli C. * Hold endodontic intervention, introduce a tooth in the alveoli and fix his tire bracket D. Promise patient that the tooth is restored prosthetics E. Insert the tooth into the alveoli and fix his tire 457. What tactics doctor at after extraction profuse bleeding from the alveoli? A. Enter Continuous IV 10% Mr. calcium chloride B. In the transitional fold enter 0.1% Mr. adrenaline C. Cover up alveoli iodoform powder D. Compress fingers edge hole E. * Tight for iodoform tampon alveoli, which permeated aminocaproic acid 458. Tactics doctor with dislocation of the mandible during the removal of the lower molars? A. Apply circular bandage bandage with a recommendation not to talk B. Immediately hospitalized patient C. By clicking on the chin upwards set dislocation D. Call the doctor therapist E. * Wrapped cloth thumbs of both hands and pressing them on the molars low jaw down and back set dislocation 459. What complication has led to numbness in the lower lip and chin after extract of the 3rd molar? A. * Trauma inferior alveolar nerve B. Hematoma C. Alveolus D. Dislocation of the mandible E. Bleeding 460. What drug tactic is prevention of alveolitis? A. Rinse alveoli p-m antibiotic B. * Compress edges alveoli and trace formation bleed bunch C. Complete alveoli iodoform swab D. Put cold on the soft tissue of the jaws E. There is no right answer 461. How to diagnose a missing root during removal? A. Palpable B. Conduct audit of alveoli C. Hold nasooral test D. * Make radiography E. All answers are correct 462. What led to the fracture of the palatal root 6 tooth during its removal? A. Luxation in vestibular side B. Fixation forceps on coronal tooth C. * Rotation during removal D. Fixation forceps on the edge of the alveolar process E. There is no right answer 463. What is the most characteristic symptom of the disclosure maxilla sinus during extraction tooth? A. Sharp pain attack-like maxilla B. * Positive test nasooral C. Pathological mobility alveolar bone D. No discharge from the alveoli E. There is no right answer 464. What complication has resulted in failure to close his mouth after tooth extraction? A. Fracture of alveolar process B. Fracture of cervical articular process C. * Dislocation of the mandible D. Fracture of mandible E. There is no right answer 465. How to stop bleeding from vessels of the mucous membrane in the area of alveoli tooth removed? A. Tamponade alveoli B. Compress edges alveoli C. Introduce 0.5 ml. 0.1% district adrenaline subcutaneously D. * Impose catgut seam E. All answers are correct 466. What tactics in pushing roots in maxilla bosom? A. Remove using a spoon curatage B. Remove using dental hook C. * Refer the patient to the hospital D. Close fingers nostril and ask the patient to blow nose E. All answers are correct 467. What do I need to do at the bottom of the maxillary sinus perforation? A. Tamponade hole iodoform turundas B. Suturing combination C. Maxilla sinusotomy with simultaneous plastic combination D. Maxilla sinusotomy by Kolduelom-Luc with simultaneous plastic combination E. * All answers are correct 468. What complication most often occurs during tooth extraction? A. Fracture of alveolar process B. Dislocation adjacent tooth C. * Fracture of tooth root D. Dislocation of tooth antagonist E. There is no right answer 469. After that period begins phase wound epithelialization after extraction? A. After 48-72 h. B. After 3-4 days C. After 6-7 days D. * After 12-14 days E. After 1 month 470. To close the connection, which arose from the maxillary sinus during extraction of the tooth?A. Good squeeze alveoli and put his fingers squeezing the swab A. B. At the edges of the alveoli stitch B. C. * Develop and mobilize mucous oxide flap and stitched alveol C. D. By tampon alveoli gauze cloth D. There is no right answer 471. How to stop the bleeding edge after extraction walls of the alveoli? A. Enter patient vikasol B. Put cold to the area of the jaw C. * Tongs squeeze edge alveoli D. Apply squeezing bandage E. All answers are correct 472. What is the main type of anesthesia used during surgery tooth extraction? A. * Local B. General (anesthesia) C. Combined D. Neuroleptanalgesia E. Application 473. Pregnant patient to remove 28 tooth. Which anesthetic should be used to remove this tooth? A. * Articaine without vasoconstrictor B. Skandonest of vasoconstrictor C. Articaine with vasoconstrictor D. Lidocaine 2% with vasoconstrictor E. General anesthesia 474. What is the best method of anesthesia during surgery at pericoronaritis? A. Infiltration anesthesia B. General anesthesia C. Stem anesthesia D. Application anesthesia E. * Regional anesthesia for Bershe-Dubovy 475. What anesthetic is used to injection anesthesia during tooth extraction? A. 0.5% solution of novocaine B. 1.0% solution of novocaine C. 0.25% solution of novocaine D. * 2.0% lidocaine E. 10.0% solution of lidocaine 476. What is the concentration of novocaine is optimal for conduction anesthesia during tooth extraction? A. 0.5% solution of novocaine B. 1.0% solution of novocaine C. 0.25% solution of novocaine D. 10.0% Novocaine E. * 2.0% Novocaine 477. What is the maximum allowable single dose of 1.0% solution of novocaine? A. 10.0 ml. B. 20.0 ml. C. 50.0 ml. D. 75.0 ml. E. * 100.0 ml. 478. Who made a significant contribution to the development of ways of conduction anesthesia, maxillofacial area? A. Yu.Yi.Bernardskyy, Ye.V.Hotsko, O.Ya.Malevych B. V.I.Vakulenko, O.V.Rybalov, OMSolntsev C. * S.N.Vaysblat, M.M.Vaysbrem, P.M.Yehorov D. O.I.Yevdokymov, H.A.Vasylyev, H.P.Ruzyn E. I.M.Hot, M.F.Danylevskyy 479. 234. What drug substance used for non-injecting methods of local anesthesia? A. Analgin B. Anestezin C. Novocaine D. * Dikain E. Sombrevin 480. 235. What drugs are used for the prolongation of local anesthetics? A. Analgin B. Amidopyrine C. * Adrenaline D. E. 481. A. B. C. D. E. 482. A. B. C. D. E. 483. A. B. C. D. E. 484. A. B. C. D. E. 485. A. B. C. D. E. 486. A. B. C. D. E. 487. A. B. C. D. E. 488. A. Timalin Sulfadimetoksin Which drug spend a color sample of Novocain? Furatsillina Rivanol Peroxide * Potassium permanganate Alcohol What drug is used for prolonged local action anesthetics? Analgin Amidopyrine * Ephedrine Sulfadimetoksin Timalin Which types of shared local anesthesia? Inhaler and noninhalation * Injecting and non-injecting Intravenous and intramuscular Neuroleptanalgesia and anesthesia Ataranalgesia and audio anesthesia Which of the following anasthetics belong to the second generation? Ubistezyn * Novocaine Lidocaine Trimecaine Cocaine What of these anesthetics belongs to the third generation drugs? Dikain Cocaine * Lidocaine Ubistezyn Ultrakain Which types of anesthesia divided? * Inhaled and noninhalation Physical and chemical Application and instilation Central and peripheral Local and conductor Which of the following drugs used for inhalation anesthesia? Hexenal Lidocaine Ketamine Septanest * Nitrous Oxide How is the anesthesia by which injected a mixture of neuroleptic analgesic? Ataranalgesia B. Audioanesthesia C. * Neuroleptanalgesia D. Acupuncture anesthesia E. Instilation anesthesia 489. Which of the following drugs used for anesthesia noninhalation? A. Ether B. * Ketamine C. Nitrous Oxide D. Ftorotanom E. Hexenal 490. What's listed below is general anesthesia? A. * Intravenous anesthesia B. Stem anesthesia C. Spinal anesthesia D. Perirenal blockade E. Epidural anesthesia 491. The patient suffers from epilepsy. Under what kind of anesthesia is necessary to the operation? A. * Under endotracheal anesthesia B. Under anesthesia mask C. Under anesthesia nasofarynx D. Under infiltration anesthesia E. Under anesthesia 492. What method of anesthesia is safe and nayibilsh enough yefektyvnym in outpatient dental practice for the treatment of patients who undergo treatment in fear of the dentist? A. Audioanesthesia B. Neuroleptanalgesia C. * Ataranalgesia D. Endotracheal anesthesia E. Hypnosis 493. What preparatvykorystovuyut in outpatient dental practice, during intravenous anesthetic thiopental sodium solution to avoid or prevent laryngo-and bronchospasm? A. Diphenhydramine B. Dyprazin C. Adrenalin D. Fentanyl E. * Atropine 494. What are the different types of anesthesia? A. * Inhaled, noninhalation, neuroleptanalgesia B. Inhaled, mask, endotracheal C. Inhaled, noninhalation, endotracheal D. Endotracheal, mask, neuroleptanalgesia E. Neuroleptanalgesia, mask, inhalation 495. In how many steps performed premedication? A. One-step B. In two stages C. D. E. 496. A. B. C. D. E. 497. A. B. C. D. E. 498. A. B. C. D. E. 499. A. B. C. D. E. 500. A. B. C. D. E. 501. A. B. C. D. E. 502. A. B. C. D. E. 503. * The three stages In four stages In the five stages What is the indications for anesthesia in a dental clinic? Acute respiratory infection Acute inflammation Endocrine pathology * Diseases of the CNS Cardiovascular disease What is the contraindications for anesthesia in a dental clinic? Fear of the treatment and removal of teeth Lactose anesthetics Pathology of CNS Asthma * Acute respiratory infection Which of complications related to anesthesia complications? Spasm of the larynx Swelling of the larynx * Angioedema Apnea Aspiration of vomit What forcepss are used for anesthesia mask? Propanidid and sodium hydroxybutyrate Viadryl and altezyn Hexenal * Chloroform and ether Trichlorethylene and Methoxyflurane In which of these injuries is not indicated general anesthesia? Fractures of the upper jaw and the type Lefor2 Lefort 3 Fractures of the mandible with damage to the tongue Fractures of the mandible with damage to the pharynx and larynx * Fractures Nose Fractures of the mandible with muscle damage floor of the mouth What forcepss are used in noninhalation anesthesia? Droperidol, fentanyl, diazepam * Viadryl, hexenal, thiopental sodium Ether, ftorotan, nitrous oxide Trichlorethylene Methoxyflurane Cyclopropane, chloroform How many stages of clinical anesthesia has? Two Three Four * Five Six What forcepss are used in neuroleptanalgesia? A. B. C. D. E. 504. A. B. C. D. E. 505. A. B. C. D. E. 506. A. B. C. D. E. 507. A. B. C. D. E. 508. A. B. C. D. E. 509. A. B. C. D. E. 510. A. B. C. D. Viadryl, hexenal, thiopental sodium Ether, ftorotan, nitrous oxide Trichlorethylene Methoxyflurane, chloroform Sodium hydroxybutyrate, propanidid * Droperidol, fentanyl, diazepam What is the contraindications for anesthesia in a dental clinic? * Severe anemia Asthma Fear of the treatment and removal of teeth Lactose anesthetics Pathology of CNS What is the indications for anesthesia in a dental clinic? Acute respiratory infection Acute inflammation * Lactose anesthetics Severe anemia Endocrine pathology What type of anesthesia is indicated for revealing severe phlegmon of maxillofacial area? Neuroleptanalgesia * Mask anesthesia Endotracheal anesthesia Noninhalation anesthesia Local anesthesia What is the contraindications for anesthesia in a dental clinic? Pathology of CNS Fear of the treatment and removal of teeth Lactose anesthetics * Violations clotting Asthma What drug can be used for premedication before removing teeth? Trimecaine * Trioksazyn Timalin Cocaine Dikain What is the duration of anesthesia when using Continuous IV sombrevin? * Within 3-5 minutes. Within 6-8 minutes. For 9-12 min. Within 13-15 minutes. Within 17-20 minutes. Coagulation theory is: Solubility of drugs in lipid membranes of celullare Change of boundary tension between the membrane and the liquid * Reverse coagulation of protoplasm of nerve cells Lock regulation of redox processes E. Formation of stable water crystals 511. In patients 6 years cleft hard and soft palate. What method of general anesthesia used during surgery - uranostafiloplastic? A. Intravenous B. Rectal C. * Endotracheal through the nose D. Intra-muscular E. Mask 512. Requirements for general anesthesia in the clinic (by Bazhanov) A. Anesthesia should be absolutely safe B. Awakening Fast C. The patient must independently go home D. No side effects after anesthesia E. * All answers are correct 513. When conducting the second phase of sedation? A. The evening before surgery B. Over 5 hours before surgery C. For 4 hours before surgery D. * By 1,5-2 hours before surgery E. There is no right answer 514. What drugs are used for classical neuroleptanalgesia? A. Chlorpromazine with droperidolom B. Omnopon with chlorpromazine C. Diazepam with pipolfenom D. * Fentanyl with droperidolom E. Thiopental sodium suprastin 515. What is the safest and enough effective method of anesthesia in dental practice to provide in outpatient treatment in a patient who is undergoing treatment in fear of the dentist? A. Audioanesthesia B. Neuroleptanalgesia C. * Ataranalgesia D. Endotracheal anesthesia E. Hypnosis 516. What kind of anesthesia for tooth extraction is appropriated to the patient with hypersensitivity to local anesthetics? A. Intravenous anesthesia B. * Endotracheal anesthesia C. Anesthesia D. Electrophoresis with novocaine E. Application anesthesia 517. What kind of anesthesia should be applied to the patient with Parkinson’s disease for tooth extraction? A. Application anesthesia B. Infiltration anesthesia C. Anesthesia D. mask inhalation anesthesia E. * Intravenous anesthesia 518. What kind of anesthesia for tooth extraction should be applied to patients with epilepsy? A. Application anesthesia B. Mask anesthesia C. * Intravenous anesthesia D. . Infiltration anesthesia E. Anesthesia 519. What kind of anesthesia for tooth extraction should be applied to the patient with spastic paralysis? A. Application anesthesia B. Infiltration anesthesia C. Anesthesia D. Electrophoresis with novocaine E. * Intravenous anesthesia 520. What are the indications for anesthesia in a dental clinic? A. Acute respiratory infection B. Acute inflammation C. Severe anemia D. * Fear of the treatment and removal of teeth E. Cardiovascular disease 521. After what anatomical formation is transmitted the pain? A. Hill maxilla B. The body of the mandible C. * Thalamus D. Pituitary E. Epiphysis 522. Pain - a kind of human condition, defined set of physiological processes in the central nervous system caused by the stimulus. This definition includes: A. Timofeev B. Danilevsky C. Hotsku D. * Anokhin E. Hotyu 523. Of which time in the literature appear first information about anesthesia in dental practice? A. In the twentieth century B. * Since the nineteenth century C. From the thirteenth century D. From the twelfth century E. From the eleventh century 524. In what year and who first used ether anesthesia in removing tooth? A. * 1842., Long B. 1844., Wells C. 1846r., Morton D. 1847., Inozemtsev E. 1847., Pirogov 525. A. B. C. D. E. 526. A. B. C. D. E. 527. A. B. C. D. E. 528. A. B. C. D. E. 529. A. B. C. D. E. 530. A. B. C. D. E. 531. A. B. C. D. E. 532. A. B. C. Who first used nitrous oxide anesthesia in dentistry? Inozemtsev Pirogov * Wells Long Morton What date is considered the discovery of ether anesthesia? * October 16, 1846 October 16, 1848 October 16, 1849 January 16, 1847 October 15, 1845 Who first publicly demonstrated ether anesthesia? Inozemtsev Pirogov * Wells Long Morton Who was the first in which he used ether anesthesia in? 1842., Long 1844., Wells 1846r., Morton * 1847., Inozemtsev 1847., Pirogov Who is the author of the first monograph of anesthesia? Inozemtsev Pirogov * Wells Long Morton What did in 1847, John Snow? Publicly demonstrated ether anesthesia First held ether anesthesia First held nitrous oxide anesthesia * First described 5 stages of anesthesia Posted monograph from anesthesia In what year was established the first union anesthesiologists? 1,894 1,895 * 1893 1,793 1,993 As the first in 1904, started applying Fedorov and Kravtsov? Inhalation anesthesia Mask anesthesia Intramuscular anesthesia D. E. 533. A. B. C. D. E. 534. A. B. C. D. E. 535. A. B. C. D. E. 536. A. B. C. D. E. 537. A. B. C. D. E. 538. A. B. C. D. E. 539. A. B. C. D. E. 540. A. * Intravenous anesthesia Rectal anesthesia Lipoid theory of narcosis is: * Solubility of drugs in lipid cellule membranes Change of boundary tension between the membrane and the liquid Contact coagulation of protoplasm of nerve cells Lock regulation of redox processes Formation of stable water crystals The theory of boundary tension is: Formation of stable water crystals Contact coagulation of protoplasm of nerve cells * Change the boundary tension between the membrane and the liquid Solubility of the drug in the lipid cell membranes Lock regulation of redox processes Theory breach of redox processes is: Formation of stable water crystals Contact coagulation of protoplasm of nerve cells Change of boundary tension between the membrane and the liquid Solubility of drugs in lipid cellule membranes * Lock the regulation of redox processes Theory of water microcrystals is: * Formed stable water crystals Contact coagulation of protoplasm of nerve cells Change of boundary tension between the membrane and the liquid Solubility of drugs in lipid membranes cellule Lock regulation of redox processes Who is the author of lipoid theory? * Herman Traube Fervorn Bernard Pauling What theory belongs to Traube? Lipoid * Of boundary tension Violation of redox processes Coagulation WATER microcrystals Who is the author of the theory of breach of redox processes Herman Traube * Fervorn Bernard Pauling Which theory was put forward in 1931, Bancroft and Richter? Lipoid B. C. D. E. 541. A. B. C. D. E. 542. A. B. C. D. A. 543. A. B. C. D. E. 544. A. B. C. D. E. 545. A. B. C. D. E. 546. A. B. C. D. E. 547. A. B. Of boundary tension Violation of redox processes * Coagulation WATER microcrystals What kind of anesthesia theory proposed in 1961 Pauling? Lipoid Of boundary tension Violation of redox processes Coagulation * Water microcrystals The fourth stage of ether anesthesia by Hvedelom this: Analgesia Excitation Surgical * Agonal Awakening The fourth stage of ether anesthesia by Zhorov this: Analgesia Excitation Surgical Agonal * Awakening How many stages lasts ethereal mononarcosis? 5 6 *4 7 8 Because of that excreted noninhalation anesthetics? Liver Heart * Kidneys Lights Stomach Way of withdrawal of inhaled drugs is through: Liver Heart Kidneys * Lungs Stomach What is anesthesia for ajar circuit: The air you breathe comes from the atmosphere and it returns * The drug comes from the container with a mixture of oxygen and exhaled into the atmosphere C. Part of the air exhaled into the atmosphere, some is returned to the patient D. E. 548. A. B. Gas recirculation system in the machine completely isolated from the atmosphere There is no right answer Anesthesia for semi type is: The air you breathe comes from the atmosphere and it returns The drug comes from the container with a mixture of oxygen and exhaled into the atmosphere C. * Part of the air exhaled into the atmosphere, some is returned to the patient D. Gas recirculation system in the machine completely isolated from the atmosphere E. There is no right answer 549. Ether and chloroform is most often used for: A. * Mask anesthesia B. Intravenous anesthesia C. Rectal anesthesia D. Intramuscular anesthesia E. There is no right answer 550. After X-ray examination diagnosed chronic granulating apical periodontitis. Describe the radiological picture in this disease. A. Alternating areas of narrowing and widening gap periodontitis B. Near the top of the root source of destruction of bone is rounded with smooth boundaries C. * Near the top of the root source of destruction of bone irregular round shape with irregular borders in the form of "tongues of flame" D. Uniform narrowing gap periodontitis E. Specific radiographic signs absent 551. After X-ray examination diagnosed chronic granulomatous apical periodontitis. Describe the X-ray picture of the disease. A. * Near the top of the root source of destruction of bone is rounded with smooth boundaries B. Near the top of the root source of destruction of bone irregular round shape with irregular borders in the form of "tongues of flame" C. Alternating areas of narrowing and widening gap periodontitis D. Uniform narrowing gap periodontitis E. Specific radiographic signs absent 552. After X-ray examination diagnosed chronic fibrotic apical periodontitis. Describe the Xray picture of the disease. A. Near the top of the root source of destruction of bone is rounded with smooth boundaries B. * Alternating areas of narrowing and widening gap periodontitis C. Near the top of the root source of destruction of bone irregular round shape with irregular borders in the form of "tongues of flame" D. Uniform narrowing gap periodontitis E. Specific radiographic signs absent 553. After examination of the oral cavity, the doctor diagnosed: acute suppurative periodontitis. What is the most characteristic symptom of this disease? A. Having a deep cavity B. Gain pain in the tooth under the influence of chemical and thermal stimuli C. Pathological tooth mobility D. * Sharply painful percussion of the affected tooth E. Painful percussion located along the teeth 554. After examination of the mouth and dental X-ray examination diagnosed: acute chronic periodontitis 36. Which symptom is not defined in this disease? A. Painful tooth percussion B. * Symptom Vincent C. Congestion and swelling of the gums D. Feeling "tooth that grew" E. Regional lymphadenitis 555. During treatment was perforation bifurcation. On radiographs mizhkoreneva granuloma. Root canals sealed to the top. What method of surgical treatment should be used? A. Hemisection B. Root amputation C. * Coronaroradicular separation D. Resection root apex E. Removal of tooth 556. In the projection of the root apex defined thickening, painful on palpation. Percussion tooth is not painful, entrance pupil channels open, probing not cause pain. X-ray: in the area of the top of the root source of destruction of bone size 5x6 mm with a clearly limited contours. Diagnosis: A. * Chronic granulomatous apical periodontitis B. Chronic apical periodontitis fibrotic C. Chronic apical periodontitis granulating D. Chronic pulpitis, apical periodontitis complicated. E. That's all right 557. The diagnosis: acute suppurative apical periodontitis 15 tooth. What is the emergency? A. Injection of a transitional fold lincomycin B. Intracanal electrophoresis with antibiotics and anesthetics C. Transapical therapy proteolytic enzymes under tight bandage D. * Create outflow of fluid. E. There is no right answer 558. Diagnosis: acute suppurative apical periodontitis 35 tooth. What disease have a differential diagnosis? A. With acute exacerbation of chronic apical periodontitis, chronic pulpitis, lymphadenitis B. With acute deep caries, periodontal abscesses form, purulent odontogenic Brush C. * In acute exacerbation of chronic apical periodontitis, acute diffuse pulpitis, acute suppurative periostitis D. With chronic pulpitis with acute deep caries, abscess under the jaw area. E. It is no correct answer 559. Constant pain in the area of the tooth 16. Asymmetry of the face. Collateral edema. Pain, swelling of the gums in the area of causal and adjacent teeth. In transitional crease within the patient tooth determined fluctuations. X-ray - expansion slot periodontitis. Diagnosis: A. Acute suppurative apical periodontitis B. Acute suppurative periostitis of the jaw C. Exacerbation of chronic apical periodontitis D. Acute odontogenic osteomyelitis of the jaw. E. There is no right answer 560. Constant pain localized nature. Tooth cavity is opened, filled with remnants of food. Probing eyes root canal painless. Percussion painful. Palpation of the mucosa in the region of the root apex painful. Electroodontodiagnosis: tooth responds to current 100 mA, radiography - nearapical no change. Put diagnosis. A. Acute diffuse pulpit B. Acute apical periodontitis serous C. Chronic apical periodontitis fibrotic D. Chronic granulomatous apical periodontitis. E. There is no right answer 561. Surgeon wash your hands with warm running water and soap for a minute, then disinfect in 0.5% solution of ammonia to 3 minutes. in the two basins. Then drained them sterile towel and processed the alcohol for 5 minutes. What a way to handle hands employed doctor? A. Method Fyurbrinhera B. Method Alfred C. * Method Spasokukotsky-Kochergina D. Method Bruno E. Scrubbing hibitanom 562. In CAP appealed patient complaining of painful ulcers presence left cheek. Diagnosed squamous cell carcinoma of the face, the second stage. You send original documents in CCCs. What documents are required? A. * Message Form 090 / O B. Protocol Forms 0242 / O C. Sending in CCCs D. Control card 6 / O E. Sending in EDB 563. Surgeon wash hands with warm soapy water, wiped them dry with a sterile towel for 2-3 minutes wiped alcohol solution chlorhexidine. What a way to handle hand applied surgeon? A. Method Fyurbrinhera B. Method Alfred C. Method Spasokukotsky-Kochergina D. Method Bruno E. * Process hands hibitanom 564. The patient, turned in dentistry. clinic about removing 36. From history revealed that the patient suffers from hemophilia. Preliminary removal was accompanied by long-term bleeding. What tactics doctor? A. * Hold intervention in hospital with pre-and postoperative training. B. Required preoperative training in outpatient C. Postoperative treatment is not necessary. D. Conduct removal outpatients with further advice. E. Hold Removal supervised hematologist in the clinic 565. In patients with deep burns of the face and torso on the affected area for more than 10% originated burn shock. In which department should be hospitalized victim? A. In therapy department B. * In the intensive care unit at the burn center C. In the surgical ward D. In the maxillofacial department E. In the casualty department 566. Dentist after the internship gets a job in a specialized institution providing care to HIVinfected and AIDS patients. What order should he carefully processed for organizing dental care these patients? A. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CARE of Ukraine № 302 of 27.12.1999, the B. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CARE Ukraine № 405 vid13.112001 was C. * MINISTRY OF HEALTH CARE of Ukraine № 120 from 25.05.2000, the D. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CARE Ukraine № 566 of 23.11.2004, the E. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CARE of Ukraine № 305 of 22.11.2000, the 567. Dentist at the end of the work shift must complete a diary account of the dentist. In what order Ministry of Health Care Ukraine it can read the instructions for completing this accounting and statistical form? A. * № 181 of 15.05.2001r. B. № 455 from 13.11.2001r. C. № 344 from 15.12.2000r. D. № 302 from 27.12.1999r. E. № 305 from 22.11.2000r. 568. Workplace dentist takes sophisticated equipment and technic who can successfully solve its tasks of diagnosis and treatment of dental diseases. Area doctor's office for 1 dental chair shall be not less than: A. 10 m2 B. 12 m2 C. 16 m2 D. * 14 m2 E. 7 m2 569. Dental care is different from other types of specialized medical care. What link leads in providing dental care? A. Ambulance B. * Outpatient care facilities C. Medical institutions D. Dental stationary units E. Private dental offices 570. Dentist in preparing statements of work is of records and reports specified sample What orders MH of Ukraine approved the accounting statistics used in dental practice? A. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CARE of Ukraine № 168 of 03.05.2000, the B. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CARE Ukraine № 455 from 13.11.2001, the C. * MINISTRY OF HEALTH CARE of Ukraine № 302 of 27.12.1999r. D. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CARE of Ukraine № 305 of 22.11.2000r. E. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CARE of Ukraine № 215 of 11.10.1993r. 571. In the analysis of dental institutions for the year indicated that the rate of sanitizing the total number of diagnosed patients in a hospital ward were 41 \%. How to evaluate the work of the regional medical office expert? A. * Satisfactory B. Unsatisfactorily C. Good D. Very good E. Very Poor 572. On the panoramic radiograph can be distinguished: cortical plate in periodontitis slit between alveolar combs, small foci of destruction and compaction of bone tissue A. * Yes, perhaps B. impossible C. depending on the film D. depending on the doctor E. all answers are correct 573. In CAP appealed patient complaining of painful ulcers presence on the left cheek. Diagnosed squamous cell carcinoma of the face, the second stage. You send original documents in CCCs. What documents are required? A. * Message Form 090 / O B. Protocol Forms 0242 / O C. Sending in CCCs D. Control card 6 / O E. Sending in EDB 574. Dentist after the internship gets a job in a specialized institution providing care to HIVinfected and AIDS patients. What order should he carefully processed for organizing dental care these patients? A. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CARE of Ukraine № 302 of 27.12.1999, the B. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CARE Ukraine № 405 vid13.112001 was C. * MINISTRY OF HEALTH CARE of Ukraine № 120 from 25.05.2000, the D. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CARE Ukraine № 566 of 23.11.2004, the E. MINISTRY OF HEALTH CARE of Ukraine № 305 of 22.11.2000, the 575. Dentist at the end of the work shift must complete a diary account of the dentist. In what order Ministry of Health Care Ukraine it can read the instructions for completing this accounting and statistical form? A. * № 181 of 15.05.2001r. B. № 455 from 13.11.2001r. C. № 344 from 15.12.2000r. D. № 302 from 27.12.1999r. E. № 305 from 22.11.2000r. 576. During the removal of 47 teeth was fractured distal tooth root at 1/2 its length. Which forceps should you choose to remove the root: A. * Corner Elevator "to itself" B. Beak pliers with cheeks that are connect C. Beak pliers with cheeks that are not connect D. Corner Elevator "by itself" E. Direct elevator? 577. When you extract a 17 tooth distal buccal root was broken remained in the cell. Select a forceps to remove abandoned root: A. Beak pliers, angled elevator B. Direct tongs, direct elevator C. S-shaped forceps, straight elevator D. * Bayonet tongs, direct elevator B. Corner elevators. Situational tasks 1. The patient is prepared for surgery under general anesthesia. What preparation to enter the patient during premedication for prevention of complications associated with vagus nerve stimulation? A. Dibazol B. * Pilocarpine C. Kordiamin D. Atropine E. Neostigmine. 2. The patient, a chronic granulating apical periodontitis 47. Tooth has a functional and aesthetic value. To the skin in the face area projection root apex 47 - fistula with purulent secretions. What is the treatment in this patient? A. Tooth B. Conservative treatment of tooth C. Tooth and excision of the fistula with subsequent suturing wounds on face D. * Tooth, excision of the scar on the skin after scarring fistulas course E. Excision of fistula with subsequent suturing wounds on face 3. The doctor put diagnosed odontogenic migrans skin granuloma. As a result of a pathological process occurs the disease? A. * Chronic apical periodontitis granulating B. Chronic hyperplastic odontogenic periostitis C. Chronic odontogenic osteomyelitis D. Chronic periodontitis E. Chronic apical periodontitis fibrous 4. In patients with chronic granulomatous periodontitis. On radiographs distal root sealed to the top, medial canal impassable, distorted, in the top center of bone thinning spherical shape with a clear outline zmirom 0,5 x 0,5 sm What tactics surgeon in choosing a method of treatment? A. Remove tooth B. Hold coronaro-root separation C. Conduct root apex resection D. Replantation E. * Hold hemisection tooth 5. Patients underwent one-stage operation 12 tooth replantation. What type of seam tooth and alveolus is optimal for such surgery? A. Periodontitis-fibrotic B. * Periodontal C. Chondral D. Osteoid E. There is no right answer 6. The man turned to the dentist. You can see 15 tooth on aproximal-chewing surfaces of large cavity. Probing percussion and reaction to thermal stimuli painless. The X-ray - pereapical observed fire destruction of bone is rounded with sharp edges in diameter. What is the diagnosis? A. * Chronic granulomatous periodontitis B. Chronic granulating periodontitis. C. Chronic fibrotic periodontitis. D. Chronic gangrenous pulpitis. E. Chronic deep cavities. 7. To the doctor turned patient with periodontitis lower molar tooth. Established that inflammation has spread to the lymph nodes. What are lymph nodes were first involved in the inflammatory process? A. Facial B. Front neck C. * Submandibulars D. Submental E. Lateral cervical 8. Teenager complains of intense, throbbing pain in the tooth, increasing with biting and touching tongue. OBJECTIVE: a 26-tooth - a seal of composite material. Vertical and horizontal percussion painful tooth, tooth moving slightly in the vestibular-oral direction. The mucous membrane of the gums in the area of lesions congestion edematous, sharply painful on palpation. Radiographic changes were detected. What is the diagnosis? A. Acute suppurative pulpitis B. Acute serous periodontitis C. Acute serous pulpitis D. Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis E. Acute suppurative periodontitis 9. The man turned with complaints of persistent pain in the area of tooth 36. Earlier repeatedly tooth pain. On examination, oral crown 36 tooth missing, percussion roots painful. On radiographs in the area of the tops of the roots 36 zone dilution with fuzzy contours. What is the diagnosis? A. Chronic granulomatous periodontitis B. Acute periodontitis C. Chronic periodontitis fibrotic D. * Chronic granulating periodontitis E. Mumps 10. A woman complains of severe pain in 38 tooth. The pain is constant, unwarranted, the intensity increases with each passing hour, marked feeling "grows tooth." When viewed in 38 deep tooth cavity, percussion sharply painful. What is the diagnosis? A. Acute periodontitis B. Acute pulpitis C. Deep caries D. Chronic pulpitis E. Trigeminal neuralgia 11. The student appealed to the dentist. OBJECTIVE: the 22 tooth on approximal - medial surface of deep cavities. On radiographs in the area of he root apex - cell destruction of bone size 0,3 x0, 3 sm What is the diagnosis? A. Chronic granulating periodontitis B. Chronic periodontitis fibrotic C. Radicular cyst D. Chronic pulpitis E. * Chronic granulomatous periodontitis 12. Patient complains of intense, acute, throbbing pain in the 26. Percussion 26 sharply painful tooth rolling, mucous membrane around 26 congestion, swollen, painful palpation. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Acute suppurative pulpitis B. Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis C. Acute diffuse pulpit D. Acute suppurative periodontitis E. Acute serous pulpitis 13. The patient complains of constant nagging pain in 26 tooth, aggravated by biting. OBJECTIVE: on the chewing surface of the cavity 26 which communicates with the cavity of the tooth. Transitional fold painful at palpation, percussion 26 sharply painful. After sensing the channel was pus. What method is necessary to study for diagnosis? A. Electroodontodiagnosis B. Termoproba C. * X-ray study D. Bacteriological study E. Deep probing 14. The patient complains of discomfort, heaviness, fullness, sometimes dull pain in the region of 36 teeth. Tooth with seal, changed in color, percussion sensitive. In the mucosa in the region. projection of the root is fistula. What is the diagnosis? A. Chronic granulomatous periodontitis B. * Chronic granulating periodontitis 36 tooth C. Acute suppurative periodontitis D. Chronic fibrous pulp E. Chronic periodontitis fibrotic 15. The patient diagnosed with chronic granulating periodontitis. What are the clinical signs characteristic of the disease? A. * Unpleasant sensation, feeling of heaviness, fullness, sometimes dull pain, percussion slightly sensual, is fistula, which periodically opens B. Pain from thermal and mechanical stimuli that disappear immediately after removal of the stimulus C. Strong torn, throbbing pain, feeling "grown tooth" collateral edema D. Asymptomatic, the tooth can be changed in color E. Constant growing pains, aggravated by biting, mucous membrane of this area may be swollen, congestion. Percussion dramatically positive 16. The patient complains of availability cavity in 26 tooth, tooth color changed, deep cavities connected with the cavity of the tooth. Probing percussion painless. EDI 100 mA. The X-ray - expansion slot periodontitis. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Chronic granulating periodontitis 36 tooth B. Chronic granulomatous periodontitis C. Acute suppurative periodontitis D. Chronic fibrous pulp E. * Chronic periodontitis fibrotic 17. The patient complained of a painful swelling in the palate that appeared 3 days ago after several times of treatment of tooth 17. OBJECTIVE: on the hard palate in the projection 17 tooth hemispherical infiltration, painful, mucous membrane over it flushed bright, elegant. Crown 17 destroyed on the radiograph: signs of granulomatous periodontitis 17 tooth. What is your tactic? A. Remove 17 tooth hole sew B. Amputation root C. Section of mucous in the palate D. * Remove 17 tooth abscess open E. Puncture infiltration, removal of tooth 17 18. The patient complains of discomfort in 36 tooth on the upper jaw to the left. Periodically, the biting the tooth, spontaneously arising aching pain and a fistula on gums, then the pain subsides. OBJECTIVE: crown 36 changed in color, tooth sealed. Vertical percussion painless. In the mucosa in the rumen of 36 fistulas. What is the most likely earlier diagnosis? A. Chronic periodontitis fibrotic B. * Chronic granulating periodontitis C. Chronic granulomatous periodontitis D. Chronic periodontitis gangrenous E. Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis 19. The patient asked the dentist about long fistula in the lower part of the left cheek. objective: fistulas move the skin up to 0.3 sm in diameter with sluggish granulations and minor bleeding, purulent exudate. When sensing probe penetrates the soft tissue in the body of the mandibule. Palpation in the thickness of the left cheek determined cord. On radiographs - 35 tooth has signs of chronic periodontitis. What is the final diagnosis in this patient? A. * Odontogenic subcutaneous granuloma face B. Chronic odontogenic osteomyelitis of the mandibule C. Tuberculosis of the mandibule D. Actinomycosis of the mandibule E. Atheroma left cheek 20. To the dentist asked the patient complaining of availability formation in the area of the right cheek. OBJECTIVE: on the right cheek, a small, clearly limited the formation of tight elastic consistency, painful on palpation, the skin over it congestion centrally defined symptom fluctuations. In the thick cheeks palpable cord from the formation to the root apex destroyed 15 tooth. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Dermoid cyst B. Suppurations atheroma C. Furuncle D. * Suppurations migrans granuloma E. Melanoma 21. The patient complained of a painful swelling in the palate that appeared 3 days ago after several times of treatment of tooth 17. OBJECTIVE: on the hard palate in the projection 17 tooth hemispherical infiltration, painful, mucous membrane over it hiperemic bright, elegant. Crown 17 destroyed on the radiograph: signs of granulomatous periodontitis 17 tooth. What is your tactic? A. Remove 17 tooth hole sew B. Amputation root C. Section of mucous in the palate D. Puncture infiltration, removal of tooth 17 E. * Remove 17 tooth abscess open 22. When X-ray examination on spot film in the projection of the root apex of tooth 27 is observed destruction of bone round with clear smooth edges size 0,7 x0, 7 sm Put the diagnosis? A. Cyst B. Granuloma C. Odontoma D. * Cystogranuloma E. Osteoma 23. In the projection of the root apex of tooth 16 - availability prominence 08 x 08 sm, which is sensitive to palpation, springy. Percussion tooth is not painful. Sign in cell free channels, sensing does not cause pain. X-ray: in the area of the root apex - a fire of destruction of bone with clearly reduced margins. Diagnosis: A. Chronic apical periodontitis fibrotic B. * Chronic granulomatous apical periodontitis, cystogranuloma C. Chronic apical periodontitis granulating D. Pulpitis, chronic apical periodontitis complicated. E. There is no right answer 24. In 47 tooth after root canal having intense pain in the jaw. Percussion sharply painful. In section 47 of the tooth mucosa edematous, congestion. The body temperature of 38,6 ° C. Lymph nodes submandibule enlarged, painful on palpation. Face symmetrical, proportional. X-ray: root canals sealed on 4/5 length: destruction of bone tissue in the tops of the roots with fuzzy edges. Diagnosis: A. * Exacerbation of chronic apical periodontitis B. Acute suppurative periostitis of the jaw C. Acute odontogenic osteomyelitis of the jaw D. Purulent radix cyst. E. That's right 25. Patient 39 years old, appealed to the dentist. After the survey was diagnosed with chronic granulating periodontitis. What state has the mucosa around teeth with chronic granulating periodontitis? A. * Cyanotic mucosa is often fistula B. Mucosa sharply congestion C. Mucous pale pink D. At mucosa observed overemphasizing E. No changes 26. The patient appealed to rehabilitate a year after treatment of chronic granulomatous periodontitis. What indicators suggest cure according to X-ray? A. Complete obturation of the root canal B. Increasing the size of the hearth dilution C. Resorption apex of the tooth root D. Signs of recovery of bone is not visible E. * Full or partial restoration of bone 27. The patient complains of constant nagging pain in 15 tooth, growing at biting. Cavity communicates with the cavity of a tooth from the mouth of the channel was pus. Which test should be carried out to establish the diagnosis? A. Termoproba B. Electroodontodiagnosis C. Fluorescent research D. Bacteriological study E. * X-ray study 28. The patient complains of painful biting the 14 tooth and a sense of fullness. From history: several times already occurred in the tooth pain, swelling of the cheek, which ended with the formation of fistulas, which for some time stood manure. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Chronic granulomatous periodontitis 14 tooth B. Chronic gangrenous pulpitis 14 tooth C. Chronic fibrotic periodontitis 14 tooth D. * Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis 14 tooth E. Acute suppurative periodontitis 14 tooth 29. The patient complains of pain in biting by 25 tooth, which began last night and growing. Cavities connected dotted with the cavity of the tooth sensing painless. Percussion sharply positive. Radiography unchanged. What is the preliminary diagnosis? A. Acute suppurative pulpitis 25 tooth B. Acute serous pulpitis 25 tooth C. Acute serous periodontitis 25 tooth D. Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis 25 tooth E. There is no right answer 30. Patient complains of throbbing pain of a 26 tooth, for 5 days. Percussion vertical and horizontal positive tooth moving, sharply congestion mucosa, palpation transition creases sharply painful. What is the diagnosis? A. Acute suppurative pulpitis 26 tooth B. Acute localized periodontitis 26 tooth C. Acute serous pulpitis 26 tooth D. Acute serous periodontitis 26 tooth E. Acute suppurative periodontitis 26 tooth 31. Patient complaints filed with the presence of tumor formation in the skin in the area of the right angle of the jaw. An objective examination: in 37 tooth - a deep cavity, which communicates with the cavity of the tooth. Probing painless. From history we found that a few years ago confounded recurring pain in 37 tooth. The doctor put diagnosed odontogenic migrans skin granuloma. As a result of a pathological process occurs the disease? A. Chronic hyperplastic odontogenic periostitis B. Chronic odontogenic osteomyelitis C. Chronic periodontitis D. * Chronic apical periodontitis granulating E. Chronic apical periodontitis fibrous 32. At the reception turned patient complaining of a sharp pain in the upper jaw. As a result of the examination the doctor made a diagnosis: acute periodontitis 16 tooth. With what is necessary to differentiate acute periodontitis? A. Acute pulpitis B. Periostitis C. Osteomyelitis D. Acute odontogenic sinusitis E. * All the above 33. The patient arrived in the morning at the reception to the surgeon-dentist. Admission started with a delay of 15 minutes. Doctor in stale in spots, crumpled robe, not listened to the end of patient complaints, asked him to open his mouth. During treatment, the patient's doctor shared with the nurse feeling about the movie. What is a violation of ethics in this case? A. Start receiving late B. Wrinkled robe doctor C. Improper ratio of doctor to patient complaints D. Discussion of the film during the admission of the patient E. * All of the above 34. On admission to the dentist-surgeon turned victim with limited thermal burns skin face I-II degree. Determine where treatment must be given affected. A. Hospitalized in the casualty department B. Out in the dentist-surgeon C. * Admitted to the burn center (branch) D. Ambulatory surgical department clinics E. Ambulatory emergency station in the place of residence 35. In the dental clinic turned sick. After physical examination oral surgeon clinics were diagnosed abscess of the right submandibular region. What should be further tactics doctor? A. Hold punction removal of purulent exudate B. Assign medication and physiotherapy C. Assign medication with dynamic observation D. Conduct section phlegmon in the clinic E. * Immediately send the patient to a specialized health care facilities 36. The patient appealed with complaints of pain in the right temporomandibular joint when you open your mouth, which appeared 3 days ago after trauma. The body temperature of 37.5 C, alignments intact, bite orthognathic. What is necessary to test for establishing the clinical diagnosis? A. * Radiography B. Total blood C. Urinalysis D. Densitometry E. Thermometry 37. Patients aged 32 years complains presence fistula in submaxillary area. OBJECTIVE: swelling in the cheek region of the mandibule on the left, while palpation - sealing soft tissue fistula with purulent content and granulation; mucosa bloodshots, 35, 36 teeth moving. The X-ry revealed destruction of bone, the presence of sequestration. Set the diagnos. A. Actinomycosis B. * Chronic osteomyelitis C. Syphilis D. Sarcoma E. Osteoma 38. The patient was diagnosed as actinomycosis of the neck’s soft tissue. What pathomorphological manifestations characteristic of actinomycosis: A. Papule B. Ulcer C. * Granuloma D. Tuberculum E. Erosion 39. Patient in age 7 years hospitalized in Maxillofacial ward for chronic odontogenic osteomyelitis of the mandibule in the region of 48, 47 teeth. Sick about 2 months. OBJECTIVE: While probing fistula, which bulge large granulation determined nude rough area of bone that moves when pressing. On radiographs of the mandibule - a fire of destruction, with focus on sequestration size 1.0 x1, 5 sm, which involved 48.47 teeth completely separated from healthy bone. Select a method of treating a patient: A. Sequestrectomy B. Stimulatory therapy C. Dental health D. Antibiotic E. * Sequestrectomy with removal of 47 and 48 teeth. 40. The patient arrived in the morning at the reception to the surgeon-dentist. Admission started with a delay of 15 minutes. Doctor in stale in spots, crumpled robe, not listened to the end of patient complaints, asked him to open his mouth. During treatment, the patient's doctor shared with the nurse feeling about the movie. What is a violation of ethics in this case? A. Start receiving late B. Wrinkled robe doctor C. Improper ratio of doctor to patient complaints D. Discussion of the film during the admission of the patient E. * All of the above 41. Surgeon wash your hands with warm running water and soap for a minute, then disinfect in 0.5% solution for 3 min ammonia alcohol two basins. Then drained them sterile towel and processed the alcohol for 5 minutes. What a way to handle hands employed doctor? A. Method Fyurbrinhera B. Method Alfred C. * Method Spasokukotskoho-Kochergina D. Method Bruno E. Scrubbing hibitanom 42. The patient, turned in dentistry clinic about removing 36. From history revealed that the patient suffers from hemophilia. Preliminary removal was accompanied by long-term bleeding. What tactics doctor? A. * Hold intervention in hospital with pre-and postoperative training. B. Required befor operation training in outpatient C. Postoperative treatment is not necessary. D. Conduct removal outpatients with further advice. E. Hold Removal supervised hematologist in the clinic 43. On admission to the dentist-surgeon turned victim with limited thermal burns skin face I-II degree. Determine where treatment must be given affected. A. Hospitalized in the casualty department B. Out in the dentist-surgeon C. * Admitted to the burn center (branch) D. Ambulatory surgical department clinics E. Ambulatory emergency station in the place of residence 44. In which department should be hospitalized victim? A. In therapy department B. * In the intensive care unit at the burn center C. In the surgical ward D. In the maxillofacial department E. In the casualty department 45. After physical examination oral surgeon clinics were diagnosed abscess of the right submandibular region. What should be further tactics doctor? A. Hold punction removal of purulent exudate B. Sign medication and physiotherapy C. Assign medication with dynamic observation D. Conduct section phlegmon in the clinic E. * Immediately send the patient to a specialized health care facilities 46. The patient appealed with complaints of pain in the right temporomandibular joint during openning mouth, which appeared 3 days ago after trauma. The body temperature of 37.5 C, alignments intact, bite orthodonthic. What is necessary to test for establishing the clinical diagnosis? A. * Radiography B. Total blood C. Urinalysis D. Densitometriyu E. Thermometry 47. Patients aged 32 years complains presence fistula in submaxillary area. OBJECTIVE: swelling in the cheek region of the mandible on the left, while palpation - sealing soft tissue fistula with purulent content and granulation; mucosa bloodshots, 35, 36 teeth moving. The X-ray revealed destruction of bone, the presence of sequestration. Set diagnosed A. Actinomycosis B. * Chronic osteomyelitis C. Syphilis D. Sarcoma E. Osteoma 48. Patient age 7 years hospitalized in Maxillofacial ward for chronic odontogenic osteomyelitis of the mandible in the region of 48, 47 teeth. Ills about 2 months. OBJECTIVE: While probing fistula, which bulge large granulation determined nude rough area of bone that moves when pressing. On radiographs of the mandible - a fire of destruction, with focus on sequestration size 1.0 x1, 5 sm, which involved 48.47 teeth completely separated from healthy bone. Select a method of treating a patient: A. Sekvestrectomy B. Stimulatory therapy C. Dental health D. * Sequestrectomy with removal of 47, 48 teeth E. Antibiotic 49. The patient was diagnosed as actinomycosis soft tissue neck. What pathomorphological manifestations characteristic of actinomycosis: A. Papule B. Ulcer C. * Granuloma D. Buhorok E. Erosion. 50. Man 25 years old turned to the clinic about removing 18 crown is destroyed by 1/2. Tooth previously repeatedly treated. During tooth avulsion occurred hill maxilla. What should be the tactic? A. Remove fragment and tampon wound B. Set fragment to the same position and fix C. * Remove fragment and stitched the wound D. Try to enter the place fragment E. Remove fragment 51. To the doctor asked people to dental health. After examination and clinical examination revealed that 31 to remove a tooth root is shaved to 1/2, mobility him the third degree. Diagnosis: gum 31 tooth. Choose forceps, you want to remove 31 teeth. A. Bayonet B. Beak with spikes on cheeks C. * Beak with cheeks that match D. Bent on a plane E. Beak with cheeks that do not match 52. On admission to the oral surgeon asked the patient 70 years for removal of central maxillary incisors to the third degree of mobility. How to delete data Teeth? A. * Direct curling B. Direct elevator C. S-shaped forceps D. Bayonet forceps E. Beak pliers 53. The patient 37 years old was removed medial root of 36, and the distal root of the tooth was broken in the middle third. Which tool to use to remove the root? A. Beak pliers, converging B. * Elevator right corner C. Elevator left corner D. Direct elevator E. Beak pliers that do not connect 54. Patients showed removal of 46 teeth. Crown of the tooth is preserved, open mouth free. Select the method of anesthesia and tools: A. Torusal anesthesia; straight and corner elevator; beak pliers with cheeks that connect B. Mandibular anesthesia, straight and corner elevator C. * Torusal anesthesia beak pliers with spines on cheeks D. Anesthesia for Bershe-Dubovy, corner and direct elevator E. Mandybular and cheek anesthesia, direct elevator, curved beak pliers on a plane 55. Patient aged 25 years indicated removal of tooth 26. Diagnosed chronic fibrotic periodontitis 26 tooth. Coronal portion retained. Which tool should be used to remove this tooth: A. Forceps S-shaped law B. * Circling S-shaped left C. Bayonet forceps D. Circling direct root E. Direct elevator 56. The patient after removal of 37 teeth appeared alveolar bleeding. Determine the most effective in this case the method of hemostasis: A. Tamponade cell iodoform swab B. Recycling alveolar’s floor and wall crystals of potassium permanganatis C. * Tamponade cell local hemostatic agents D. Overall hemostatic therapy E. Recycling cell solution of hydrogen perperiosteum. 57. A patient aged 44 years during tooth extraction was cast his crown part. When to further manipulation by the elevator, forceps remove residual tooth failed. What manipulations should make a surgeon to successfully remove residual tooth: A. * Disconnect roots by drills and fissur bur B. Apply corner elevator C. Refer the patient to outpatient D. Complete removal during another visit E. Apply elevator Leklyza 58. A woman aged in 49 years addressed the surgeon-dentist to remove the tooth 17 is diagnosed exacerbation of chronic granulomatous periodontitis 17 tooth. Select a tool to remove: A. * S-like law curling B. Bayonet root curling C. Bayonet crowns curling D. S-shaped left forceps E. Direct forceps. 59. Patient age in 45 years asked the doctor to remove 13 teeth. Select a tool to remove the tooth: A. S-shaped forceps B. S-shaped curling right C. Bayonet curling D. Direct elevator E. * Direct forceps. 60. The dental surgeon put cheeks forceps on the crown of the tooth 17, which had a thin walls at closing forceps appeared fractured crown. Used direct elevator, entered with vestibular by focusing a 16 tooth. This arose from the upper jaw department mound with 17 and 18 teeth. What further tactic doctor: A. * Laminationr muco-periosteum flap, remove the piece from 17, 18 teeth and stitched lining B. Produce tire cap on the upper jaw, assign UHF C. Perform radiography and electroodontodiagnosis record 17.18 teeth with tires D. Process mouth antiseptics and wait for wound healing E. Remove a piece of the 17, 18 teeth and wound tampon? 61. Patients aged 43 years shows the operation to remove the 16 tooth. Select receptions tooth extraction forceps, which you want to apply for removal of 16 teeth: A. Overlay, promotion, interlocking, luxation, rotation, traction B. Overlay, promotion, interlocking, luxate outside and inside, traction C. Overlay, closing, luxate inward and outward traction D. Overlay, promotion, luxate inside andoutside, traction E. * Overlay, promotion, interlocking, luxate inward and outward traction. 62. Patients aged 33 years appealed to the dental clinic for rehabilitation. According to indication he needs to remove the 37 tooth. Select receptions tooth extraction forceps, which should be used when removing 37 teeth: A. Overlay, promotion, luxate inside and outside, traction B. Overlay, promotion, interlocking, luxate outside and inside, traction C. Overlay, closing, luxate inward and outward traction D. Overlay, promotion, interlocking, luxate inward and outward traction E. E. * Overlay, promotion, interlocking, luxation, rotation traction. 63. The dental surgeon during vydalyennya 38 tooth used elevator Leklyza. Once cheek elevator was put between 37 and 38 teeth and carried attempt to dislocate 38 tooth, there malocclusion. What is the most likely complications can occur: A. Fracture collar branching mandible B. * Fracture of the mandible angle C. A partial dislocation 37 tooth D. Anterior dislocation of the lower jaw E. Posterior dislocation of the mandible? 64. Patients showed removal of 46 teeth. Crown of the tooth is preserved, open mouth free. Select the method of anesthesia and tools: A. Mandibular anesthesia, direct elevator bent on plane beak pliers B. Mandibular anesthesia straight and corner elevator, beak pliers with cheeks that connect C. Torusal anesthesia; straight and corner elevator; beak pliers with cheeks that connect D. Anesthesia for Bershe-dubovy, corner and direct elevator E. * Torusal anesthesia beak pliers with spines on the cheeks. 65. Patient aged 25 to 26 to remove the tooth. Which tool should I have to remove: A. Forceps S-shaped left B. * Circling S-shaped law C. Bayonet forceps (bayonet) D. Circling direct root E. Direct elevator? 66. The patient was to receive 2 days after removal of 37 teeth. In section 37 of the tooth observed cell inflammation (pain, soft tissue swelling, redness of the mucous membrane, increasing pain and regional lymph nodes). On radiographs in the lateral projection celebrated piece of root in a cell of the tooth, which was removed. Have shown how long surgery to remove the fragment root: A. The folly operation as willfully chip root expulsion granulation tissue B. After 7-10 days without inflammation C. * Fragment to remove more faster D. After 2 months when around fragment significantly atrophied bone E. Hold atypical root removal under narcosis? 67. After 3 hour after removal of 45 teeth in the patient began bleeding from the cell. During examination revealed a gap gum tissue in the area of cell 45 tooth, which goes to the cheek mucosa. What is the doctor's tactics in this case: A. Tamponade cell catgut B. * Tamponade cell iodoform turundas C. Pressing bandage and per oss input aminocapronic acid D. Cell wound closure and cheeks E. Tamponade cells and wound swab with aminocapronic acid? 68. Patients showed removal of 46 teeth. Crown of the tooth is preserved, open mouth free. Select the best method of conduction anesthesia and tools: A. * Mandibular and cheek anesthesia, direct elevator, rip bented forceps with spines on cheeks B. Anesthesia for Bershe-Dubovy, corner and direct elevator C. Mandibular anesthesia, straight and corner elevator; beak pliers with cheeks that connect D. Torusal anesthesia beak pliers E. Torusal anesthesia; straight and corner elevator: beak pliers with cheeks that connect. 69. A woman aged in 56 years addressed the surgeon-dentist to remove the tooth 17. Select required tools to remove 17 teeth: A. * S-like curling B. Bayonet root curling C. Direct curling D. S-shaped forceps E. Bayonet crowns forceps. 70. Boy aged 6 years dental therapist sent a surgeon to remove the 51 tooth about its physiological mobility. Which tool should be used in this case: A. Nipper, bent on a plane B. Direct elevator C. Corner elevator D. * Direct curling E. Beak pliers with schichka_my not connect? 71. A man aged in 28 years addressed the surgeon-dentist to remove the tooth 38. What should I use forceps to remove the 38 tooth: A. Beak with cheeks that do not connect B. * Beak bent on plane C. Beak with cheeks that connect D. Rib bented with the spines 72. Patient asked to remove 14 teeth with exacerbation of chronic periodontitis after uneffective therapeutic treatment. Choose necessary tools to remove 14 teeth: A. S-shaped curling right B. Bayonet crowns curling C. * S-like forceps D. Direct curling E. Bayonet root curling. 73. Patient age 48 years complained of constant pain in the tooth 28. Sick 3 days. 28 tooth crown is destroyed. Select forceps, with which you can remove the tooth root 28: A. Forceps for eight upper teeth B. Beak pliers C. Direct curling D. S-shaped forceps E. * Bayonet forceps. 74. Patients aged 42 years appealed to the clinic for dental surgery tooth on the upper jaw. The patient showed 25 tooth removal under local anesthesia. Where should the doctor be in relation to the patient during removal of the tooth: A. Ahead and to the left of the patient B. Ahead of the patient C. * Ahead and to the right of the patient D. Behind and to the right of the patient E. Behind and to the left of the patient? 75. When you delete a 17 tooth distal buccal root broke remained in the cell. Select a tool to remove abandoned root: A. Corner elevators B. Direct forceps, direct elevator C. S-shaped forceps, direct elevator D. Beak pliers, angled elevator E. * Bayonet forceps, straight grain elevator. 76. Patients showed removal of 46 teeth. Where should be the doctor during removal of the tooth: A. Ahead and to the left of the patient B. To the left and behind the patient C. * The case and back on the patient D. Ahead and to the right of the patient E. Behind and centered on the patient? 77. The man turned to the clinic over the removal of the tooth 17. During one tooth roots hit the maxillary sinus. What tactics doctor in this situation: A. Do not start any action B. * X-ray examination and referral to hospital hvo_roho C. Removing the root perforation through hole formed D. The operation maxillary sinusotomy E. Suturing cell extracted tooth? 78. Men must remove tooth root 17 to prosthetics. Crown 17 tooth broken below the gumline. What tools are not necessary to apply: A. S-shaped curling right. Direct elevator B. S-shaped forceps. Direct elevator C. Straight forceps with cheeks that connect. Direct elevator D. * Bayonet forceps. Direct elevator E. Straight forceps with cheeks that do not connect. Direct elevator? 79. Patients aged 30 turned to the clinic about 16 tooth removal. In the process of tooth extraction was a gap mucosal collar bone, accompanied by significant bleeding. Indicate the most appropriate way to stop the bleeding in this case: A. Hemostatic tamponade sponge B. Longing gauze tamponade C. * Suture D. Tamponade gauze pad with aminocaproic acid E. Parenteral administration stop bleeding funds. 80. A man aged 25 years asked to the clinic about removing 18 tooth crown is destroyed by 1/2. Tooth previously many times was treated. During tooth avulsion occurred hill maxilla. What actions are right in this case: A. * Debris removal and wound suture B. Trying to enter the piece into place C. Set pieces on staree place and fix it D. Wreck removal E. Debris removal and tampon wounds? 81. Patient age in 47 years to remove 14 tooth coronal tooth preserved. Select tools, identify steps remove: A. * S-like forceps, blending, promotion, closing, luxation in buccal, palate, traction B. Direct forceps, blending, moving, closure, rotation, traction C. Direct elevator, blending closing, luxation in palate and buccal sides, traction D. S-shaped forceps, blending closing, luxation in palate and buccal sides, traction E. S-shaped forceps with spikes, blending, promotion, interlocking, luxation in buccal and palate sides traction. 82. To the doctor asked the patient complaining of intermittent pain in the region of the angle of the mandible and difficulty opening the mouth. Displaying 38 tooth removal. Select forceps, you want to remove 38 teeth: A. Bayonet B. Beak with cheeks that do not connect C. Beak with cheeks that connect D. Beak with spikes on cheeks E. * Bent on the plane. 83. A patient aged 70 complains of tooth mobility 21. Tooth previously treated. 21 tooth driven (II stage) bare root to 1/2. Which tool should be used to remove the 21 tooth: A. Bayonet curling B. S-shaped forceps C. * Direct curling D. Direct elevator E. Beak pliers? 84. Men must remove tooth root 17 to prosthetics. Crown 17 tooth broken below the gumline. What tools should be applied: A. S-shaped forceps B. * Bayonet Forceps C. Straight forceps with cheeks that connect D. S-shaped curling right E. Straight forceps with cheeks which do not connect? 85. On examination, her husband was diagnosed with acute odontogenic sinusitis. Source disease - 15 tooth which must be removed. Crown of the tooth is preserved. Which tool should the use wadding: A. Bayonet forceps B. Straight forceps with cheeks that do not connect C. * S-like forceps D. Straight forceps with cheeks that connect E. S-shaped curling right? 86. To the doctor asked people to dental health. After examination and clinical examination revealed that 31 to remove a tooth root is shaved to 1/2, mobility III degree. Select forceps, you want to remove 31 teeth: A. Beak with cheeks that connect B. * Beak with cheeks that do not connect C. Beak with spikes on cheeks D. Bent on a plane E. Bayonet. 87. Patient age in 47 after ineffective treatment therapist-dentist chronic granulomatous periodontitis tooth 15 was to remove it. What type of forceps should be used to remove this tooth: A. Direct B. S-shaped law C. * S-like D. S-shaped left E. Bayonet? 88. Patient age in 38 after ineffective treatment 26 tooth for chronic granulomatous periodontitis to see a doctor for removal of the tooth. In which way the first time and which movements should luxate tooth: A. Rotational movements B. In the buccal side luxate and rotary movements C. In the buccal side luxate movements D. In palatal side luxate and rotary movements E. * The palatal side luxate movements? 89. A man aged in 48 asked to the oral surgeon about removing the roots of the tooth 37. What tools should be used ing: A. Bayonet curling B. * Beak pliers with spine and spines that do not connect C. S-shaped forceps D. Beak pliers with spines that connect E. Beak pliers, bent on a plane? 90. Patients aged 20 years had sought to oral surgeon to remove the roots of the tooth 47. Comorbidity - hemophilia. In what circumstances is necessary to remove 47 teeth: A. In a hospital with before operation preparation B. In the hospital C. Conditions do not matter D. In the outpatient E. * In hematology outpatient with preoperative and postoperative observation? 91. Patients aged 30 to see a doctor to remove 26 teeth on the exacerbation of chronic periodontitis. 26 tooth crown is destroyed. Select forceps to remove this tooth: A. S-shaped without thorns B. * S-similar to the spike on the right cheek C. Direct curling D. Bayonet curling E. S-shaped with a spike on the left cheek. 92. Patient age in 26 asked the doctor to remove 24 teeth on the exacerbation of chronic periodontitis. 24 tooth crown is destroyed. Select a tool to remove the tooth: A. Direct curling B. * S-similar to the spike on the left cheek C. S-shaped with a spike on the right cheek D. S-shaped without thorns E. Direct elevator. 93. Patient age in 57 asked the doctor to remove 34 teeth on the exacerbation of chronic periodontitis. Select a tool to remove this tooth: A. * Beak pliers with cheek not connected B. Beak pliers with cheek that connect C. Beak pliers, bent on a plane D. Direct elevator E. Lateral elevators. 94. Patient age in 37 was removed medial root of the tooth 36 and the distal root of the tooth was broken in the middle third. What tools should be used to remove root: A. Direct elevator B. Elevator angle to the left C. * The elevator angle right D. Beak pliers that do not connect E. Beak pliers, converging? 95. Patient is showed to remove 38 tooth. The doctor is in front and to the left of the patient puts on the crown 38 tooth forceps, curved in the plane, and after luxation movement holds traction tooth. This arose complication - the gap mucosa ribbon form with language side. What is the cause of complications: A. We had to rotary motion B. Improper luxation movements C. Improper stages overlap and fixation forceps D. Missing stage fixation forceps E. * Improper stages overlap, promotion and fixation forceps? 96. Patient, 45 years old, asked to remove 13 tooth. What forceps should be used to remove the 13 tooth: A. *Direct forceps B. S-shaped forceps right C. Bayonet forceps D. Direct elevator E. S-shaped forceps? 97. Patients showed to removal of the root of the tooth 36. OBJECTIVE: crown 36 tooth missing, medial root is removed. The distal root is deep in the cell. Select a forceps to remove the distal root of tooth 36: A. Rostral root forceps B. Elevator Lekluze C. Corner Elevator "by itself" D. Direct elevator E. * Corner Elevator "from itselves." 98. A woman, 49 years old, addressed the surgeon-dentist to remove the tooth 17. Diagnosed exacerbation of chronic granuloma-comatose periodontitis 17 tooth. Select a forceps to remove the 17 tooth: A. * S-shaped law forceps B. Bayonet root forceps C. Bayonet crowns forceps D. S-shaped left forceps E. Direct forceps. 99. A woman, 56 years old, addressed the surgeon-dentist to remove the tooth 17. Select forceps to remove 17 teeth: A. S-shaped B. * Bayonet root C. Direct D. S-shaped law E. Bayonet crown. 100. A boy, 6 years old, directed physician-dentist to remove the tooth 51 on the physiological motion. Which forceps should be used in this case: A. * Direct forceps B. Direct elevator C. Corner elevator D. Nipper, bent on a plane E. Beak forceps with cheeks that do not agree? 101. Patients, 49 years old, plexual Articaine anesthesia with vasoconstrictors removed tooth on the upper jaw. After cell operation not overflow step fade clot. How can you prevent alveolitis in a patient: A. Rinse the cell solution Microcide B. Fill cell hemostatic sponge C. * Loose fill cell iodoform swab D. Rinse cell solution 0,1% chlorhexidine E. Fill cell powder antibiotic? 102. Patients, 24 years old, to turn las dentist with complaints on pain in the area of tooth 26. After physical examination diagnosed exacerbation of chronic periodontitis 26 tooth. During removal was fractured coronal tooth. During subsequent manipulations using bagnetlike forceps to remove the tooth root failed. What manipulation should hold the surgeon to remove the tooth root: A. Apply elevator Lekluze B. Refer the patient to in-patient hospital C. * Disconnect roots by help drills and fissure bur D. Complete removal of the tooth next visit E. Apply corner elevator? 103. A man, 28 years old, addressed the surgeon-dentist to remove the tooth 38. What forceps should choose to remove the tooth: A. *Beak forceps, bent on a plane B. Beak forceps with cheeks_that are not connect C. Beak forceps with cheeks that are connect. D. Beak forceps with spine E. Bayonet forceps root? 104. Patient, 48 years old, complained of constant pain in the tooth 28. Sick during 3 days. 28 tooth crown is destroyed. What forceps should be used to remove the top 28 of the tooth: A. Direct forceps B. Beak forceps C. * Bayonet forceps D. S-shaped forceps E. Forceps for eight upper teeth? 105. Men must remove tooth root 17 to prosthetics. Crown 17 tooth broken below the gumline. What forceps should be applied: A. S-shaped forceps, straight elevator B. * Bayonet Forceps, straight elevator C. Straight forceps with cheeks that converge, direct elevator D. S-shaped forceps right hand, direct elevator E. Straight forceps with cheeks that do not converge, direct elevator? 106. Patient, 35 years old, addressed the surgeon-dentist about oral preparation for prosthetics. On examination of the oral cavity revealed many decayed teeth to be removed. Patient very emotional, easily excitable. To the dentist is not addressed because of fear of pain. Under what kind of anesthesia is advisable to remove the roots? A. Infiltration anesthesia B. Pain by needless injector C. *Mask anesthesia D. Regional anesthesia E. Electroanesthesia 107. The patient asked the dentist to remove the tooth for 36 Sanitation indicators. Patient year ago suffered myocardial infarction, angina suffering. Which method is most efficient? A. Narcosis B. Infiltration anesthesia C. Conduction anesthesia D. Application anesthesia E. * Conduction anesthesia potentiated 108. The patient appealed to the surgeon - a dentist. On examination of the oral cavity revealed many decayed teeth to be removed. Patient very emotional, easily excitable. To the doctor dentist is not addressed because of fear of pain. Under what kind of anesthesia is advisable to remove the roots? A. Infiltration anesthesia B. * General anesthesia C. Pain relief through needless injector D. Anesthesia E. Electroanesthesia 109. The patient is prepared for surgery under general anesthesia. What preparation to enter the patient during premedication for prevention of complications associated with vagus nerve stimulation? A. Dibazol B. * Pilocarpine C. Kordiamin D. Atropine E. Neostigmine. 110. The patient arrived in the morning at the reception to the surgeon-dentist. Admission started with a delay of 15 minutes. Doctor in stale in spots, tired robe, not listened to the end of patient complaints, asked him to open his mouth. During treatment, the patient's doctor shared with the nurse feeling about the movie. What is a violation of ethics in this case? A. Start receiving late B. Wrinkled robe doctor C. Improper ratio of doctor to patient complaints D. Discussion of the film during the admission of the patient E. * All of the above 111. The patient, turned in dentistry. clinic about removing 36. From history revealed that the patient suffers from hemophilia. Preliminary removal was accompanied by long-term bleeding. What is the doctor’s tactics? A. * Hold intervention in hospital with pre-and postoperative training. B. Required preoperative training in outpatient C. Postoperative treatment is not necessary. D. Conduct removal outpatients with further advice. E. Hold Removal supervised hematologist in the clinic 112. The patient appealed with complaints of pain in the right temporomandibular joint when you open your mouth, which appeared 3 days ago after trauma. The body temperature of 37,5 C, alignments intact, bite orthodonthic. What is necessary to test for establishing the clinical diagnosis? A. * Radiography B. Total blood C. Urinalysis D. Densitometry E. Thermometry 113. Patient, 35 years old, addressed the surgeon-dentist about oral preparation for prosthetics. On examination of the oral cavity revealed a lot of decayed teeth that are subject to extraction. Patient very emotional, easily excitable. To the dentist is not addressed because of fear of pain. Under what kind of anesthesia is advisable to remove the roots? A. Infiltration anesthesia B. Pain by needless injector C. * Mask anesthesia D. Regional anesthesia E. Electroanesthesia 114. The patient asked the dentist to remove the tooth for 36 sanitation indicators. Patient year ago suffered myocardial infarction, angina suffering. Which method is most efficient? A. Narcosis B. Infiltration anesthesia C. Conduction anesthesia D. Application anesthesia E. * Conduction anesthesia potentiated 115. The patient appealed to the surgeon - a dentist. On examination of the oral cavity revealed many decayed teeth to be removed. Patient very emotional, easily excitable. To the doctor dentist is not addressed because of fear of pain. Under what kind of anesthesia is advisable to remove the roots? A. Infiltration anesthesia B. * General anesthesia C. Pain relief through needless injector D. Anesthesia E. Electroanesthesia Test tasks to figures 1. What is shown on the Picture 26? A. *Primary sequester B. Radicular cyst C. Follicular cyst D. Sequester secondary E. Sequester third 2. What is the anatomical area marked with number 9 on the Picture 32? A. Palatal appendage of the upper jaw B. Horizontal plate palatine C. *Incisive channel D. Upper ridge E. Lower nasal sink 3. What is the anatomical area marked with number 8 on the Picture 32? A. *Palatal process of maxilla B. Horizontal plate palatine C. Nasal bone D. Alveolar process of maxilla E. Lower turbinate 4. What is the anatomical area marked with number 10 on the Pictures 32? A. *Front nose sinus B. Horizontal plate palatine C. Incisive canal D. Alveolar process of maxilla E. Lower turbinate 5. What is the anatomical area marked with number 1 on the Picture 32? A. *Processus frontalis B. Marqo infraorbitalis C. Crista lacrimalis D. Facies anterior E. Foramen infraorbitalis 6. What is the anatomical area marked with number 2 on the Picture 32? A. Processus frontalis B. *Marqo infraorbitalis C. Crista lacrimalis D. Facies anterior E. Foramen infraorbitalis 7. What is the anatomical area marked with letter D on the Picture 27? A. *Processus coronoideus B. Incisura mandibulae C. Foramen mandibulae D. Linea oblique E. Linea mylohyodea 8. What is the anatomical area marked with letter F on the Picture 27? A. Processus coronoideus B. Incisura mandibulae C. Foramen mandibulae D. *Processus condylaris E. Linea mylohyodea 9. What is the anatomical area marked with letter E on the Picture 27? A. *Ramus mandibulae B. Incisura mandibulae C. Foramen mandibulae D. Processus condylaris E. Linea mylohyodea 10. What is the anatomical area marked with letter B on the Picture 27? A. Ramus mandibulae B. Incisura mandibulae C. Foramen mandibulae D. Processus condylaris E. *Anqulus mandibulae 11. What is the anatomical area marked with letter C on the Picture 27? A. Ramus mandibulae B. Incisura mandibulae 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. C. Foramen mandibulae D. *Corpus mandibulae E. Anqulus mandibulae What is the anatomical marked with letter A on the Picture 27? A. Ramus mandibulae B. Incisura mandibulae C. *Protuberantia mentalis D. Corpus mandibulae E. Anqulus mandibulae What is shown on the Picture 28? A. *Radicular cyst B. Follicular cyst C. Traumatic cyst D. Chronic periodontitis E. No right answer What group of teeth can be removed with forceps on the Picture 29? A. 15,16,17,25,26,27 B. 11,12,13,21,22,23 C. 31,32,33,41,42,43 D. 35,36,37,45,46,47 E. *26,27 What group of teeth can be removed with forceps on the Picture 30? A. 11,12,21,22 B. Correct response C, E C. 37,38,47,48 D. 33,34,36,43,44,46 E. *31,32,41,42 Which elevator is shown on the Picture 31? A. Right elevator B. *Direct C. Left elevator D. Curette E. Bayonet similar What group of teeth can be removed with forceps on the Picture 33? A. Large molar teeth B. Canines and small molar teeth C. *The root of all teeth of the mandible D. Incisor teeth E. Large molar teeth What group of teeth can be removed with forceps on the Picture 34? A. Incisors and canines of the upper jaw B. Large molar teeth of upper jaw C. *Small molar teeth of upper jaw D. Large molar teeth of the mandible E. No right answer What group of the teeth can be removed with forceps on the Picture 35? A. Large molar teeth of the mandible B. *Incisors, canines and small molar teeth of the mandible C. Roots of all teeth of the mandible D. Mandibular incisors E. No right answer What group of teeth can be removed with forceps on the Picture 36? A. incisors and canines of the mandible B. small and large root teeth C. *Large molar teeth of the right mandible D. large molar teeth of the left mandible E. No right answer 21. What group of teeth can be removed with forceps on the Picture Fiq.37? A. incisors and canines of the upper jaw B. small root teeth of the upper jaw C. *Large molar teeth of upper jaw D. large molar teeth of upper jaw E. No right answer 22. What group of teeth can be removed with forceps on the Picture 38? A. Small root teeth of the mandible B. Incisors and canines of the mandible C. For the roots of mandibular D. No right answer E. *Large molar teeth of the mandible 23. What group of teeth can be removed with forceps on the Picture 39? A. *48,38 B. 47,46,45,35,36,37 C. 18.28 D. 17,16,26,27 E. No right answer 24. What group of teeth can be removed with forceps on the Picture 40? A. *14,15,24,25 B. 11,12,13,21,22,23 C. 16,17,26,27 D. 31,32,41,42 E. No right answer 25. What shown in Pic. 1 under the number 1? A. *Enamel B. Dentine C. Alveolar process D. Pulp E. All answers are correct 26. What is marked in Pic 1 under the number 2? A. Enamel B. *Dentin C. Alveolar process D. Pulp E. All answers are correct 27. What is marked in Pic 1 under the number 3? A. Enamel B. Dentine C. Alveolar process D. *Pulp E. All answers are correct 28. What is marked in Pic 1by the number 7? A. Enamel B. Dentine C. *Alveolar process D. Pulp E. All answers are correct 29. What is marked in Pic 1 under the number 9? A. Enamel B. Dentine C. Alveolar process D. All answers are correct E. *Circular ties 30. What is marked in Pic 1 under the number 12? A. *Cement B. Dentine 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. C. Alveolar process D. All answers are correct E. Circular ties What is marked in Pic 2 under the number 3? A. Eye-socket B. Infraorbital hole C. *Rear alveolar plexus D. Central hanhlion E. Etmoyidal sinus What is marked in Pic 2 under number 5? A. Eye-socket B. Infraorbital hole C. *Rear upper alveolar nerve D. Central hanhlion E. Etmoyidal sinus What is marked in Pic 2 under the number 6? A. Eye-socket B. Infraorbital hole C. *Average upper alveolar nerve D. Central hanhlion E. Etmoyidal sinus What is marked in Pic 2 under the number 7? A. Eye-socket B. Infraorbital hole C. *Front upper alveolar nerve D. Central hanhlion E. Etmoyidal sinus What is marked in Pic 2 under the number 9? A. Eye-socket B. *Infraorbital hole C. Front upper alveolar nerve D. Central hanhlion E. Etmoyidal sinus What is marked in Pic 2 under the number 10? A. Eye-socket B. Infraorbitalnyy hole C. front upper alveolar nerve D. *maxillary sinus E. No correct answer What is marker in Pic 3 under the number 1? A. *node trigemenus B. Maxillary nerve C. Mental nerve D. Mandibular nerv E. Infraorbital nerv What is marked in Pic 3 under the number 2? A. node trigemenus B. *Maxillary nerve C. Mental nerve D. Mandibular nerv E. Infraorbital nerv What is marked in Pic 3 under the number 3? A. node trigemenus B. Maxillary nerve C. *ophtalmic nerve D. Mandibular nerv E. Infraorbital nerv 40. What is marked in Pic 3 under the number 7? A. node trigemenus B. Maxillary nerve C. ophtalmic nerve D. Mandibular nerv E. *Infraorbital nerv 41. What is marked in Pic 3 under the number 8? A. node trigemenus B. *Maxillary nerve C. ophtalmic nerve D. Mandibular nerv E. Infraorbital nerv 42. What is marked in Pic 3 under the number 9? A. node trigemenus B. Maxillary nerve C. ophtalmic nerve D. *Mental nerv E. Infraorbital nerv 43. What is marked in Pic 3 at number 10, 11? A. node trigemenus B. Maxillary nerve C. ophtalmic nerve D. *Mandibular nerv E. Infraorbital nerv 44. What is marked in Pic 3 under the number 15? A. node trigemenus B. *Buccal nerve C. ophtalmic nerve D. Mandibular nerv E. Infraorbital nerv 45. What is marked in Pic 3 under the number 16? A. node trigemenus B. Maxillary nerve C. *tounge nerve D. Mandibular nerv E. Infraorbital nerv 46. Palpation of which group of lymph nodes is shown in Pic 4? A. Submental B. The upper neck nodes C. *Submandibular D. Rear neck E. The front neck nodes 47. Which methods of examination we see in Pic 4? A. *Objectively B. Subjective C. Laboratory D. Instrumental E. All answers are correct 48. Palpation of which group of lymph nodes is shown in Pic 5? A. Submental B. The upper neck nodes C. Rear neck D. Submandibular E. *Anterior cervical average 49. Which methods of examination we see in Pic 5? A. *Objectively B. Subjective 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. C. Laboratory D. Instrumental E. All answers are correct Palpation of which of lymph nodes is shown in Pic 6? A. *Tongue B. The upper lip C. Under lip D. Nose E. All answers are correct Which methods of examination we see in Pic 6? A. *Objectively B. Subjective C. Laboratory D. Instrumental E. All answers are correct What type of X-ray shown in Pic 7? A. Sighting intra oral B. Segmental C. Combined D. *Panoramic x-rays E. All answers are correct What type of maxillary sinus shown in Pic .7? A. *Pneumatic B. Sclerotic C. Combined D. Capsular E. All answers are correct What is shown in Pic 8? A. Caries B. PulPictis C. Alveolitis D. Sinusitis E. *Periodontitis What type periodontitis shown in Pic 8? A. Acute pus B. *Acute serous C. Fibrous chronic D. No correct answer E. All answers are correct Which anesthesia should be conducted for the extraction of teeth marked on Pic 8? A. Mental B. Incisor C. Infraorbital D. *Palatine and tuberal E. All answers are correct What type of periodontitis shown in Pic 9? A. Mental B. Incisor C. Infraorbital D. Palatine and tuberal E. *granuloma How called forceps shown in Pic 10? A. *Direct B. Slanting C. Bent on a plane D. Bent on the edge E. All answers are correct 59. What is the name of X-ray image shown in Pic 11? A. *Sighting intra oral radiographs B. Tomogram of the head and skull C. Panoramic x-rays D. All answers are correct E. X-ray Contrast 60. How called anesthesia which is shown in Pic 12? A. *incisor B. Mandibular C. Torusal D. Central E. All answers are correct 61. What is the target point, of anesthesia is shown in Fig. 12? A. Infraorbital hole B. Mandybular C. *incisor hole D. Big hole E. All answers are correct 62. What nerve anestesiting during anesthesia is shown inPic 12? A. Infraorbital hole B. Mandybular C. *incisor hole D. Big hole E. All answers are correct 63. How called anesthesia is shown in Pic 13? A. *Infraorbital anesthesia B. Mandybular C. incisor hole D. Big hole E. All answers are correct 64. What nerve anesthesitin during anesthesia is shown in Pic 14? A. Incisor B. Mandibualar C. Mental D. Torusal E. * infraorbital 65. How called anesthesia is shown in Pic 15? A. Incisor B. Mandibualar C. Mental D. *Torusal E. palatine 66. What is the target point, anesthesia is shown in Pic 15? A. Infraorbital hole B. *Mandibular hole C. Incisor foramen D. Palatal hole E. All answers are correct 67. What type of anesthesia is shown in Rys.Fig.16 A. *Mental intraoral B. Torusalna C. Tuberalna D. Mandybulyarna E. For Akinozi 68. What destination point anesthesia shown in Rys.Fig.16 A. Mandibular canal B. *Mental hole 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. C. Increase in mandibular D. Transitional fold lower jaw E. Picdboridkovyy symphysis What local complications can occur during anesthesia shown in .Fig.16 A. *The formation of ischemic areas on the skin B. arterial bleeding C. DiploPica D. root of the tongue E. All the above What local complications can not occur after anesthesia shown in .Fig.16 A. The formation of hematomas in the thickness of the lower lip B. euralgic pain in the area of ??anesthesia C. Reduced pain sensitivity zone D. Iatrogenic inflammation in the area of ??anesthesia E. *Keloid scar What type of anesthesia is shown in Fig.17 A. *Mental extraoral B. Torusal C. Tuberal D. Mandibular E. For Akinozi What destination point anesthesia shown in .Fig.17 A. Mandibular canal B. *Mental hole C. Increase in mandibular D. Oblique E. No right answer Put a diagnosis based on radiographs Fig.18 A. *Chronic osteomyelitis of the mandible on the right B. Chronic osteomyelitis of the mandible on the left C. Acute osteomyelitis of the mandible on the right D. Tsementoma right mandible E. Retynovanyy tooth left mandible What type of anesthesia is shown in Rys.Fig.19 A. Nasopalatinal B. Incisival C. *Palatine D. Anesthesia for Vajsblat palatal path E. Anesthesia for Bershe-Dubov Diagnose the position 3 lower molars on radiographs presented on Rys.Fig.20. A. * DystoPicya, horizontal position B. Retention C. DystoPicya and retention D. Transverzal shift E. Displacement around the axis Put a diagnosis based on radiographs Rys.Fig.21 A. *Nearside odontogenic sinusitis B. Right-sided odontogenic sinusitis C. Cancer left maxillary sinus D. Right maxillary sinus cancer E. Maxillary sinus Osteoblastoklastoma left Which anatomical holes indicated by green arrows on Rys.Fig.22 A. Oval holes B. Infraorbitalni holes C. *Round holes D. Small holes E. Big holes 78. What branch of the trigeminal nerve pass through the holes provided on the anatomical Fig.22 A. *II B. I C. III D. IV E. V 79. What types of surgical procedures are performed using the surgical instrument shown in Rys.Fig.23 A. Detachment mucous-periosteal flap B. Dissection of the oral mucosa C. Curettage holes after removal of teeth D. Resection of the apex of the root E. *Remove the roots of teeth on the upper and lower jaws 80. What anatomical hole indicated a black arrow on Rys.Fig.24 A. Oval hole B. Infraorbitalnyy hole C. Lower internal crack D. *Round hole E. Big hole 81. What branch of the trigeminal nerve passes through the hole shown in the anatomical Rys.Fig.24 A. I B. *II C. III D. IV E. V 82. What branch of the trigeminal nerve passes through the hole shown in the anatomical Rys.Fig.25 A. I B. *II C. III D. IV E. V 83. What a forceps shown on Pic 41? A. S-shaped tongs B. *Direct tongs C. All answer are corect D. rostral forceps E. no corect answer 84. What teeth extracted by forceps in Pic 41? A. lower incisors B. lower molars C. *The upper incisors and canines D. upper premolars E. lower premolars 85. Which forceps are shown on Fig.42? A. S-like forceps. B. straight forceps C. *forceps for 3th molar D. rostral forceps E. all answer are corect 86. What teeth you can extract by forceps on Pic. 42? A. lower incisors B. lower molars C. upper incisors and canines D. upper premolars E. *Upper third molars 87. What teeth you can extract by forceps on Pic 42? A. upper molars on the right side B. upper molars on the left side 88. 89. 90. 91. 92. 93. 94. 95. 96. C. *Upper third molars from the left and right side D. upper premolars E. lower premolars Which forceps shown on Pic 43? A. S-shaped tongs. B. straight forceps C. *forceps for 3th molar D. rostral forceps E. all answer are correct How call forceps on Pic 43? A. S-shaped tongs. B. straight forceps C. *forceps for 3th molar D. rostral forceps E. all answer are correct What anatomical structure you can extract by forceps shown on Pic 43? A. upper molars on the right side B. upper molars on the left side C. upper third molars from the left and right sides D. *Roots of upper molars of the left and right parties also E. lower premolars What anesthesia is shown on Pic 44? A. Extraoral infraorbital B. *Extraoral tuberal C. Extraoral near incisor chanel D. Extraoral mental E. All answer are correct What anesthesia is shown on Pic 45? A. Infraorbital B. Tuberal C. Incisor D. *Palatine E. All answer correct What anesthesia is shown in Fig.46? A. infraorbital B. tuberal C. *incisor D. Palatine E. All answer correct What anesthesia is shown on Pic 47? A. infraorbital B. tuberal C. incisor D. Palatine E. *torusal What anesthesia is shown on Pic 48? A. Infraorbital B. Tuberal C. Torusal D. *Mental E. Palatine Which forceps shown on Pic 49? A. *S-like forceps B. straight forceps C. forceps for 3th molar D. rostral forceps E. all answer are correct 97. What teeth you can extract by forceps on Pic 49? A. upper molars on the right side B. upper molars on the left side C. upper premolars on the right side D. *Upper premolars of the left and right sides E. lower premolars 98. What teeth you can extract by forceps on Pic 50? A. *All the teeth in upper jaw B. all teeth in the mandible C. only premolars in upper jaw D. roots of teeth on upper jaw E. incisors in the upper jaw 99. What teeth you can extract by forceps on Pic 51 ? A. All the teeth in upper jaw B. *all teeth in the mandible C. only premolars in upper jaw D. roots of teeth on upper jaw E. incisors in the upper jaw 100. Which forceps shown on Pic 52? A. S-shaped tongs. B. straight forceps C. forceps for 3th molar D. *Rostal forceps E. All answer are correct 101. What tooth you can extract by forceps on Pic 52? A. lower incisors B. lower molars C. upper incisors and canines D. lower premolars E. *Roots of lower teeth 102. What disease is shown on x-ray Pic 53? A. *Fibrotic periodontitis B. Granulom C. Odontogenic cyst D. All answer correct E. cancer 103. What is the pathological process is shown in x-ray object on Pic 54? A. *Radix cyst of tooth 12 B. Follicular cyst of tooth 12 C. Chronic osteomilities D. Odontogenic sinusitis E. All answer are correct 104. What is marked by № 1 on Pic 55? A. *Filling material B. Root of the tooth C. structure of bone D. tooth crown E. pulp camera 105. What is marked by №4 .on Pic 55? A. Filling material B. Root of the tooth C. structure of bone D. *metallic tooth crown E. pulp camera 106. What you can see on Pic 56? A. no correct answer B. *Panoramic x-rays 107. 108. 109. 110. 111. 112. 113. 114. 115. C. sighting radiograph D. tomography E. no correct naswer What you can see in x- ray on Pic 57? A. fibrotic periodontitis B. *chronic periodontitis C. cyst odontogenic D. no correct answer E. all answer are correct What anesthesia is shown on Pic 58? A. Infraorbital B. Tuberal C. Incisor D. Mental E. *palatine What is the target point of anesthesia in Pic 58? A. *Big palatine foramen B. Small palatine hole C. Incisor hole D. All answer correct E. No right answer What you can see on x-ray Pic 59? A. fibrotic periodontitis B. chronic periodontitis C. odontogenic cyst D. *odontogenic cyst-granuloma E. all answer are correct Which manipulation you can see on Pic 60? A. *tooth extraction B. Crown separation C. Extraction of pulp D. All answer are correct E. No correct answer What is marked on the x-ray Pic .61? A. *retention of third molar B. No correct answer C. All answere correct D. PulPictis E. caries Which manipulation you can see on .Pic 61? A. *tooth extraction B. Crown radicular separation C. Root amputation D. Therapeutic treatment E. All answer corect What mark on the x-ray on Pic 62? A. *Retention and dystopy of 3th molar B. PulPictis C. Periodontitis D. Caries E. All answer corect What manipulation is shown on Pic 62? A. *tooth extraction B. Crown radicular separation C. Amputation of crown D. Therapeutic treatment E. All answer are corect 116. 117. 118. 119. 120. 121. 122. 123. 124. 125. What indicated by the arrow on the x-ray on Pic 63? A. Retention and dystopy of 3th molar B. PulPictis C. Periodontitis D. Caries E. *Resorbtion of bone behind 3th molar Which method of treatment is shown on Pic 63? A. *tooth extraction B. Crown radicular separation C. Hemisection D. root amputation E. therapeutic treatment What shown in Pic. 1 under the number 1? A. *Enamel B. Dentine C. Alveolar process D. Pulp E. All answers are correct What is marked in Pic 1 under the number 2? A. Enamel B. *Dentin C. Alveolar process D. Pulp E. All answers are correct What is marked in Pic 1 under the number 3? A. Enamel B. Dentine C. Alveolar process D. * Pulp E. All answers are correct What is marked in Pic 1by the number 7? A. Enamel B. Dentine C. *Alveolar process D. Pulp E. All answers are correct What is marked in Pic 1 under the number 9? A. Enamel B. Dentine C. Alveolar process D. All answers are correct E. *Circular ties What is marked in Pic 1 under the number 12? A. * Cement B. Dentine C. Alveolar process D. All answers are correct E. Circular ties What is marked in Pic 2 under the number 3? A. Eye-socket B. Infraorbital hole C. Rear alveolar plexus D. *Central hanhlion E. Etmoyidal sinus What is marked in Pic 2 under number 5? A. Eye-socket B. Infraorbital hole 126. 127. 128. 129. 130. 131. 132. 133. 134. C. *Rear upper alveolar nerve D. Central hanhlion E. Etmoyidal sinus What is marked in Pic 2 under the number 6? A. Eye-socket B. Infraorbital hole C. * Average upper alveolar nerve D. Central hanhlion E. Etmoyidal sinus What is marked in Pic 2 under the number 7? A. Eye-socket B. Infraorbital hole C. *Front upper alveolar nerve D. Central hanhlion E. Etmoyidal sinus What is marked in Pic 2 under the number 9? A. Eye-socket B. * Infraorbital hole C. Front upper alveolar nerve D. Central hanhlion E. Etmoyidal sinus What is marked in Pic 2 under the number 10? A. Eye-socket B. Infraorbitalnyy hole C. front upper alveolar nerve D. *maxillary sinus E. No correct answer What is marker in Pic 3 under the number 1? A. * node trigemenus B. Maxillary nerve C. Mental nerve D. Mandibular nerv E. Infraorbital nerv What is marked in Pic 3 under the number 2? A. node trigemenus B. *Maxillary nerve C. Mental nerve D. Mandibular nerv E. Infraorbital nerv What is marked in fig. 3 under the number 3? A. node trigemenus B. Maxillary nerve C. *ophtalmic nerve D. Mandibular nerv E. Infraorbital nerv What is marked in Pic 3 under the number 7? A. node trigemenus B. Maxillary nerve C. ophtalmic nerve D. Mandibular nerv E. *Infraorbital nerv What is marked in Pic 3 under the number 8? A. node trigemenus B. *Maxillary nerve C. ophtalmic nerve D. Mandibular nerv E. Infraorbital nerv 135. 136. 137. 138. 139. 140. 141. 142. 143. 144. What is marked in Pic 3 under the number 9? A. node trigemenus B. Maxillary nerve C. ophtalmic nerve D. * Mental nerv E. Infraorbital nerv What is marked in Pic 3 at number 10, 11? A. node trigemenus B. Maxillary nerve C. ophtalmic nerve D. *Mandibular nerv E. Infraorbital nerv What is marked in Pic 3 under the number 15? A. node trigemenus B. *Buccal nerve C. ophtalmic nerve D. Mandibular nerv E. Infraorbital nerv What is marked in Pic 3 under the number 16? A. node trigemenus B. Maxillary nerve C. *tounge nerve D. Mandibular nerv E. Infraorbital nerv Palpation of which group of lymph nodes is shown in Pic 4? A. Submental B. *The upper neck nodes C. Submandibular D. Rear neck E. The front neck nodes Which methods of examination we see in Pic 4? A. *Objectively B. Subjective C. Laboratory D. Instrumental E. All answers are correct Palpation of which group of lymph nodes is shown in Pic 5? A. Submental B. *The upper neck nodes C. Rear neck D. Submandibular E. Anterior cervical average Which methods of examination we see in Pic 5? A. *Objectively B. Subjective C. Laboratory D. Instrumental E. All answers are correct Palpation of which of lymph nodes is shown in Pic 6? A. *Tongue B. The upper lip C. Under lip D. Nose E. All answers are correct Which methods of examination we see in Pic 6? A. * Objectively B. Subjective 145. 146. 147. 148. 149. 150. 151. 152. 153. C. Laboratory D. Instrumental E. All answers are correct What type of X-ray shown in Pic 7? A. Sighting intra oral B. Segmental C. Combined D. * Panoramic x-rays E. All answers are correct What is shown in Pic 8? A. Caries B. PulPictis C. Alveolitis D. Sinusitis E. *Periodontitis What type periodontitis shown in Pic 8? A. Acute pus B. Acute serous C. *Fibrous chronic D. No correct answer E. All answers are correct Which anesthesia should be conducted for the extraction of teeth marked on Pic 8? A. Mental B. Incisor C. Infraorbital D. *Palatine and tuberal E. All answers are correct What type of periodontitis shown in Pic 9? A. Mental B. Incisor C. Infraorbital D. Palatine and tuberal E. *granuloma Which anesthesia should be conducted for the extraction of teeth marked on Pic 9? A. Mental B. Torusal C. Palate and tuberal D. Infraorbital E. All answers are correct How called forceps shown in Pic 10? A. *Direct B. Slanting C. Bent on a plane D. Bent on the edge E. All answers are correct For removal of which teeth are used tongs shown in Pic 10? A. 48 B. 18 C. *21, 22,11,12 D. 36 E. 32 What is the name of X-ray image shown in Pic 11? A. *Sighting intra oral radiographs B. Tomogram of the head and skull C. Panoramic x-rays D. All answers are correct E. X-ray Contrast 154. 155. 156. 157. 158. 159. 160. 161. 162. 163. How called anesthesia which is shown in Pic 12? A. * incisor B. Mandibular C. Torusal D. Central E. All answers are correct What is the target point, of anesthesia is shown in Fig. 12? A. Infraorbital hole B. Mandybular C. * incisor hole D. Big hole E. All answers are correct What nerve anestesiting during anesthesia is shown inPic 12? A. Infraorbital hole B. Mandybular C. * incisor hole D. Big hole E. All answers are correct How called anesthesia is shown in Pic 13? A. *Infraorbital anesthesia B. Mandybular C. incisor hole D. Big hole E. All answers are correct What is the target point, anesthesia is shown in Pic 13? A. * Infraorbital hole B. Mandibular hole C. Incisor hole D. Big hole E. All answers are correct What nerve anestesiting during anesthesia is shown in Pic 13? A. Incisor B. Mandibular C. Mental D. Torusal E. * infraorbital How called anesthesia is shown in Pic 14? A. Incisor B. Mandibular C. Mental D. Torusal E. * infraorbital What is the target point, anesthesia is shown in Pic 14? A. *Infraorbital hole B. Mandibular hole C. Big hole D. Incisor hole E. All answer are correct What nerve anesthesitin during anesthesia is shown in Pic 14? A. Incisor B. Mandibualar C. Mental D. Torusal E. * infraorbital How called anesthesia is shown in Pic 15? A. Incisor B. Mandibualar 164. 165. 166. 167. 168. 169. 170. 171. 172. C. Mental D. * Torusal E. palatine What is the target point, anesthesia is shown in Pic 15? A. Infraorbital hole B. * Mandibular hole C. Incisor foramen D. Palatal hole E. All answers are correct What type of anesthesia is shown in Rys.Fig.16 A. * Mental intraoral B. Torusalna C. Tuberalna D. Mandybulyarna E. For Akinozi What destination point anesthesia shown in Rys.Fig.16 A. Mandibular canal B. * Mental hole C. Increase in mandibular D. Transitional fold lower jaw E. Picdboridkovyy symphysis What local complications can occur during anesthesia shown in .Fig.16 A. *The formation of ischemic areas on the skin B. arterial bleeding C. DiploPica D. root of the tongue E. All the above What local complications can not occur after anesthesia shown in .Fig.16 A. The formation of hematomas in the thickness of the lower lip B. Neuralgic pain in the area of ??anesthesia C. Reduced pain sensitivity zone D. Iatrogenic inflammation in the area of ??anesthesia E. * Keloid scar What type of anesthesia is shown in Rys.Fig.17 A. *Mental extraoral B. Torusal C. Tuberal D. Mandibular E. For Akinozi What destination point anesthesia shown in .Fig.17 A. Mandibular canal B. *Mental hole C. Increase in mandibular D. Oblique E. No right answer Put a diagnosis based on radiographs Fig.18 A. *Chronic osteomyelitis of the mandible on the right B. Chronic osteomyelitis of the mandible on the left C. Acute osteomyelitis of the mandible on the right D. Tsementoma right mandible E. Retynovanyy tooth left mandible What type of anesthesia is shown in Rys.Fig.19 A. NosoPicdnebinna B. Riztseva C. *Palatine D. Anesthesia for Vajsblat palatal path E. Anesthesia for Bershe-oak 173. 174. 175. 176. 177. 178. 179. 180. 181. 182. 8. Diagnose the position 3 lower molars on radiographs presented on Rys.Fig.20. A. *DystoPicya, horizontal position B. Retention C. DystoPicya and retention D. Transverzal shift E. Displacement around the axis Put a diagnosis based on radiographs Rys.Fig.21 A. *Nearside odontogenic sinusitis B. Right-sided odontogenic sinusitis C. Cancer left maxillary sinus D. Right maxillary sinus cancer E. Maxillary sinus Osteoblastoklastoma left Which anatomical holes indicated by green arrows on Rys.Fig.22 A. Oval holes B. Infraorbitalni holes C. *Round holes D. Small holes E. Big holes What branch of the trigeminal nerve pass through the holes provided on the anatomical Fig.22 A. *II B. I C. III D. IV E. V What types of surgical procedures are performed using the surgical instrument shown in Fig.23 A. Detachment mucous-periosteal flap B. Dissection of the oral mucosa C. Curettage holes after removal of teeth D. Resection of the apex of the root E. *Remove the roots of teeth on the upper and lower jaws What anatomical hole indicated a black arrow on Rys.Fig.24 A. Oval hole B. Infraorbitalnyy hole C. Lower internal crack D. *Round hole E. Big hole What branch of the trigeminal nerve passes through the hole shown in the anatomical Rys.Fig.24 A. I B. *II C. III D. IV E. V What branch of the trigeminal nerve passes through the hole shown in the anatomical Rys.Fig.25 A. I B. *II C. III D. IV E. V What a forceps shown on Pic 41? A. S-shaped tongs B. *Direct tongs C. All answer are corect D. rostral forceps E. no corect answer What teeth extracted by forceps in Pic 41? A. lower incisors B. lower molars 183. 184. 185. 186. 187. 188. 189. 190. 191. C. *The upper incisors and canines D. upper premolars E. lower premolars Which forceps shown on Rys.Fig.42? A. S-like forceps. B. straight forceps C. *forceps for 3th molar D. rostral forceps E. all answer are corect What teeth you can extract by forceps on Pic 42? A. lower incisors B. lower molars C. upper incisors and canines D. upper premolars E. *Upper third molars What teeth you can extract by forceps on Pic 42? A. upper molars on the right side B. upper molars on the left side C. *Upper third molars from the left and right side D. upper premolars E. lower premolars Which forceps shown on Pic 43? A. S-shaped tongs. B. straight forceps C. *forceps for 3th molar D. rostral forceps E. all answer are correct How call forceps on Pic 43? A. S-shaped tongs. B. straight forceps C. *forceps for 3th molar D. rostral forceps E. all answer are correct What anatomical structure you can extract by forceps shown on Pic 43? A. upper molars on the right side B. upper molars on the left side C. upper third molars from the left and right sides D. *Roots of upper molars of the left and right parties also E. lower premolars What anesthesia is shown on Pic 44? A. extraoral infraorbital B. *extraoral tuberal C. extraoral near incisor chanel D. extraoral mental E. all answer are correct What anesthesia is shown on Pic 45? A. infraorbital B. tuberal C. incisor D. *Palatine E. All answer correct What anesthesia is shown in Rys.Fig.46? A. infraorbital B. tuberal C. *incisor D. Palatine E. All answer correct 192. 193. 194. 195. 196. 197. 198. 199. 200. 201. What anesthesia is shown on Pic 47? A. infraorbital B. tuberal C. incisor D. Palatine E. *torusal What anesthesia is shown on Pic 48? A. Infraorbital B. Tuberal C. Torusal D. *Mental E. Palatine Which forceps shown on Pic 49? A. *S-like forceps B. straight forceps C. forceps for 3th molar D. rostral forceps E. all answer are correct What teeth you can extract by forceps on Pic 49? A. upper molars on the right side B. upper molars on the left side C. upper premolars on the right side D. *Upper premolars of the left and right sides E. lower premolars What teeth you can extract by forceps on Pic 50? A. *All the teeth in upper jaw B. all teeth in the mandible C. only premolars in upper jaw D. roots of teeth on upper jaw E. incisors in the upper jaw 17. What teeth you can extract by forceps on Pic 51 ? A. All the teeth in upper jaw B. *all teeth in the mandible C. only premolars in upper jaw D. roots of teeth on upper jaw E. incisors in the upper jaw Which forceps shown on Pic 52? A. S-shaped tongs. B. straight forceps C. forceps for 3th molar D. *Rostal forceps E. All answer are correct What tooth you can extract by forceps on Pic 52? A. lower incisors B. lower molars C. upper incisors and canines D. lower premolars E. *Roots of lower teeth What disease is shown on x-ray Pic 53? A. *Fibrotic periodontitis B. Granulom C. Odontogenic cyst D. All answer correct E. cancer What is the pathological process is shown in x-ray object on Pic 54? A. *Radix cyst of tooth 12 B. Follicular cyst of tooth 12 202. 203. 204. 205. 206. 207. 208. 209. 210. C. Chronic osteomilities D. Odontogenic sinusitis E. All answer are correct What is marked by № 1 on Pic 55? A. *Filling material B. Root of the tooth C. structure of bone D. tooth crown E. pulp camera What is marked by №4 .on Pic 55? A. Filling material B. Root of the tooth C. structure of bone D. *metallic tooth crown E. pulp camera What you can see on Pic 56? A. no correct answer B. *Panoramic x-rays C. sighting radiograph D. tomography E. no correct naswer What you can see in x- ray on Pic 57? A. fibrotic periodontitis B. *chronic periodontitis C. cyst odontogenic D. no correct answer E. all answer are correct What anesthesia is shown on Pic 58? A. Infraorbital B. Tuberal C. Incisor D. Mental E. *palatine What is the target point of anesthesia in Pic 58? A. *Big palatine foramen B. Small palatine hole C. Incisor hole D. All answer correct E. No right answer What you can see on x-ray Pic 59? A. fibrotic periodontitis B. chronic periodontitis C. odontogenic cyst D. *odontogenic cyst-granuloma E. all answer are correct Which manipulation you can see on Pic 60? A. * tooth extraction B. Crown separation C. Extraction of pulp D. All answer are correct E. No correct answer .What is marked on the x-ray Pic .61? A. * retention of third molar B. No correct answer C. All answere correct D. PulPictis E. caries 211. 212. 213. 214. Which manipulation you can see on .Pic 61? A. * tooth extraction B. Crown radicular separation C. Root amputation D. Therapeutic treatment E. All answer corect What mark on the x-ray on Pic 62? A. * Retention and dystopy of 3th molar B. PulPictis C. Periodontitis D. Caries E. All answer corect What manipulation is shown on Pic 62? A. * tooth extraction B. Crown radicular separation C. Amputation of crown D. Therapeutic treatment E. All answer are corect What indicated by the arrow on the x-ray on Pic 63? A. Retention and dystopy of 3th molar B. PulPictis C. Periodontitis D. Caries E. *Resorbtion of bone behind 3th molar