emergency and clinical care - Rutgers: School of Health Related
advertisement

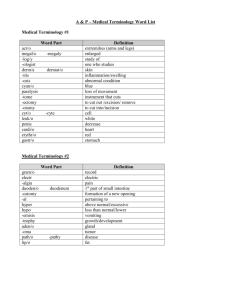
Emergency and Clinical Care IDST 1100 Course Description Emergency and Clinical Care is a course that deals with emergencies before medical help arrives. The course is designed to give the student the knowledge of how to recognize and respond to an emergency. The intent of the course is to help the student feel more confident in his/her ability to act appropriately in the event of an emergency. Students will be prepared to 1) obtain a patient medical history, 2) take and record vital signs relative to medical/dental treatment, and 3) acquire cardiopulmonary resuscitation American Red Cross certification. Credits/Modes of Instruction This is a 2-credit undergraduate course in lecture format that relies on regular activities, assignments, and completion of weekly topics. Pre/Co requisites Successful high school completion of Dynamics of Health Care in Society Instructor The instructor will be a Rutgers SHRP faculty (or adjunct) member. Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Identify ways to prevent injury and/or illness. Describe the major organ systems and their functions. Recognize when an emergency has occurred. Describe the four emergency action principals in any emergency. Describe first aid care for victims of respiratory distress. Recognize and provide care for sudden illness involving the heart. Recognize and describe the care necessary for internal and external bleeding. Describe the care necessary for soft tissues. Assess and provide care for musculoskeletal injuries. Describe and provide care for specific injuries to the head, face, and neck. Describe the signs of, and care for different injuries to the chest, abdomen, pelvis and extremities. Describe the care for sudden illness such as syncope, diabetic shock, seizures and stroke. Describe the care for poisoning, bites and stings. Describe the care necessary for victims of substance misuse and abuse. 15. 16. Recognize and describe the care necessary for temperature-related emergencies. Describe how to safely move victims on land and water. Suggested Text Healthcare First Aid with CPR and AED American Heart Association ISBN 0-87493-415-X American Red Cross Community First Aid and Safety Staywell Publishing 1100 Geundy Lane San Bruno, CA. 94066 ISBN 1-58480-105-0 Teaching/Learning Aids Lecture, classroom discussion and demonstration Visual Aids - Transparencies, video, slides, diagrams, handouts and manikins Computer Software Standard First Aid/ CPR Exam (Written and Demonstration) The students are required to successfully participate in class, complete all homework assignments and keep an organized notebook. The students must pass quizzes, tests and exams. The students must also pass Standard First Aid/ CPR. The following criteria will be used: Evaluation and Grading Grade Determination The minimum level of satisfactory performance in this course is a ‘C’ or better. To receive a ‘C’ or better, students must complete ALL course requirements specified above, including meeting the minimum attendance expectation. Upon successful completion of the course with a final high school grade of a “C” the student will be eligible to earn Rutgers SHRP college credit. In combination with high school grades the high school students must attain a C (74) or better on the Emergency and Clinical Care exam as administered by the high school through the American Red Cross or the American Heart Association’s standardized exam to earn college credits. Health Science Careers Program Grading System 2 Weighted Average of All Requirements Final Letter Grade 94-100 A 90-93 A- 87-89 B+ 84-86 B 80-83 B- 77-79 C+ 74-76 C 70-73 C- Unsatisfactory Performance/Progress Unsatisfactory performance which may include late assignments, failing grades, and/or attendance or progress problems will be discussed individually on an as needed basis. Honor Code and Academic Integrity (Refer to your Rutgers SHRP Student Handbook at http://shrp.rutgers.edu/current_students/handbook.pdf) The faculty of Rutgers School of Health Related Professions believes that students must observe and support high standards of honesty and integrity. For this reason, all students in this course are expected to abide by the School's Honor Code and uphold its Code of Academic Integrity. As described in detail in your Student Handbook, violations of the Code of Academic Integrity include cheating, plagiarism, fabrication and/or academic misconduct. All such violations will be considered with gravest concern and may be punishable with sanctions as severe as suspension or dismissal. If you have not previously affirmed the School's Honor Code (either in writing or electronically), you must submit a signed and dated copy of the Honor Code to the instructor by the end of the first week of the semester. The Honor Code form is provided in the current Rutgers SHRP Student Handbook. Health Science Careers 3 Emergency & Clinical Care Major Competency Areas Student Competency Achievement Evaluate the student using the rating scale below and check the appropriate number to indicate the degree of competency achieved. The numerical rating of 4,3,2,1 and 0 are not intended to represent the traditional school grading system of A,B, C,D, and F. The description associated with each of the numbers focus on the level of student achievement for each of the areas listed below. Rating Scale: 4 - Highly Satisfactory 3. - Satisfactory 2 - Needs Improvement 1 - Unsatisfactory 0 - Below Acceptable Level of Competency 4 3 2 1 0 I. Introduction Emergency Emergency Preparation __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ II. Body Systems Major Organs Functions of Each System First Aid-Related Problems __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ III. Assessment of Emergencies Primary Survey Secondary Survey Transporting Victims __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ IV. Respiratory Emergencies Normal Respiration Rescue Breathing First Aid for the Conscious Victim First Aid for the Unconscious Victim __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ V. Circulatory System Risk Factors of Heart Disease Prevention of Heart Disease Signs and Symptoms of Heart Attacks CPR in an Adult CPR in a Child CPR in an Infant __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 4 3 2 1 0 4 VI. Bleeding Blood and Blood Vessels Controlling Internal and External Bleeding Care of the Shock Victim __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ VII. Soft Tissue Injuries Types Preventing Infection Types of Bandages Care of Open and Closed Wounds Types of Burns Burn Care __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ VIII. Muscular/Skeletal Injuries Types Care Splinting __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ IX. Head and Spine Injuries Common Injuries General Care Specific Care __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ X. Chest, Abdominal and Pelvic Types Care __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ XI. Extremities Types of Injuries Care __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ XII. Medical Emergencies/Sudden Illness Types of Emergencies Care __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ XIII. Poisoning, Bites and Stings Types of Injuries Care Prevention __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ XIV. Substance Misuse and Abuse Types Recognizing Misuse/Abuse First Aid Response Prevention __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 4 3 2 1 0 5 XV. Exposure to the Elements Control of Body Temperature Types of Heat Emergencies Care of Heat Emergencies Types of Cold Emergencies Care of Cold Emergencies __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ XVI. Reaching and Moving Victims Methods of Emergency Moves Water Rescue __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ I. INTRODUCTION 6 CONTENT OBJECTIVES I. Introduction I. Introduction A. The Citizen Responder 1. Outline how the emergency medical system works. B. Emergency Prevention 2. C. Emergency Preparations Define the role of a Citizen Responder in the Emergency Medical Service System (EMS). 3. State the most important action a Citizen Responder can take in an emergency. 4. List the four most common indicators of an emergency. 5. List the five common barriers to action. 6. Identify the appropriate telephone numbers to handle specific emergencies. 7. Describe the value of first aid training. 8. List the content of a basic first aid kit. 9. Define important terms. I. INTRODUCTION 7 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS METHOD OF EVALUATIONS 1. Have students complete vocabulary/terminology worksheets. 1. Terminology and Spelling quiz. 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Discuss vocabulary/terminology words and pronunciation. 4. Prepare a list of emergency numbers for home use. 5. Visit EMS Dispatch Post. 6. Small Group Activity: Assemble First Aid Kit. 2. Unit Exam II. BODY SYSTEMS 8 CONTENT OBJECTIVES A. Respiratory 1. List the major body systems. B. Circulatory 2. Identify the major organs of each body system. C. Integumentary 3. D. Muscular / Skeletal Outline the functions of each body system. E. Nervous 4. Describe how the body systems are interrelated. F. Interrelationship of Body Systems 5. G. Identify Body Parts List the problems that require first aid related to each system. 6. Define important terms. II. BODY SYSTEMS 9 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS METHOD OF EVALUATION 1. Have students complete vocabulary / terminology worksheets. 1. Terminology and spelling quiz. 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Discuss vocabulary / terminology words and pronunciation. 4. Use dissected mannikin to locate organs and identify corresponding organ system. 5. Prepare a chart of injuries common to each organ system. 2. Unit exam. III. ASSESSMENT OF EMERGENCIES 10 CONTENT OBJECTIVES A. Emergency Action Principles 1. List and describe the four Emergency Action Principles. B. Transporting Victim 2. Explain the reasons for following emergency action principles. 3. Identify four important questions that must be answered when evaluating an emergency. 4. Explain what to do if you cannot reach a victim because of an unsafe setting. 5. List the three steps required to obtain consent to provide care to the victim. 6. Explain why you should do a primary evaluation in every emergency situation. 7. List the steps involved in a primary survey. 8. Identify the important facts that must be included when you call the EMS for help. 9. List five conditions that require a call for professional help. 10. List the steps involved in a secondary survey. 11. Explain why you should do a secondary survey in every emergency situation. 12. List the steps involved in a secondary survey. 13. Identify the reasons why you should not transport a victim. 14. Identify the things that must be done if transportation of the victim to the hospital is indicated. 15. Define important terms. III. ASSESSMENT OF EMERGENCIES 11 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS METHOD OF EVALUATION 1. Have students complete vocabulary worksheets. 1. Terminology and spelling quiz. 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Discuss vocabulary / terminology words and pronunciation. 4. Show video of emergency situations. 5. Skill Practice: Working in pairs, simulate positioning of the victim, the primary survey and the secondary survey. 2. Unit Exam. IV. RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES 12 CONTENT OBJECTIVES A. Breathing Process 1. Describe the process of breathing. B. Respiratory Distress 2. List five (of the many) signals of respiratory distress. C. Respiratory Distress 3. D. Airway Obstruction State three specific causes of respiratory distress. 4. Describe the care necessary for a victim of respiratory distress. 5. Identify the purpose of rescue breathing. 6. List the special consideration for rescue breathing. 7. Describe when to provide rescue breathing. 8. Outline the steps involved in rescue breathing. 9. State at least three causes of choking. 10. Describe and demonstrate the first aid care involved for a conscious and an unconscious person. 11. Demonstrate rescue breathing for an adult. 12. Demonstrate rescue breathing for a child. 13. Demonstrate rescue breathing for an infant. 14. Define important terms. IV. RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES 13 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS METHOD OF EVALUATION 1. Have students complete vocabulary / terminology worksheets. 1. Terminology and spelling quiz. 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Discuss vocabulary / terminology words and pronunciation. 4. Show video demonstrating rescue breathing. 5. Skill Practice: working in pairs, simulate the following situations: 2. Unit Exam. a. First Aid for conscious/ unconscious victim. b. Rescue breathing for an adult. c. Rescue breathing for a child. d. Rescue breathing for an infant. V. CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 14 CONTENT OBJECTIVES A. Heart Attack 1. Describe the heart. B. Cardiac Arrest 2. List three common causes of a heart attack. C. CPR 3. List five signals of a heart attack. 4. Describe the care necessary for a heart attack victim. 5. Identify the common causes and signals of cardiac arrest. 6. Describe the purpose of CPR. 7. Outline the steps involved in giving CPR. 8. List 5 conditions in which a rescuer may stop CPR. 9. Identify ways to prevent cardiovascular disease. 10. Identify risk factors of heart disease. 11. List three risk factors of heart disease. 12. Demonstrate CPR on an adult. 13. Demonstrate CPR on a child. 14. Demonstrate CPR on an infant. D. 1. Adult 2. Child 3. Infant Cardiovascular Disease Prevention V. CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 15 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS METHOD OF EVALUATION 1. Have students complete vocabulary/ terminology worksheets. 1. Terminology and spelling quiz. 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Discuss vocabulary / terminology words and pronunciation . 4. Show video demonstrating CPR. 5. Skill Practice: working in pairs, demonstrate CPR in the following situations: a. Adult b. Child c. Infant 6. Guest speaker: Dietitian from American Heart Association. 7. Supermarket Tour: Low fat, low cholesterol, low sodium products. 2. Unit Exam. VI. BLEEDING 16 CONTENT OBJECTIVES A. Blood and Blood Vessels. 1. Identify the components of blood. B. Bleeding Emergencies 2. List three functions of blood. C. Shock 3. Explain why severe bleeding must be controlled. 4. Outline the chain of events that occur when one is bleeding. 5. Identify the signals of external and internal bleeding. 6. Describe the methods for control of external and internal bleeding. 7. Explain the methods to minimize the risk of disease transmission when attempting to control external bleeding. 8. List two signals that can result in shock. 9. Identify six signals of shock. 10. Outline the process of "going into" shock. 11. Identify the care necessary for a victim of shock. 12. Define important terms. VI. BLEEDING 17 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS METHOD OF EVALUATION 1. Have students complete vocabulary / terminology worksheets. 1. Terminology and spelling quiz. 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Discuss vocabulary/terminology words and pronunciation. 4. Video: Bleeding and Shock. 5. Skill Practice: Working in pairs, simulate the care of a victim of shock. 2. Unit Exam. VII. SOFT TISSUE INJURIES 18 CONTENT OBJECTIVES A. Types 1. Describe soft tissues B. Infection 2. Identify the two types of open tissue wounds. C. Wound Care 3. D. Burn Care List four main types of open tissue wounds. 4. Describe the process involved in preventing infection. 5. Identify the signals of infection. 6. Describe how to care for an infection. 7. List the types of bandaging. 8. Describe how to care for open and closed wounds and those involving an impaled object. 9. Identify the causes of burn injury. 10. Identify the three types of burns. 11. Describe the basic steps of burn care. 12. Identify the causes of thermal, chemical, electrical and radiation burns. 13. Define important terms. VII. SOFT TISSUE INJURIES 19 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS METHOD OF EVALUATION 1. Have students complete vocabulary / terminology worksheets. 1. Terminology and spelling quiz. 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Video: Soft Tissue Injuries. 4. Skill Practice: Working in pairs, simulate the following: 2. Unit Exam. a. b. c. Types of bandaging Controlling bleeding Care of Burn Victim VIII. MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES 20 CONTENT OBJECTIVES A. Types 1. Identify the major structures of the e musculoskeletal system. B. Care 2. C. Transport considerations Describe the four basic types of injuries than can occur to the musculoskeletal system. 3. Identify the signals of a musculoskeletal injury. 4. Outline the care necessary for a musculoskeletal injury. 5. Identify considerations for transport of a victim of musculoskeletal injury. 6. List the four principles of splinting. 7. Identify and demonstrate the application of a(n) anatomic, soft and rigid splint. 8. Define important terms. VIII. MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES 21 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS METHOD OF EVALUATION 1. Have students complete vocabulary / terminology worksheets. 1. Terminology and spelling quiz. 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Discuss vocabulary / terminology words and pronunciation. 4. Video: Musculoskeletal Injury. 5. Skill practice: working in pairs, simulate splinting. 2. Unit Exam IX. HEAD AND SPINE 22 CONTENT OBJECTIVES A. Recognizing Serious Injuries 1. List the most common types of head and spinal injuries. B. General Care 2. C. Specific Care Identify five causes of head and spinal injuries. 3. Identify the signals of head and spinal injuries. 4. Describe the care necessary for head and spinal injuries. 5. Describe the care necessary for concussions, scalp, cheek, nose, eye, ear, mouth, jaw, and teeth injuries. 6. Describe how to minimize movement of the victim's head and spine. 7. List seven ways to prevent head and spinal injuries. 8. Define important terms. IX. HEAD AND SPINE 23 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS 1. Have students complete vocabulary / terminology worksheets. 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Discuss vocabulary / terminology words and pronunciation. 4. Skill Practice: Working in pairs, simulate the following: a. b. METHOD OF EVALUATION 1. Terminology and spelling quiz. 2. Unit Exam. Care of Head Injuries Care of Spine Injuries X. CHEST, ABDOMINAL, AND PELVIC INJURIES 24 CONTENT OBJECTIVES A. Types 1. Describe the injuries that can occur to the chest, abdomen and pelvis. B. Care 2. Explain why chest, abdominal and pelvic injuries can be fatal. 3. Identify signals of chest, abdominal and pelvic injuries. 4. List the steps involved in the care of chest/rib, abdominal and pelvic injuries. 5. Describe the care involved with "sucking" chest injuries. 6. Describe the care for injuries to the genitals. 7. Define important terms. X. CHEST, ABDOMINAL AND PELVIC INJURIES. 25 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS METHOD OF EVALUATION 1. Have students complete vocabulary /terminology worksheets. 1. Terminology and spelling quiz. 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Discuss vocabulary / terminology words and pronunciation. 4. Skill Practice: Working in pairs, simulate the following: 2. Unit Exam a. b. Care of chest injuries Care of genital injuries XI. EXTREMITIES 26 CONTENT OBJECTIVES A. Types 1. Describe the injuries that can occur to the extremities. B. Care 2. List five signals that indicate serious extremity injury. 3. Describe how to care for injuries to the extremities. 4. Define important terms. XI. EXTREMITIES 27 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS METHOD OF EVALUATION 1. Have students complete vocabulary / terminology worksheets. 1. Terminology and spelling quiz. 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Discuss vocabulary / terminology words and pronunciation. 4. Skill practice: Working in pairs, simulate the care of injuries to extremities. 2. Unit Exam XII. MEDICAL EMERGENCIES/SUDDEN ILLNESS 28 CONTENT OBJECTIVES A. Types 1. Identify five signals of sudden illness. B. Care 2. Describe the care necessary for fainting. 3. Describe the care necessary for diabetic emergencies. 4. Describe the care necessary for seizures. 5. Describe the care necessary for stroke victims. 6. List at least three instances when EMT services are required. 7. Define important terms. XII. MEDICAL EMERGENCIES / SUDDEN ILLNESS 29 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS METHOD OF EVALUATION 1. Have students complete vocabulary / terminology worksheets. 1. Terminology and spelling quiz. 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Discuss vocabulary / terminology words and pronunciation. 4. Skill practice: working in pairs, simulate the care necessary for the following: 2. Unit exam. a. b. c. d. fainting diabetic emergencies seizures stroke XIII. POISONING, BITES AND STINGS 30 CONTENT OBJECTIVES A. Types 1. Identify the four ways that poisons can enter the body. B. Care 2. Identify the signals of poisoning. C. Prevention 3. List the questions to be answered if poisoning is suspected. 4. Identify the specific are necessary for ingested, inhaled and absorbed poisoning emergencies. 5. Identify the specific care necessary for an insect bite or sting, marine life sting, snake bite, tick bite or animal bite. 6. Identify five factors to prevent poisoning. 7. Describe the signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis. 8. Describe the role of a Poison Control Center. 9. Define important terms. \ ]XIII. POISONING, BITES AND STINGS 31 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS METHOD OF EVALUATION 1. Have students complete vocabulary / terminology worksheets. 1. Terminology and spelling quiz. 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Discuss vocabulary / terminology words and pronunciation. 4. Skill practice: working in pairs, simulate the care necessary for: a. b. poisoning insect, snake, and animal bites 2. XIV. SUBSTANCE MISUSE AND ABUSE 32 Unit Exam CONTENT OBJECTIVES A. Types 1. Identify three categories of commonly abused or misused substances. B. Forms 2. List the effects of misuse and abuse. C. Common Substances 3. D. Recognizing Misuse/Abuse Identify five signals of substance misuse or abuse. E. First Aid/Response 4. F. Prevention Describe the first aid or general care necessary for someone suspected of substance abuse or misuse. 5. Identify six factors that can lead a person to substance misuse or abuse. 6. Outline the ways to prevent unintentional substance misuse or abuse. 7. Define important terms. XIV. SUBSTANCE MISUSE AND ABUSE 33 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS METHOD OF EVALUATION 1. Have students complete vocabulary / terminology worksheets. 1. Terminology and spelling quiz. 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Discuss vocabulary/terminology words and pronunciation. 4. Skill practice: working in pairs, simulate the first aid for legal and illegal substance misuse/abuse. 2. Research Paper: Choose a substance and describe its physiological effect on the body. 5. Role Play: Counseling techniques for substance abuse. 3. Unit Exam XV. EXPOSURE TO THE ELEMENTS 34 CONTENT OBJECTIVES A. Body Temperature 1. Describe how body temperature is controlled. B. Types 2. C. Prevention Identify those people who are at risk for heat or cold illness. 3. Identify two types of heat emergencies. 4. List the signals of heat exhaustion. 5. List the signals of heat stroke. 6. Identify two types of cold emergencies. 7. List the signals of frostbite. 8. List the signals of hypothermia. 9. Describe three general care steps to be immediately followed after heat or coldrelated emergencies. 10. List five example of first aid for heat and cold emergencies. 11. Identify two signals of heat or coldrelated illness that require EMT services. 12. Define important terms. XV. EXPOSURE TO THE ELEMENTS 35 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS METHOD OF EVALUATION 1. Have students complete vocabulary / terminology worksheets. 1. Terminology and spelling quiz 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Discuss vocabulary / terminology words and pronunciation. 4. Skill practice: working in pairs, simulate the care necessary for the following: 2. Unit Exam a. b. heat emergencies cold emergencies: frostbite, hypothermia XVI. REACHING AND MOVING VICTIMS 36 CONTENT OBJECTIVES A. Reaching 1. B. Moving List three situations in which an emergency move of a victim is necessary. C. Water 2. Identify your limitations before you decide to move a victim. 3. List and demonstrate five emergency moves. 4. Identify the most appropriate move for a person suspected of a spinal injury. 5. List five methods of water rescue. 6. Describe "self rescue." 7. Describe survival swimming. 8. List five precautions to take around water. 9. Define important terms. XVI. REACHING AND MOVING VICTIMS 37 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS METHOD OF EVALUATION 1. Have students complete vocabulary / terminology worksheets. 1. Terminology and spelling quiz. 2. Prepare lecture on material. 3. Discuss vocabulary / terminology words and pronunciation. 4. Skill practice: working in pairs, simulate the care necessary for water rescue. 2. Unit Exam. 38