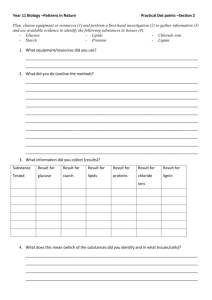
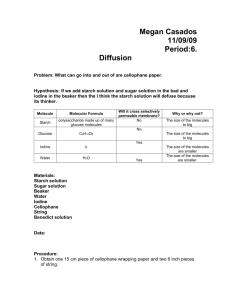
Diffusion Lab Target Concepts: Understanding diffusion and how it
advertisement
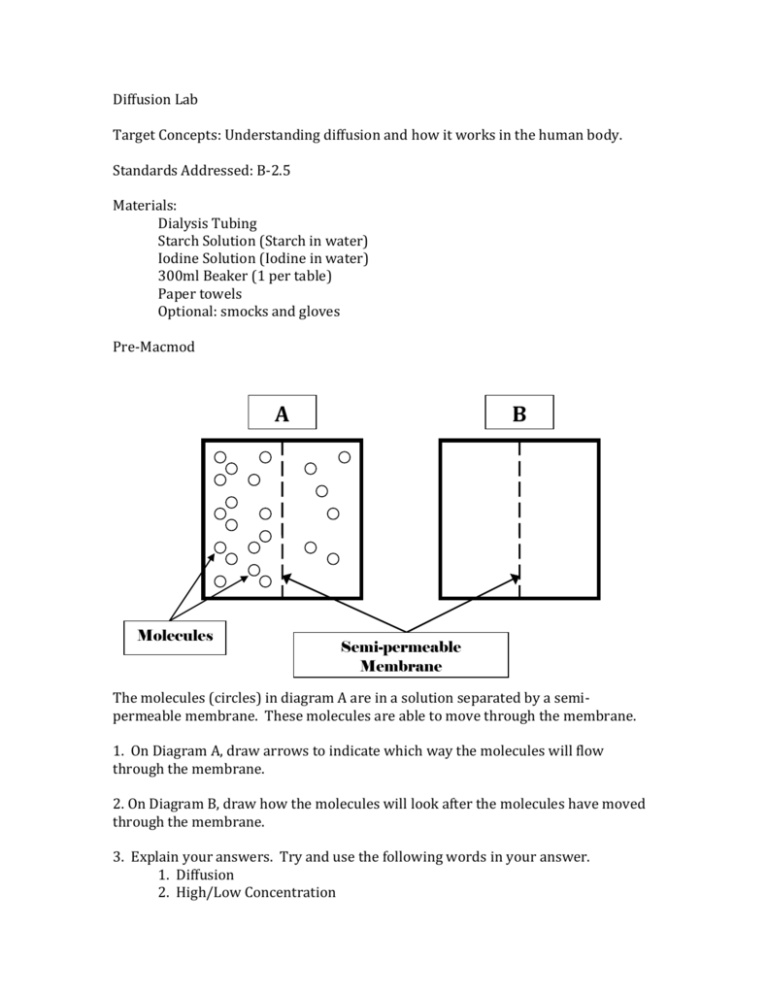
Diffusion Lab Target Concepts: Understanding diffusion and how it works in the human body. Standards Addressed: B-2.5 Materials: Dialysis Tubing Starch Solution (Starch in water) Iodine Solution (Iodine in water) 300ml Beaker (1 per table) Paper towels Optional: smocks and gloves Pre-Macmod A Molecules B Semi-permeable Membrane The molecules (circles) in diagram A are in a solution separated by a semipermeable membrane. These molecules are able to move through the membrane. 1. On Diagram A, draw arrows to indicate which way the molecules will flow through the membrane. 2. On Diagram B, draw how the molecules will look after the molecules have moved through the membrane. 3. Explain your answers. Try and use the following words in your answer. 1. Diffusion 2. High/Low Concentration Introduction: Explain to the students they will be performing a lab today. Talk about each component they will be in contact with. For example, discuss starch, what it is and have a picture of what it looks like. Also, discuss iodine, what it is and what it looks likes. It’s helpful to have these pictures on the same slide. The students can notice the size differences of the molecules. Explain to the students that in the presence of iodine, starch turns black. Each group should have a list of directions. Let the students collect the equipment needed and get started on the lab. While doing the lab, they must be filling out and answering questions along the way. During the lab they should be able to see the reaction occurring inside the dialysis tubing but not outside in the beaker. Walk around to each group and ask them leading questions as to why it is only occurring in the tube and not outside the tube. Refer back to your power point, which shows the size differences in iodine and starch molecules. This can help explain why iodine was able to move through the membrane and starch was not (selectively permeable). Also, introduce the idea of concentrations and discuss the concentration gradients by asking leading questions. Have the students clean up and take out their notebooks. Post-Discussion: Talk about what happened inside and outside the tube as a class. Introduce the idea about the different concentrations within the beaker and the tubing. Discuss how molecules move from high concentrations to low concentrations (concentration gradient). Also talk about the movement of iodine into the tube without the starch moving out of the tube. Explain possible reasons for this (i.e. size of molecule) and discuss how the tubing is selectively permeable. Relate how the tubing is like a cell membrane. Post Mac Mod The semi-permeable membrane is permeable to both types of molecules (dark and light circles). 1. On diagram A draw arrows to show the direction each type (black and white) of molecule is moving. 2. On Diagram B show how the molecules will look after the molecules have moved through the membrane. 3. Explain your answers. Use the following words in your answer. a. Diffusion b. High/Low concentration c. Equal