CHap 6 Qns

Chapter 6 – Reproduction
Name:___________________
1. Explain why organisms produced by asexual reproduction are referred to as clones
2. Explain why asexual reproduction is advantageous to some species.
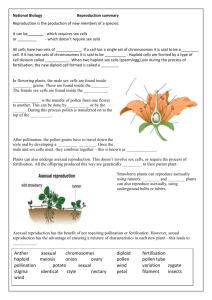
3. Prepare a table of the four methods of asexual reproduction in eukaryotes. Your table will have three columns, headed: Name of method, Description of method,
Example.
6. What features characterise sexual reproduction? Explain how it is different to asexual reproduction.
7. Why might sexual reproduction be advantageous to a species living in a changeable environment?
8. Explain how gametes are produced. What feature characterises gametes compared to normal body cells?
11. What are the survival advantages of being able to produce both asexually and sexually?
12. State the purpose of the following flower parts:
12a. Flower
12b. Petals
12c. Stigma
12d. Anther
12e. Pollen tube
13. List the processes that need to occur before pollination can occur.
18. Draw a concept map that illustrates the processes that occur between pollination and seed germination.
21. Draw a concept map to show where sperm moves in the male reproductive system from its development to its release. Make sure you name each organ it moves through.
24. List the major organs in the female reproductive system. What is the function of each?
25. Draw up a table to show the three main hormones involved in the female reproductive system. Where is each produced and how does it affect the female reproductive system.
29. What are the differences between a zygote, embryo and foetus?
Apply Understandings
1. Organisms that reproduce asexually through budding rarely have a large number of different cell types. Can you explain this?
3. Some species produce only one offspring per year or even fewer. Others produce more; some produce very large numbers. Suggest why some species produce more offspring than others.
Concept Map
Make a concept map of the chapter using the following words, use some more if you life. Remember on your arrows you can use joining words helping descriptions or understandings.
Asexual
Binary Fission
Bisexual
Budding
Fragmentation
Gestation Period
Implantation
Life Cycle
Self-pollination
Semen
Sexual
Sperm
Clones
Conjugation
Daughter cells
Dormant
External Fertilisation
Fertilisation
Foetus
Gametes
Meiosis
Menstrual Cycle
Mitosis
Motile
Ovary
Ovulation
Pollination
Seed
Stamen
Zygote