Module 11: Motivation
Group Challenges:
1) Motivation:
a) What is the definition of motivation
b) Give 2 original examples that show how motivation “energizes” &
“directs” behavior
2) Instinct theory
a) What is an instinct? Give an example
b) Who are some of the key proponents of instinct theory?
c) What’s one problem with instinct theory
3) Drive reduction theory
a) Create a flow chart to show how drive reduction theory would plot the
course for a specific need or desire
b) How is drive reduction theory different from instinct theory?
c) What’s one problem with drive reduction theory?
4) Arousal theory
a) How is arousal theory different from drive reduction theory? Give an
example
b) What is homeostasis?
c) What is Yerkes-Dodson’s law? Give an example
5) Intrinsic & extrinsic motivation
a) Come up with an example that shows the difference between intrinsic
& extrinsic motivation
b) Come up with an example that demonstrates the “overjustification
effect”
c) Which motivation do you think is best? Why?
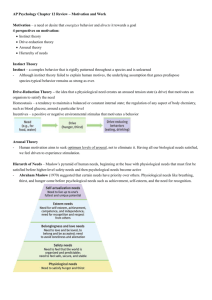
6) Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
a) Come up with 2 examples for each type of need
b) Which of Maslow’s needs do you spend the most time worrying
about?
7) Achievement motivation
a) What is achievement motivation? Give 2 examples
b) Who researched achievement motivation?
c) Which of Maslow’s needs does achievement motivation sound like?
d) What are high achievers like? How are they different from low
achievers?
e) Which are you: a high achiever or a low achiever?
8) Motivating yourself and others
a) What are 3 ways to better motivate yourself?
b) What are 3 ways to motivate others?
c) What is the difference between social leadership & task leadership?
GAE of each
9) Hunger
10)
11)
12)
13)
14)
a) Explain how the following effect hunger: glucose, insulin, leptin,
orexin
b) If you wanted to lose weight, would you want to increase your levels
of leptin or orexin?
c) What part of the brain controls hunger?
d) How does eating “junk food” affect hunger?
Set point theory
a) What is set point theory?
b) How does it explain why overweight people often find it so hard to
lose weight?
Basal metabolism rate
a) Give an example of an activity that would keep us at our basal
metabolic rate
b) Who usually has the higher BMR: Men or women? Obese people or
non-obese people?
c) Does this help explain why is dieting often so much harder for women
and for obese people?
d) What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic exercise?
External vs. internal eaters
a) Give an example that shows the difference between internal &
external eaters
b) Which one are you: external or internal?
c) Generate a list of helpful hints to lose weight
Give two examples of how culture effects hunger?
Eating disorders
a) What is anorexia nervosa?
b) What is bulimia nervosa?
c) Which eating disorder is more dangerous?
d) Who usually suffers from AN?
e) What are 2 factors that contribute to eating disorders?
f) Do AN & BN appear to be culturally universal or culturally relative?
Explain.
Extra Credit:
15) What is sociobiology?
16) What is incentive theory?
17) What are the 4 types of social conflicts? GAE of each
18) What is affiliation motivation?
a) Who were some of its proponents?
b) How do evolutionary psychologists explain affiliation motivation?
c) What are some of the advantages and disadvantages of affiliation?
19) What subfield of psychology applies psychological research to improve
conditions in the workplace?
20) Chemistry of hunger?
a) What is glucagon?
b) What is cholecystokinin?
c) What is the difference between the lateral and ventromedial
hypothalamus?
d) What is the paraventricular nucleus?
e) How do the neurotransmitters norepinephrine, GABA, neuropeptide Y
and serotonin effect hunger?
21) What parts of the brain and the endocrine system affect thirst? How?
22) Research on sex
a) Who was Alfred Kinsey? What did he discover? How reliable was
his research?
b) What are the 5 stages of the sexual response cycle according to
Masters and Johnson?
c) What is the biggest difference between the male and female response
cycle?
d) What parts of the brain and endocrine system regulate sexual
behavior?
e) How influential are hormone levels to human sexual behavior as
opposed to animals?
f) What are two other important influences to human sexual behavior?
g) How does male and female sexual fantasizing differ?
h) How common are sexual disorders?
a) What sexual disorders are most common to men?
b) What sexual disorders are most common to women?